Search Results for Tag: Rio+20
New Directions for the Brazilian Amazon
The Amazon rainforest is spread out over nine national states of the South American continent. As trees bind carbon dioxide (CO2), the Amazon forest plays a crucial role in climate protection measures. Home to 60 percent of the world’s rainforest area, Brazil contains the largest part of this precious ecosystem.
GLOBAL IDEAS asked Brazilian forest activist Pedro Soares to write a guest article for our blog. Pedro stresses that we can only protect the Amazon by providing an adequate income to those living in the forest.
By Pedro Soares
The Brazilian Amazon area covers about 50 percent of Brazil’s territory. That is a total an area of 4,196,943 square kilometers.
The biggest stock of tropical forest in the world has always been seen as a barrier to regional economic development. In fact, deforestation occurs mainly due to an economic rationale: the forest does not provide sufficient income for landowners and forest dwellers, when compared to the income they could obtain for more profitable activities such as logging, agriculture or cattle ranching. But the lack of an economic value for the stand forest is the main caveat towards the promotion of forest conservation policies and programs.
![]() read more
read more
Rio plus you

Stefan Rostock, Germanwatch
Author: Kerstin Schnatz
A huge disappointment, a good basis to work from or “a major step forward in achieving a sustainable future” as the United Nations have put it? Depending on who you ask, the outcome of the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development in Rio de Janeiro in June 2012 is evaluated differently.
In the run-up to the so called Rio+20 Earth Summit, we had asked our Global Ideas crowd to forward their questions to participants of the summit. In Rio, our reporters Philipp and Kerstin asked Stefan Rostock from the non-governmental organisation Germanwatch to answer them. Stefan followed the negotiation process very closely – listen to his answers:
Stefan Rostock Germanwatch by ideasforacoolerworld
About Germanwatch
The non governmental organisation Germanwatch advocates for a more sustainable future in countries of the so-called “South”. It researches and highlights the global consequences that economies and politics of industrialized states have on developing and threshold states – situated mostly in the geographical South of the planet. Germanwatch is based in Bonn and Berlin.
About Rio+20
The United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development took place in June 2012 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. With almost 30,000 participants from all around the world including representatives of 191 UN member states as well as 10,000 NGO people and almost 4,000 journalists, it was the biggest conference in the history of the United Nations. Download the 50-page outcome document “The future we want”.
“Far less than we know is needed”
What should the delegates at the Rio+20 summit agree on? What will the outcome most likely look like? That’s what we asked visitors of the UN conference. The United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development is going to end on Friday.
A stronger UNEP: Almost off the table?
Author: Kerstin Schnatz
How can we better tackle global environmental problems – such as the loss of biodiversity or air pollution? Many countries believe that the United Nations should have a bigger say in solving these problems – one of the most controversial issues at the Earth Summit at Rio de Janeiro, where over 115 world leaders come together to discuss global challenges.
The European Union for example favors an „upgrade“ of the United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP) to the same level as more powerful UN bodies, such as the Food and Agriculture Organisation or the World Health Organisation.
But other nations are opposed to this change – including Brazil, host of the summit. According to non governmental organizations watching the Rio+20 negotiations closely, a full scale upgrade of UNEP is by now almost off the table.
German Environment Minister Peter Altmaier sticks to the European position:
“The only living thing that can be seen from the moon”

Don Henry, Australian Conservation Foundation
Interview: Kerstin Schnatz
The Australian Conservation Foundation (ACF) is Australia’s main environment group. With the United Nation’s Earth Summit starting this Wednesday, Global Ideas reporter Kerstin Schnatz spoke to ACF’s executive director Don Henry in Rio de Janeiro. The conference is also known as Rio+20 as it marks the anniversary of the first Earth Summit twenty years ago. Over one hundred world leaders are in Rio to seek answers to global challenges such as climate change or marine pollution.
Global Ideas: If there was one thing you were free to write into the Rio+20 final paper what would it be?
Don Henry: I think there is a very straightforward issue at the moment and that is cutting subsidies for fossil fuels around the world. In Australia, we have subsidies worth billions of dollars that go into making fossil fuels cheaper for the mining industry.
But I would love to also ensure there is much stronger investment into renewable energy and energy efficiency around the world. I’d really like to see the international financial institutions like the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) cut any loan programms to the fossil fuel sector and really boost loan portfolios to renewables and efficiency.

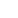
Activists at the Rio+20 summit protesting against fossil fuel subsidies
What impacts of climate change do you feel in Australia?
In recent years, we have had some terrible bushfires that have killed a lot of people in extreme, hot weather that has never been seen before in Australia. If the world doesn’t act, our best scientists are saying we are going to get double the amount of droughts and they will be twice as severe over the next 20-30 years. That will also have a big impact on food production in Australia.
And another example, something that is dear to my heart: We are very privileged in Australia that we are the custodians of the Great Barrier Reef, the largest reef system on earth and the only living thing on the planet that can be seen from the moon. The Great Barrier Reef is at grave risk from climate change. The best science out there is saying if global average warming goes beyond two degrees, we will see a severe impact on the reef. It would be a tragedy if our generation allowed one of the great global treasures, the Great Barrier Reef, not to be handed on in good condition to our children.
What is the most important goal Australians have achieved in the last twelve months to tackle climate change?
We’ve had a very big effort from Australian civil society to put a price on carbon emissions. Our government last November passed legislation for a carbon trade scheme. The legislation is complemented by a ten-billion dollar investment into clean energy and a carbon farming initiative that rewards farmers for tree planting and for holding on to forest areas. That’s been an important step forward for us as a nation.
At a side event at Rio+20, nuclear power was promoted as a sustainable way of producing energy. What’s the perception of nuclear power in Australia?
When you look at whether nuclear power is a solution for climate change in Australia, most Australians would say the risk associated with accidents and long lived nuclear waste is not a solution to action on climate change.
Apart from that, Australia is lucky because we receive twice the amount of solar energy per square meter than Germany does. So we have huge potential for renewable energies. We also have extensive gas reserves – which is still a problem with emissions, but gas plants still have less emissions than coal. So I think most Australians feel we don’t have to go there and we shouldn’t.
Australia may not have any commercial nuclear power plants. But the country has a strong mining industry exporting uranium for nuclear power plants around the world.
ACF strongly opposes uranium mining. Because often the mines have been imposed on Aboriginal people, on Aboriginal land without their full consent.
There are also real problems with safety for workers at the mines. For instance one of the mines in the Northern Territory, the Ranger uranium mine, has got a legacy of hundreds of accidents that have affected workers’ health.

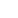
Indiginous land owner Yvonne Margarula in front of the Ranger uranium mine. The mining site is surrounded by world heritage listed Kakadu National Park.
And then there is another huge problem: What do you do with the radioactive waste from the mining process itself? For example, a condition of mining operations is they have to make safe the waste ponds for ten thousand years. Human beings are not good at making things safe for one hundred years, much less ten thousand years.
And of course many Australians are very worried with what happens with uranium from Australia overseas. We do know for example, it was Australian uranium in the Fukushima reactors. So in an indirect way, Australia has contributed to the problems associated with the accidents.
What are you expecting to come out of Rio+20?
We are very worried that it will be quite a modest outcome at a time when environmental degradation and sustainability issues are so urgent and pressing globally.
Pictures: Global Ideas/ Dominic O’Brien






Feedback