Understanding your target audience
By Bettina Ruigies
Today’s fast moving media environment requires a lot of flexibility from media workers. Multimedia skills are a must. Journalists need to be able to produce stories for radio or television, print or online. At the same time, digitization, the Internet and affordable equipment enables anyone who wishes to open a TV station on YouTube or at least run a blog site.
All this technical innovation offers tempting perspectives for hard working and talented journalists. But frustration and failure might set in when it turns out that hardly anybody is watching or reading.
![]() read more
read more
Reporting on natural disasters
By Riazul Islam
Natural disasters like cyclones and floods are a regular phenomenon in my native country Bangladesh.
As a result, the media there frequently reports on natural disasters. But working on these types of stories requires a special approach, two journalists working in the Bangladeshi capital Dhaka told me.
Mustafizur Rahman is a journalist from New Age, a daily English newspaper published in Dhaka. Iftekhar Mahmud works for Prothom Alo, the leading Bengali newspaper in Bangladesh. They shared their experiences and opinions on what preparations journalists should take before and while covering a natural disaster. Mustafizur and Iftekhar say a reporter faces many challenges when going to cover an area hit by a natural disaster. Before departing to the region, a journalist should of course be sure to check his equipment. But there are other key issues to remember when writing a report on the affected area and its people.
![]() read more
read more
Creating Asian guidelines for user-generated content
The Asian tsunami of 2004 and the Japanese earthquake and tsunami this year were two occasions where broadcasters around the globe relied heavily on user-generated content (UGC). They aired videos people had taken with their mobile phones, pictures snapped with digital pocket cameras or they simply broadcast information users had sent in via e-mail or as text messages from remote places.
These days, many radio and TV stations encourage their audiences to contribute material to their broadcasts. This gives them access to footage professional crews couldn’t otherwise get – or couldn’t get that quickly. And it gives the audience a voice, creating a two-way conversation with the broadcasters and making people feel like the broadcaster is there for them, picking up their stories and addressing their concerns.
Making the most of user-generated content
But how can broadcasters safeguard the quality and suitability of such content? After all, it’s supplied by regular listeners or viewers: amateurs, not trained journalists. Citizen reporters haven’t necessarily been taught the journalistic basics every professional has learned, like how to research facts, how to report accurately and how to be fair to all sides.
![]() read more
read more
Using an “axis of importance” diagram to evaluate sources
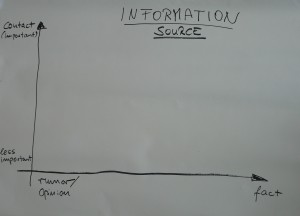 Out of one workshop at NUOL came a good tool that fits perfectly into that quest. It’s a diagram that helps journalists evaluate their sources (see photo at left, click to enlarge).
Out of one workshop at NUOL came a good tool that fits perfectly into that quest. It’s a diagram that helps journalists evaluate their sources (see photo at left, click to enlarge).![]() read more
read more
Educators embark into a new era of journalism in Laos
 Is there a proper definition of journalism in the Lao language? Since DW-AKADEMIE’s first workshop on journalism at the National University of Laos in Vientiane, there is. It was conceived by 15 staff teachers of the Department of Mass Communication at the Faculty of Letters – after long discussions revolving around somewhat abstract terms like “media”, “the public”, “society” and “information”.
Is there a proper definition of journalism in the Lao language? Since DW-AKADEMIE’s first workshop on journalism at the National University of Laos in Vientiane, there is. It was conceived by 15 staff teachers of the Department of Mass Communication at the Faculty of Letters – after long discussions revolving around somewhat abstract terms like “media”, “the public”, “society” and “information”.
Lao is not a language that lends itself to describing abstract ideas. Yet the 15 teachers feel it was worth the effort to lay a foundation they now can build upon. They are learning the mindset, tools and skills that in combination make a journalist. The reasoning behind this is that they are the ones training a new generation of Lao students who are eager to take on the profession.
![]() read more
read more