Exploring the North – Further North
Arriving in Tromso, Norway, we are now located just at the Arctic’s doorstep. It is a quiet strange feeling, when you suddenly stand at the edge of something, that is normally so incredibly far away. If it’s far away from you as well and you derive from that that you don’t have to care – hang on. You actually should, as the Arctic often is referred to as earth’s air conditioner. And on hot summer days without (working) air conditioning, you feel perfectly well what it is good for.
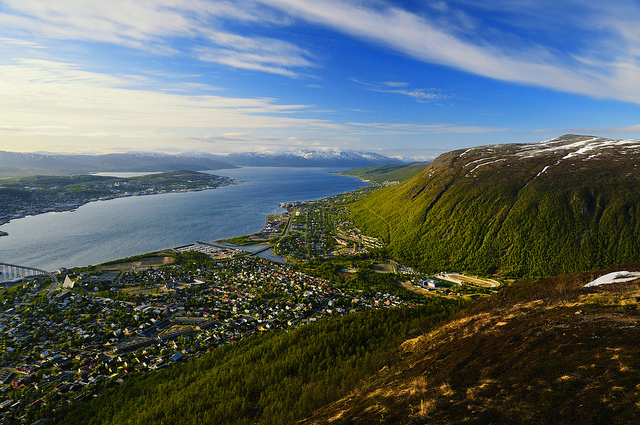

Thought you might have seen enough snow, so I found this Tromso view of June 2010 for you (Photo: CC-BY-NC-SA-2.0: Nietnagel)
If you look at such pictures of the Arctic region it does not at all like an air conditioning. I was actually suprised that it can be that green in the Arctic region, as I always associate of snow and ice with Artic. What about you?
But this ice is only there in winter time – that’s when it fulfils it’s cooling job, by reflecting 80 percent of sunlight back to space which then cannot heat up the ocean or earth anymore. But from March on, ice starts melting due to increasing temperatures. The decreasing sea ice cover uncovers the dark oceans that absorbs the sunlight instead of reflecting it – the cooling air conditioning turns into a heating facility.
So far, the Arctic yet hasn’t been completely ice-free during the warm summer period. But you might remember scientists worrying last summerabout the small area that is left ice covered: The larger the ice free part, the more heat is absorbed by the ocean underneath – in turn, even more ice melts and a vicious circle starts.
Not on the edge of the Arctic, but on the edge of Arctic research, you find scientists working on how this influences the Arctic environment. Sometimes this influence can even be positive: Researchers recently found that microbes in the soil can fix more carbon in a warmer climate.
But yet, researchers cannot tell how Arctic ice cover will evolve, but they work for example on better models to predict what is going to happen. That is especially important, as many earth systems are connected: A warming Arctic sea also affects ocean currents for example, that – connected to each other – span over the whole planet. In turn, oceans take up less CO2 for example, and in consequence more of this greenhouse gas in the air, warms up the whole planet.