Search Results for Tag: energy
Climate Change: The longer we wait the more expensive it will get.
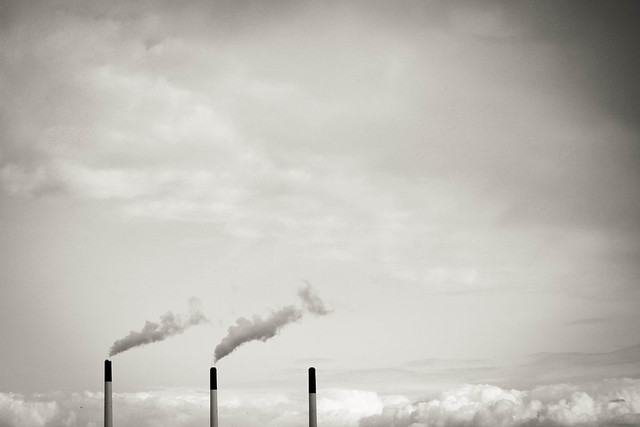

The Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) recently released a new study that offers two different and probably controversial results. At first the researches say that everything is going to be extremely expensive the longer we wait until political leaders get active. „Global economic growth would be cut back by up to 7 percent within the first decade after climate policy implementation if the current international stalemate is continued until 2030“, the paper says. That‘s an awful lot compared to the 2 percent that are expected if there‘s a climate agreement reached by 2015.
The researchers conclude that it is most relevant to not further postpone mitigation to keep climate targets (the 2 degrees above pre-industrial levels-target e.g.) in reach. “Economists tend to look at how things balance out in the long-term, but decision-makers understandably worry about additional burdens for the people and businesses they are responsible for right now. So increased short-term costs due to delaying climate policy might deter decision-makers from starting the transformation. The initial costs of climate policies thus can be more relevant than the total costs”, lead-author Gunnar Luderer says.
On the other hand Ottmar Edenhofer, he’s the co-author of the study and chief-economist of PIK, formulates a goal that could make it possible to keep the earth’s rising temperatures below the 2 degrees-target mentioned above. But his demands seem to be quite optimistic. At first, he said, a wordwide carbon trading system must reach prices for CO2 emission rights of 20 to 50 Euro (27 to 67 Dollar) per ton. That would be the only way to increase the price of fossil energy sources at a level that could force the industries to switch over to green energy alternatives. Here we should keep in mind that a ton of CO2 is currently traded at just about 3 Euro (4 Dollar) in Europe.
According to Edenhofer especially technologies for carbon dioxide removal from the atmosphere might be required in the future to reach the climate targets. This implies the use of bio-energy alongside wind or solar power, with plants consuming CO2, combined with carbon capture storage (CCS), storing underground the emissions from biomass combustion. The longer it takes to start climate policies the higher is the world’s reliance on these technologies will be, the study adds.
For the study the scientists produced 285 alternative climate change mitigation scenarios, with varying assumptions on the course of international climate negotiations on the one hand and on the other hand the availability of low carbon technologies from solar and wind power to bio-energy, CCS and energy efficiency. For the economic evaluation, they considered indicators like mitigation costs, energy prices or potential financial transfers induced by an international carbon market.
Water blog Part II – should water be privatized?
 In the second part of our special blog series on water, Julian Claudi asks – is it necessary to privatize water, what are the different approaches around the world and what has happened in instances where a private corporation has indeed got its hands on the neighborhood pump or the household tap?
In the second part of our special blog series on water, Julian Claudi asks – is it necessary to privatize water, what are the different approaches around the world and what has happened in instances where a private corporation has indeed got its hands on the neighborhood pump or the household tap?
To pick a prominent example of the kind of passions and conflicts water privatization can unleash, let’s go back to the year 2000 – to Bolivia. There, the Andean city of Cochamaba erupted in protest after a private, foreign-led consortium took over the city’s water system. The previous year, in September 1999, the Bolivian government privatized the water supply in Cochamaba and allocated the rights to Aquas del Tunari, an affiliated company of Bechtel Corporation (Bechtel Group) which is ranked as the fifth-largest privately owned company in the US.
It must be said that Cochabamba suffered from a chronic water shortage. Most of the poorest neighborhoods were not hooked up to the network, so state subsidies to the water utility went mainly to industries and middle-class neighborhoods. In the World Bank’s view, it was a city that was crying out for water privatization.In a nutshell, the World Bank threatened to freeze credit to Bolivia if it did not privatize water.
But the consequences for the people were drastic – Aquas del Tunari raised the water rates many times over, which led to a national uprising. As a result, the Bolivian government backtracked and disbanded the contract with the company. In turn, Bechtel tried to sue Bolivia for over $50 million in compensation. Battered by several years of bad publicity, Bechtel finally settled the $50 million lawsuit for a symbolic amount of about 30 cents on January 19, 2006.
To get a glimpse of what happened in Bolivia in 2000, it’s worth watching “Abuela Grillo,“ an animated short film by a group of Bolivian artists which is based on the events in Cochamaba as well as on a myth from the Bolivian lowlands and deals in a metaphorical way with the issue:
Abuela Grillo from Denis Chapon on Vimeo.
The European Union may be far away from such a scenario nowadays, but there are already over one million Europeans who have signed the citizen’s initiative “Water is a human right“. Their biggest worry is that the EU will privatize European waterworks in the mid-term and through the back door.
The reason for the concerns are a much quoted proposal from the EU Commission to change a concessions directive to bring more market competition between public and private water suppliers “to ensure that EU companies have access to business opportunities and that public authorities get the best value for money.”
At the same time, the Commission insisted repeatedly in several press releases earlier this year that “the proposed directive will therefore not lead, under any circumstances, to imposed privatization of water services.” So will that really be the case? Not exactly, according to the non-profit foundation and campaign group Corporate Europe Observatory (CEO). It says the planned directive on concessions of the EU commission could have unforeseen consequences.
“Municipalities who have some form of private participation in their water supply, even a small part, would have to offer their water contracts for EU-wide bidding. This would give private water multinationals like Suez and Veolia new opportunities to expand,” the group says.
At the end of June this year, the EU Commission then unexpectedly said it would reconsider its position in light of “the concerns expressed by so many citizens.”
It’s probably not the last word in the public discussion about water privatization in the European context. Meanwhile, in many places around the world, water privatization is already a hot button issue with various models and strategies being discussed, practiced and fought against.
Advocates of privatization have many arguments. A common one is that “private entrepreneurs are more efficient in increasing access to clean drinking water and have more technological skills and more assets for investment.”
Another is that privatization is the right thing in general if “a government that is strong enough to uphold regulations and to force the private company to do a good job.”
Meanwhile, opponents have their own list of convincing points – mainly that the environmental price for privatization is simply too high. “Privatization has been accompanied by the degradation of water quality, increase in water loss, deterioration of infrastructure and increase in prices,” according to some.
There are yet other, more moderate voices that suggest that say that water must have a certain price to avoid ongoing water scarcity in many places. The Irish think tank, Institute of International and European Affairs (IIEA), for instance, comes to the conclusion that “water pricing” is an option which must be considered:
Another school of thought sees a constructive solution in re-municipalization – that means putting the water supply back in public hands. That’s what happened in Paris and Argentina:
A project from Greece called “Initiative 136” takes a different tack. It’s an attempt at a third way by avoiding both water privatization as well as public-private-partnerships.
“The idea is that if every water user bought a non-transferable share, ‘the public could own the water company through a system of neighbourhood co-operatives of water users coming together through a single overall co-operative.’136 euros is the figure you get from dividing the 60 million euros for which the company is to be put on the stock market by the number of water meters in the city.”
At the time, activists from the citizen campaign “Human Right to Water” are going in the same direction but aiming at high level EU institutions directly. “We are taking up the challenge to get implementation of the human right to water and sanitation’ on the European political agenda,” they say.
Meanwhile in Bolivia, residents of Cochabamba’s southern zones “frustrated with both the private and public water management models,[…] are increasingly relying on traditional community-run water systems as an alternative.”
There are a host of players involved in the water privatization debate – public state supply advocates, private companies, public-private-partnerships and cooperative citizen shareholder movements. They all have their own concepts about how access to water can be best ensured. In the best case, the different ideas will merge into a sustainable and resilient supply system and contribute to a fair and free global right to water distribution for everyone.
Surely this goal is only achievable under the premise of a local and global framework of sustainability and participation and not with an overarching focus on profit.
Meeting the Arabian stallion in Lebanon
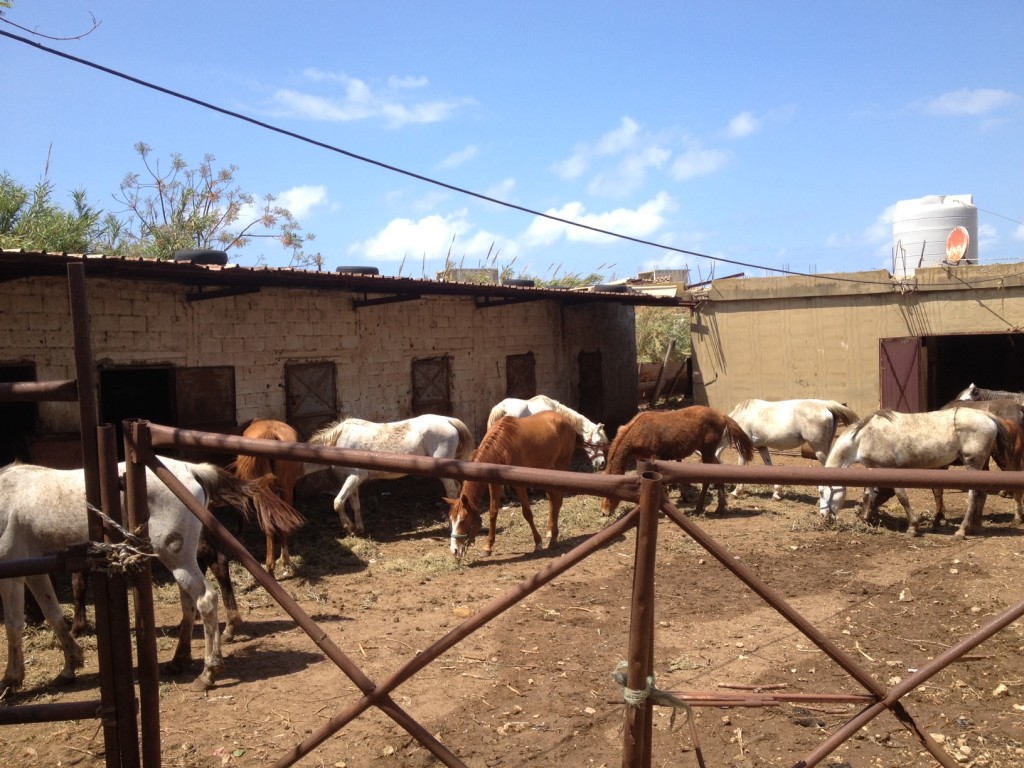 Can you imagine pounding a race track amid temperatures of 40 degrees Celsius? That’s no problem for the purebred Arabian stallion as our reporter Dan Hirschfeld found out while filming in Lebanon.
Can you imagine pounding a race track amid temperatures of 40 degrees Celsius? That’s no problem for the purebred Arabian stallion as our reporter Dan Hirschfeld found out while filming in Lebanon.
Horse racing is a popular sport in Lebanon with annual races held in Beirut. And the country is also home to the famed Arabian horse, one of the oldest breed of horse. It’s believed it was developed by the Bedouins of the Middle East specifically to last long distances. The powerful beasts, characterized by their flowing manes and proud heads, are used in endurance riding in equestrian sport as well as on traditional race tracks.
Dan Hirschfeld, who is doing a feature on a smart electricity grid to counter chronic power cuts, met a horse breeder near Tripoli in northern Lebanon, who has several Arabian horses.
Tackling power cuts with renewables in Lebanon
 Our reporter Dan Hirschfeld, who is filming in Lebanon, came upon an unusual sight on Tuesday – quiet streets in the usually bustling capital Beirut.
Our reporter Dan Hirschfeld, who is filming in Lebanon, came upon an unusual sight on Tuesday – quiet streets in the usually bustling capital Beirut.
The country is going through political change with newly appointed Lebanese Prime Minister, Tammam Salam, opening talks to cobble together a government. Salam, a former culture minister, has vowed to work toward ending divisions in the nation and preventing the civil war in neighboring Syria from spilling over into his country.
But Lebanon is struggling with infrastructure challenges too, especially daily power shortages. Many people rely on polluting diesel-powered generators for electricity. That’s the focus of Dan Hirschfeld’s upcoming feature for Global Ideas. He’ll be looking at a planned smart electricity grid which is meant to store renewable energy from the sun and wind and curb power breakdowns in the country. Germany is helping train Lebanese engineers to operate the smart grid.
Renting or buying – A difficult decision!
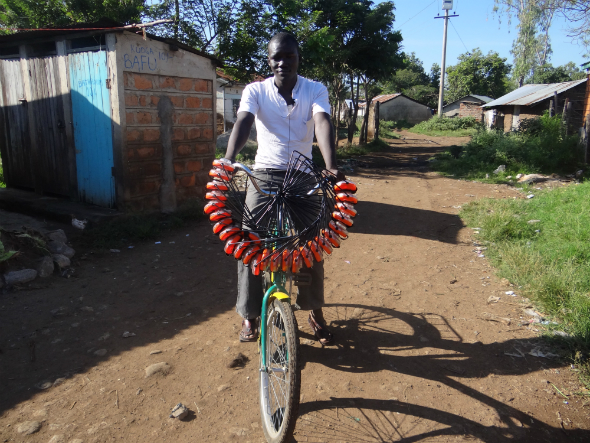

“Take a gap year and save the planet!” This could be the motto of the Kenyan based organisation “Ecofinder”. Founded in 1995 the Kenyan grass roots organisation helps communities around Lake Victoria to lead a more sustainable life. GLOBAL IDEAS has invited Nicolas, one of Ecofinder’s numerous volunteers, to write about his experience:
As a volunteer one of my main tasks is the so called “green energy promotion”. Here I try to drive the distribution of solar lamps forward. In this field we are running two different projects. The first one is called “Right Light”, it gives users of sooty kerosene lanterns the opportunity to rent a solar lamp over night for a very low price. So they don’t need to buy more expensive, health and environment damaging kerosen. The second project we call “Villageboom.” Here we encourage people to buy solar lamps as an investment in their future.
The major difference both is obvious, a person is either the owner of a solar lamp or the person rents the lamp. Both have advantages and disadvantages. For example: Almost everybody can afford the rent of one solar lamp for one night (about 9 Euro Cent). Another positive aspect is that the person who rents does not bear a risk if the lamp fails and is broken. But by possessing a solar lamp users can save a lot more money, because the sun will charge their lamp for free every day. Unfortunetaly for most of the people without electricity a good solar lamp is still very expensive.
In the long run renting a lamp will be more expensive than buying one. After one year of renting a lamp the rent will equal the value of buying a lamp twice. In conclusion I think installment payments are the best solution for poorest who are looking for a clean and cheap light. Therefore it could be very interesting and succesful to combine both concepts. For example our Solar Lamp Entrepreneurs-SLE could offer to their customers to buy a solar lamp bit by bit and not at once.
I’ll keep you updated how our solar lamp distribution is going on in future. But if you have any idea, suggestion or proposal about this issue feel free to comment and to share your thoughts.
In your opinion: “What is the best way to enable as much people as possible a solar lamp?”





Feedback