Sealevel rises quicker than expected
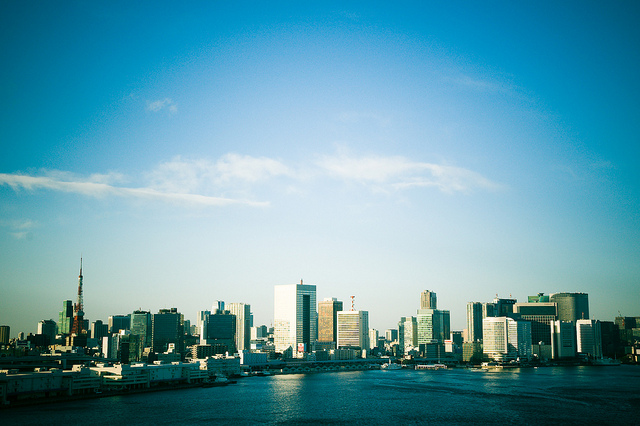

Many coastal cities, as for example Tokyo, will have to find a way to cope with rising sealevels (CC BY 2.0: oisa/flickr.com)
At the Doha climate change conference, delegates of the COP18 again try to find a practical way how to (further) reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The importance of this goal was again highlighted by a new study released recently by the Potsdam Institute of Climate Impact Research (PIK): Researchers found out that sealevel rose much quicker than projected by the latest IPCC report.
That’s what they saw when comparing the model calculation with real satellite data from 1990 to 2011. According to those satellite measurements, oceans are rising 60 percent faster than previously thought. In absolute numbers: the IPCC report from 2007 projected additional 2 mm sealevel per year, satellite data revealt a rate of 3.2 mm per year.
Which might seem less in numbers, can make a huge difference in reality. Already for the projected 2 mm, researchers warned this might lead to flood waters, more extreme storms, and salted ground water. Yet, nobody can forecast what exactly is to happen with a higher rate of sealevel rise. But nonetheless, threat for coastlines and megacities continues to increase. Especially if no reliable mechanism will be found to reduce CO2 emissions – as in consequence sealevels will rise by several meters at the end of this century.