Search Results for Tag: wood
Creating a water filter from wood
1.1 billion people in the world don’t have access to safe drinking water. In fact, even though it’s 2014, we still have 1.6 million people dying from infections caused by the lack of safe drinking water and basic sanitation – 9 out of 10 of these are children under the age of 5.
For several years Rohit Karnik, a mechanical engineer at MIT, had been working on the development of membranes for water filtration. But during a conference in Israel, listening to someone talking about fluid motion in trees, inspiration struck.
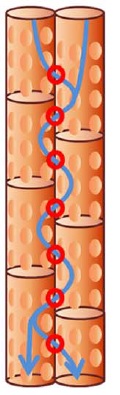
*
Apart from water, of course, trees transport so called “sap”, a fluid enriched with nutrients, up and down their trunks. On it’s way through the xylem, the wooden part of the tree, either fluid gets filtered at many points (circled in red). Now, why not investigate if these tree-membranes are capable of filtering water for humans as well? No sooner thought than done.
Karnik and his team started out developing a very minimalistic, low-cost filter – the problem with existing filters is often that they either need energy or are not affordable for those in need. So, Karnik’s first filters were built by peeling off the bark and plugging the piece of wood into a tube. Not suitable on a large scale, but elaborate enough for testing filter properties.

Construction of water filter system using wood*
The team’ s results: These filters got 99,9 percent of pathogens out of the water. The xylem filters managed to eliminate Escherichia coli, the most common type of gut bacteria that can cause severe diarrheal diseases if present in contaminated water.
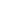
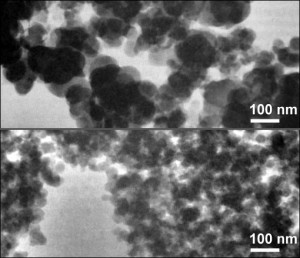
Using advanced microscope technology, the scientists even traced down, where bacteria where filtered: they all accumulated on the so called pits – membranes permeable for water – but not for the “larger” bacteria. Talking about size: the E. coli bacteria can be anything from 2 to 6µm in length. This is already quite small, but not the end of it when it comes to pathogens: viruses are almost a thousand times smaller than this. That is also where the xylem filters surrender: they don’t present an obstacle to anything smaller than 20 nm – a size comparable to that of the smallest viruses, the scientists report.
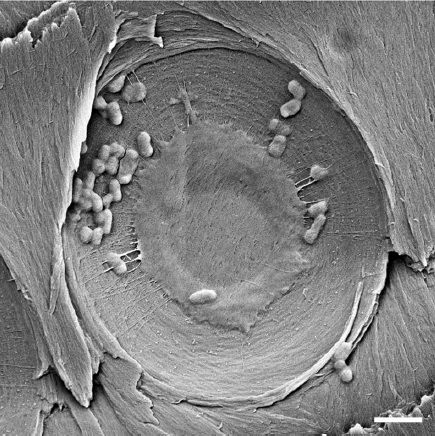
Pit membrane with accumulated E. coli bacteria. Scale bar: 2µm.*
To achieve a decent flow rate of 4 litres per day, researchers applied a pressure of 5 psi: “This value approximately corresponds to the pressure at the bottom of a 3 m column of water. Filtration will also occur at lower pressures, but at proportionally lower flow rates,” Karnik says. “The pressure of water supplied to households is typically 10 times this value. A container placed a few feet above the ground with a hose coming down to ground level will be able to generate sufficient pressure for filtration.”
Questions to be solved
Having this problem solved, there are still several left. “Can we store or dry sapwood xylem filters?” is one of the questions Karnik and his team are currently investigating. So far, to perform properly, filters have to stay wet all the time – once they’ve dried, they are useless. To safely get rid of such unusable or already “overused” filters, one way would be to burn them.
Also crucial for success of this filtration method is the type of wood used. For their experiments the team used the Eastern White Pine Pinus strobus, a tree that is abundant mostly across North America but not in those regions most in need of feasible water filtration: “We used the tree because it is common here, and it was easy to access. There are so many species of plants, and the question as to which endemic plants are suitable for making xylem filters in a particular area is certainly worthy of investigation,” Karnik writes.
Low cost solution in two years
Karnik’s idea is not yet feasible on large scales but he is optimistic: “This is a very new technology with lot of work to be done. A filter could take various forms, but one that is especially appealing is a compact device that simply attaches to a faucet, with a replaceable xylem filter inside it. It may take 2-3 years to develop the first prototypes for larger scale use, but I believe that there will be many developments to follow.”
*Credits for all images: CC BY: Boutilier et al. 2014, PLoS One 2014, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0089934.g001
Deforestation means less hydropower
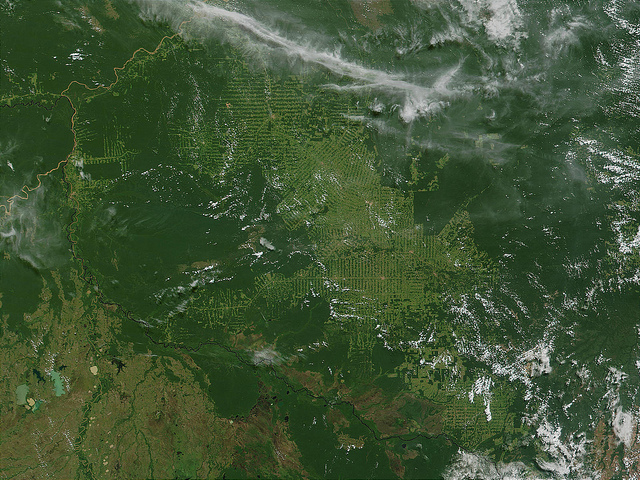

Satellite image of the Rondonia region of Brazil showing the massive deforestation underway in the south-central Amazon Basin. (Photo: CC BY 2.0: Banco de Imágenes Geológicas)
The Amazon deforestation rate rocketed to 88 percent during the last year: From August 2012 to April 2013, 606 squaremiles of forest were cut down compared with 322 square miles within the previous year, claimed as a record low.
That’s the conclusion of researchers from the National Institute of Space Research, who frequently monitor forest coverage with help of satellite images. Until recently, they could announce a slowing of deforestation. But, now it seems that the fate of one of the world’s biodiversity hotspots has changed.
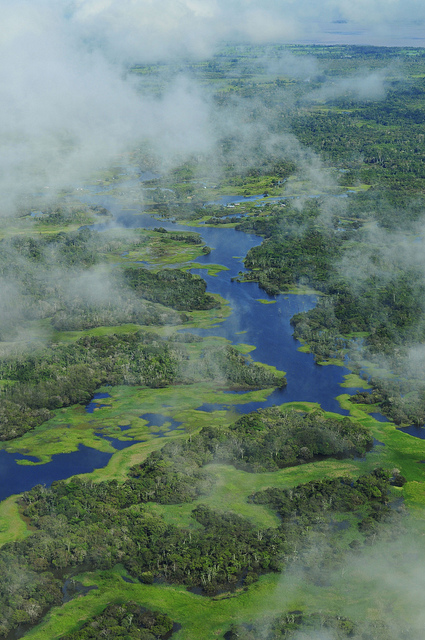

Trees take more water from the ground than crops do – and release more water vapour into the atmosphere. There, it turns to rain and finally feeds hydropower plants (Photo: CC BY SA 2.0: International Center for Tropical Agriculture)
The report comes on the heels of another study: scientists recently drew a connection between deforestation and energy supply. They looked at the Xingu river region in Brazil and found that cutting trees also cuts rainfall, resulting in reduced hydropower generation. That could lead to the country’s biggest dam project, Belo Monte, delivering a third less energy.
The link between deforestation and energy supply is often ignored, according to the study. “Feasibility studies of hydropower plants typically ignore the effect of future deforestation or assume that deforestation will have a positive effect on river discharge,” it says.
Rainfall does not depend on regional forest cover in the Amazon region alone. Major tropical forested regions in Central Africa and Southeast Asia also play a major role. “This dependence could affect hydropower expansion plans of a large number of developing nations in these regions “, the study concludes.
Soot as second worst greenhouse gas
Whenever your candle’s wick is too long, the lit candle produces something called soot. Soot consists of 80 to 95 percent carbon particles, which is why it’s also known as “black carbon”. Researchers have found that black carbon aerosols are actually twice as harmful to the climate as previously thought; in fact, soot is now as the second worst greenhouse gas after CO2.
But of course, it’s not the few candles in your home that are sparking global warming. Scientists trace the damaging effects mainly back to burnt wood and coal in industry and private households. Apart from savanna and bush fires, traditional, simple fires for cooking are the main source of black carbon emissions, researchers say. Another major source are diesel engines that don’t have particle filters.
Black carbon can scatter in the air and land on earth’s surface. It absorbs or disperses sunlight and thereby influences cloud formation and accelerates the melting of snow and ice.
In contrast to CO2, it’s more difficult to evaluate the consequences of black carbon emission because its effect varies depending on air circulation and humidity.
Despite that uncertainty, scientists are confident that climate change could be slowed down by reducing black carbon. They believe it would be possible to reduce global warming by half a degree.
But it’s not only the climate that would gain from slashing black carbon emissions. People’s health would also benefit – diesel smoke, for example, has been linked to lung cancer.
Yet cutting back on black carbon is easier said than done. Most emissions are generated in less developed regions, where the technology needed to avoid or reduce emissions are simply not yet available on a large scale.



Feedback