Search Results for Tag: madagascar
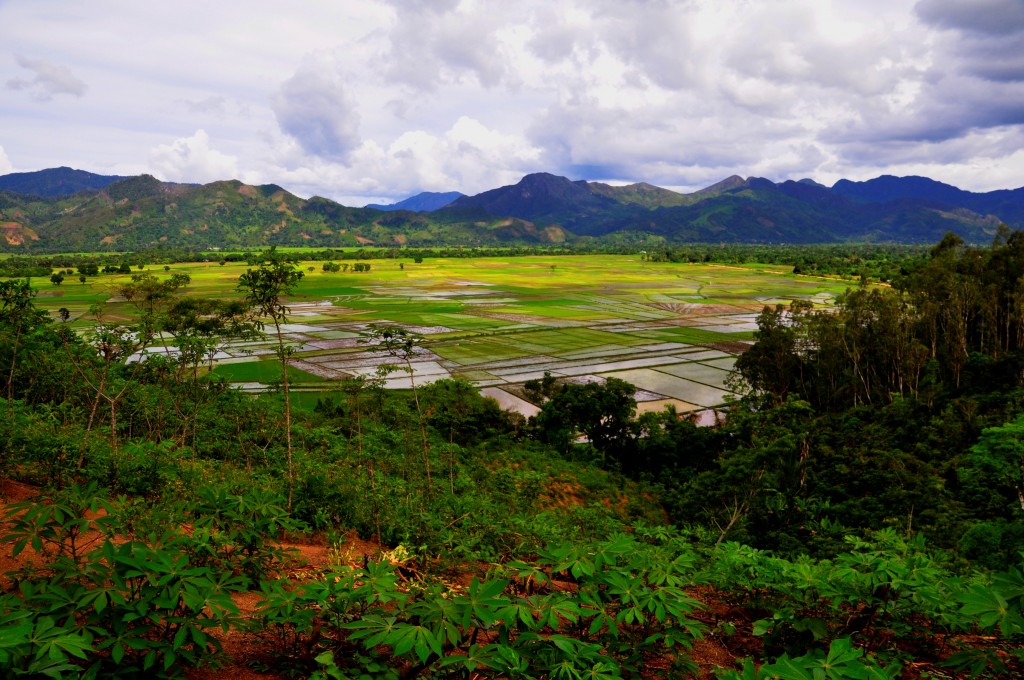
Rice crop in danger in Madagascar
In the coming days, rice fields will be buzzing with activity again in Madagascar – at least that’s the hope. The end of November usually spells harvest time in the small island country. But last November, there was simply no rice to harvest in the northeast of the country, near the Marojejy National Park. When I visited the director of the park, Jean Hervé Bakarizafy, in early 2012, he told me that cultivating rice is supposed to run like clockwork. “In Andapa, a small town near the entrance of the park, people plant rice twice a year. They plant at the end of January and harvest in May. In July, they prepare their fields for the second season. They plant again in August and harvest for the second time at the end of November,” he said.
But Bakarizafy’s face dropped when he told me about the changes that occurred in 2011. “In the middle of 2011 – during our winter season – it was too dry to plant the second round of rice. There was absolutely no water left,” he said. And he’s certain that it wasn’t just a fluke. Elderly villagers who have lived in the area their entire lives started to speak up, and they all seemed to agree: in recent years, the weather seemed to be getting drier and drier.
The World Bank’s climate data portal confirms their concerns. “In the central regions and along the east coast, the amount of rainfall has fallen steadily between 1961 and 2005, accompanied by longer periods of drought,” said the World Bank, identifying the declining precipitation as a “major trend” for Madagascar. The organization also said that rainfall was noticeably less in winter and spring months – the middle of the year for Madagascar, which is located in the southern hemisphere.
Bakarizafy added that those weather patterns could spell disaster for rice farmers. “The people are very worried because if it goes on like this, they might not be able to get in the second harvest of the year anymore,” he said. That would mean the people in and around Andapa wouldn’t have enough rice for themselves, and they would be forced to sell less. At the market, prices for one kapoka, or scoop, of rice would go up.
And that in a country that is one of the largest consumers of rice in the world. The average person in Madagascar eats nearly 100 kilograms of rice a year. There is rice soup in the morning, and at lunch and dinner there is rice with white beans, green beans and carrots, a chili paste or meat. Back in 2010, the island’s agricultural minister said that rice accounts for more than half of all calories consumed in the country and 80 percent of all village families worked in rice cultivation. At that time, Madagascar had just joined the non-profit research center AfricaRice, and the organization estimated that Madagascar would need to import some 200,000 tons of rice a year to meet the growing demand.
So it’s no wonder that the farmers of Andapa are hoping they can harvest as much rice as possible in the next few days.
Author: Franziska Badenschier
Editor: Sumi Somaskanda
Dossier: Harnessing the energy of water
Hydroelectric power plants can generate vast amounts of electricity. The technology is emissions-free, reliable and safe. But large dams and hydropower facilities can sometimes create more problems than they can solve. Learn more in the latest GLOBAL IDEAS multimedia dossier http://bit.ly/GI_dossierHydro

Learning to save water in Madagascar
The efficient use of the rare water resources in Madagascar is a huge problem. A water-management program, set up by the WWF is not only serving to protect forests, but also helps locals use their water resources sustainably, and therefore improve their farming opportunities. 35,000 people are living on the Mahafaly Plateau, one of the driest corners of Madagascar, and climate change poses a serious threat to people’s livelihoods.
Madagascar’s New Species

For scientists looking to discover new species, Madagascar is the treasure trove: according to a new World Wildlife Fund study, scientists have found more than 600 new types of plant and animal life in the last decade alone! Why is Madagascar such a breeding ground for diverse creatures? The island is pretty isolated, and it’s stayed that way for centuries. Plus, the landscape is varied: there’s mountains, rainforest, and everything in between.
Researchers have discovered everything from the 10 cm-long Berthe’s mouse lemur to the “Glam Rock” chameleon in the picture above. National Geographic has some great shots of the new species, from tiny and furry to scaly and thorny.
But the report is also a reminder that some of these very special – and unique – creatures are under threat due to climate change and the practice of clearing forests in Madagascar for wood and other natural resources.
The WWF says the only way to protect all those species is for the locals themselves to get involved.
GLOBAL IDEAS goes HD
The GLOBAL IDEAS project has been running for nearly one and a half years now. And if there’s one thing our climate reporters have learned in this time it’s that climate change is super-complex and that important but small details are easy to miss. So, as a first step in the way to get the whole picture more accurately we have started to put on better goggles – and equipped our cameras with sharper vision.
Starting today we’ll put online video footage from our reporters in High Definition quality. We hope to be following this up very soon with our first GLOBAL IDEAS documentary that you can watch online in HD.
For starters here’s some HD footage of the amazing biodiversity our reporters came across on their recent trip to Costa Rica:
And here another one from Madagascar:









Feedback