Coal, climate, cryosphere
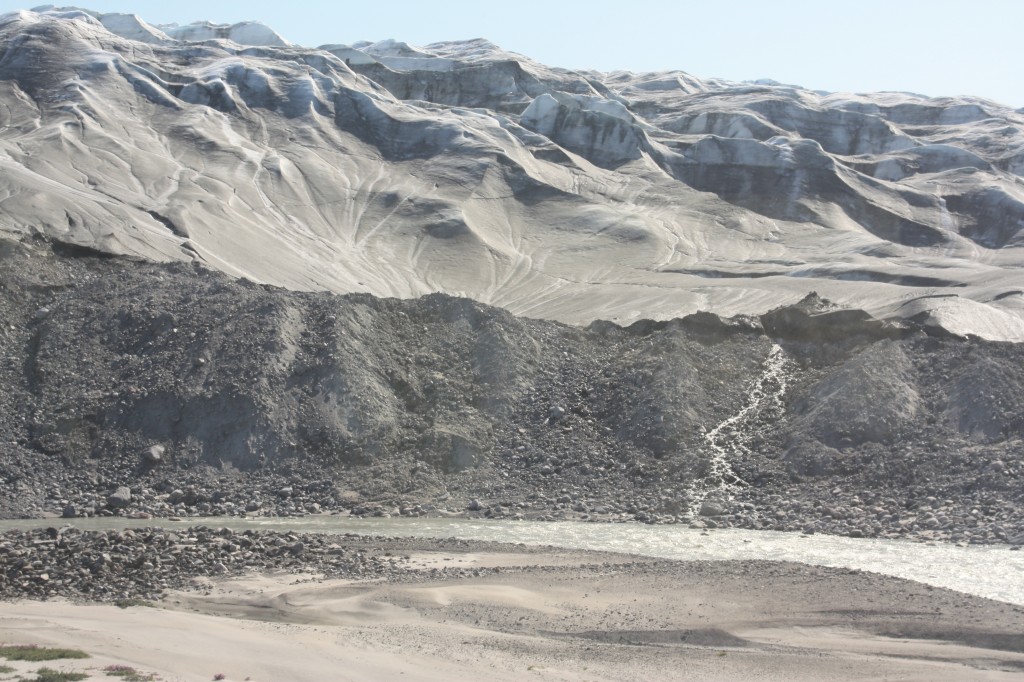

The Greenland ice sheet is melting faster. Scientists also report a decreasing albedo with snow becoming darker. (Pic: I.Quaile)
Fossil fuel power plants are still on the increase – committed carbon emissions are rising fast. At first glance you might respond to that with “so what’s new”? Well, a study is new, which indicates that in spite of all the political rhetoric in a lot of places about switching to renewable energies and moving away from fossil fuels, we are building more fossil fuel power plants than ever before. Unsurprisingly, that is leading to an increase of carbon dioxide emissions, which is bad news for plans to keep global temperature rise below 2°Celsius. It is extremely bad news for those of concerned about the cryosphere and the increasing melt rates of Greenland and parts of Antarctica. The main problem, the authors tell us, is that we have already committed to huge emissions by investing in polluting technologies.
Steven Davis of the University of California, Irvine and Robert Socolow of Princeton University in the US, report in the journal Environmental Research Letters that existing power plants will emit 300 billion tons of additional carbon dioxide into the atmosphere during their lifetimes. In this century alone, emissions from these plants have grown by 4% per year.
The two scientists have already reported on the increasing costs of delay in phasing out fossil fuel sources of energy, notes Tim Radford of the Climate News Network. Thanks again to you people for drawing attention to the study. Their latest research looks at the steady future accumulation of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere from power stations.
“Despite international efforts to reduce CO2 emissions, total remaining commitments in the global power sector have not declined in a single year since 1950 and are in fact growing rapidly,” the report states.
Massive emissions already committed
Governments worldwide have in principle accepted that greenhouse gas emissions should be reduced and average global warming limited to a rise of 2°C.
At the current pace though, scientists have warned that the world is on track for at least 4° Celsius by the end of the century. That could mean drastic rises in sea levels and catastrophic drought in some areas of the world.
“We are flying a plane that is missing a crucial dial on the instrument panel,” said Socolow. The needed dial would report committed emissions. Right now, as far as emissions are concerned, the only dial on our panel tells us about current emissions, not the emissions that capital investment will bring about in future years.”
In the latest study, scientists asked: once a power station is built, how much carbon dioxide will it emit, and for how long? They assumed a functioning lifetime of 40 years for a fossil fuel plant and then tallied the results.
The fossil fuel-burning stations built worldwide in 2012 alone will produce 19 billion tons of carbon dioxide over their lifetimes. The entire world production of the greenhouse gas from all of the world’s working fossil fuel power stations in 2012 was 14 billion tons.
“Far from solving the problem of climate change, we’re investing heavily in technologies that make the problem worse,” the experts stress.
The US and Europe between them account for 20% of committed emissions, but these commitments have been declining in recent years. Facilities in China and India account for 42% and 8% respectively of all committed future emissions, and these are rapidly growing in number. Two-thirds of emissions are from coal-burning stations ad the share from gas-fired stations had risen to 27% by 2012.
Fossil fuel wind-down not fast enough
Davis says more fossil fuel-burning facilities have to be retired than new ones built. “But worldwide we’ve built more coal-burning power plants in the past decade than in any previous decade, and closures of old plants aren’t keeping pace with this expansion”, he added.
According to Socolow, a high-carbon future is being locked in by the world’s capital investments: “current conventions for reporting data and presenting scenarios for future action need to give greater prominence to these investments,” he said.
The current draft of a summary report to the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) due to be released in November and viewed by the Times this week, warns of “severe, pervasive and irreversible impacts” unless carbon emissions are brought under control. The IPCC stresses that human-induced climate change will lead to the devastation of homes and property, a scarcity of food and water and human mass migration, as sea levels rise through warming temperatures and – alas – melting ice.
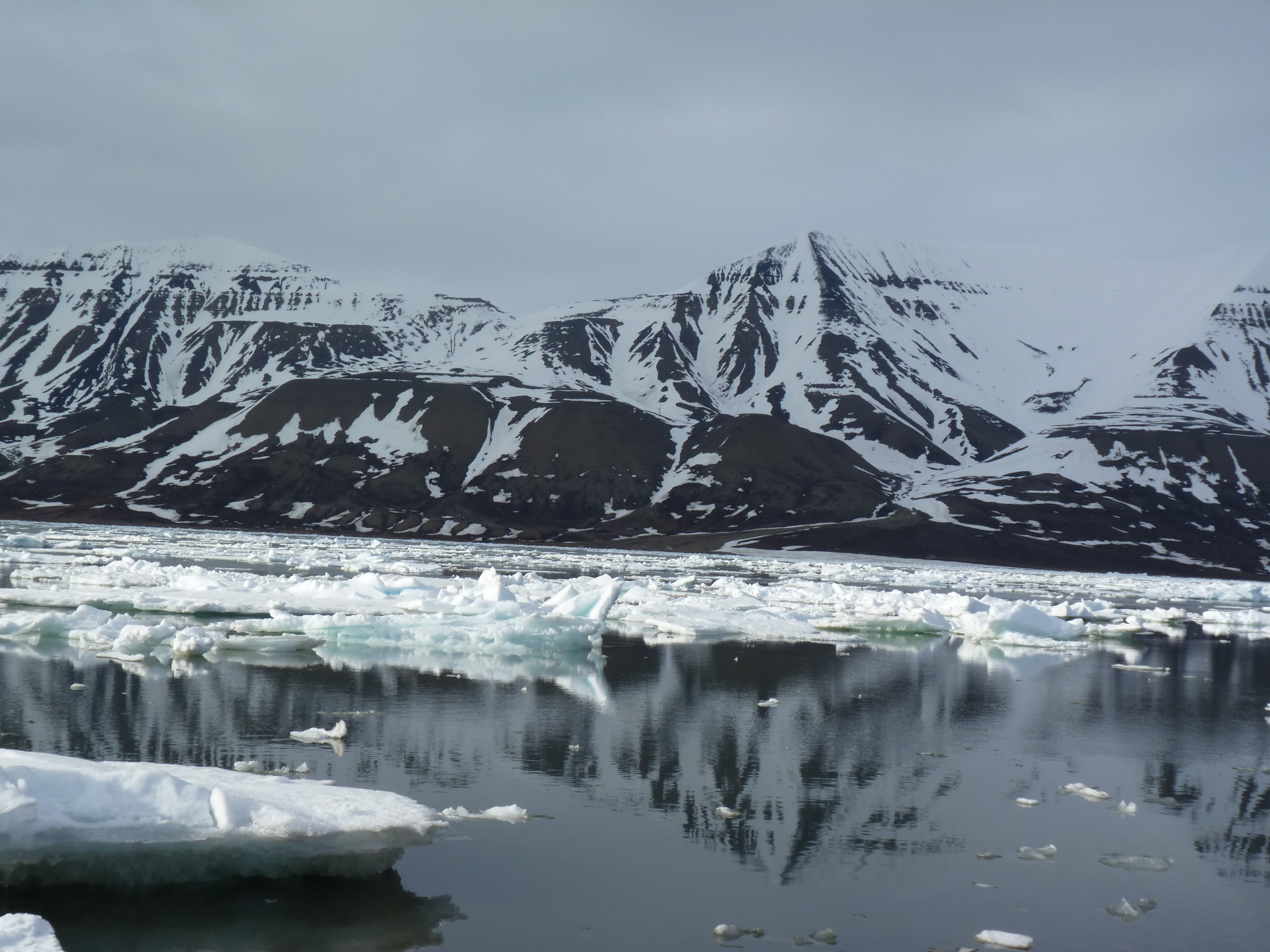
Polar melt confirmed from space
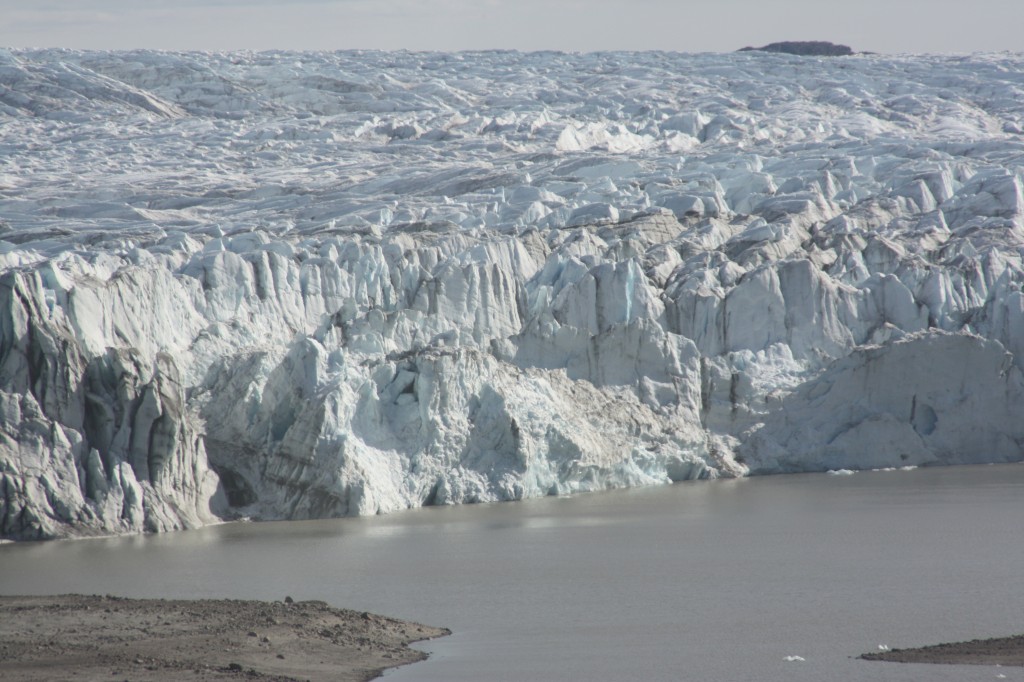
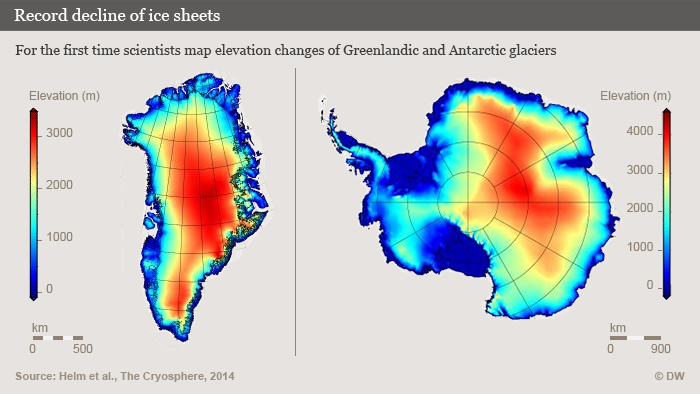
I am disappointed that there was so little mainstream media coverage (please correct me if I am wrong) of a report from a team of scientists from Germany’s Alfred Wegener Institute (AWI) in Bremerhaven who have analysed just over two years of data from the CryoSat-2 satellite. Their conclusion that the Greenland ice sheet and Antarctica’s glaciers are melting at record pace, dumping some 500 cubic kilometers of ice into the oceans every year, twice as much in the case of Greenland and three times as much in the case of Antarctica, by comparison with 2009 – yes, you read right, we are talking about a very short period for such a dramatic increase in ice loss – should have made more news headlines and not just the science pages.
To understand the scale of that, the researchers say it would be the equivalent of an ice sheet that’s 600 meters thick and covers an area as big as the German city of Hamburg – or, my colleagues here at DW calculate, as big as Singapore.
The research team headed by Veit Helm used around two years’ worth of data from the ESA CryoSat-2 satellite to create digital elevation models of Greenland and Antarctica. The results were published in the online magazine of the European Geoscience Union (EGU) The Cryosphere.
“The new elevation maps are snapshots of the current state of the ice sheets,” Helm says. “The elevations are very accurate, to just a few meters in height, and cover close to 16 million square kilometers of the area of the ice sheets.” He says this includes an additional 500,000 square kilometers that weren’t covered in previous elevation models from altimetry.
Space technology shows declining ice mass
Helm and his team analyzed all data from the CryoSat-2 radar altimeter SIRAL in order to come up with the detailed maps. The satellite with this new radar equipment was launched in 2010. Satellite altimeters measure the height of an ice sheet by sending radar or laser pulses which are then reflected by the surface of the glaciers or surrounding areas of water and recorded by the satellite.
The researchers used other satellite data as well to document how elevation has changed between 2011 and 2014.
Rapid ice loss over a short period of time
The team used more than 200 million SIRAL data points for Antarctica and some 14 million data points for Greenland to create the elevation maps. The results show that Greenland alone is losing around 375 cubic kilometers of ice per year.
Compared to data which was collected in 2009, the loss of mass from the Greenland ice sheet has doubled. The rate of ice discharge from the West Antarctic ice sheet tripled during the same period.
I think this is definitely worth talking about. We know the huge implications of polar ice melt for global sea levels. Other research from this year also tells us that, at least in the case of parts of Antarctica, the ice melt is probably irreversible.
We cannot afford to ignore what is happening to the ice sheets. The extent of ice loss in Greenland is particularly dramatic. I am losing patience with those people who respond to studies like this and our reporting on it by saying “but the East Antarctic is gaining volume” and “the Antarctic sea ice has grown”. It is so easy to take things out of context and mix different factors up when trying to understand a very complex system.
I will give the last word here to AWI glaciologist Angelika Humbert, who co-authored the study: “If you combine the two ice sheets (Greenland and Antarctic), they are thinning at a rate of 500 cubic kilometers per year. That is the highest rate observed since altimetry satellite records began about 20 years ago.” It seems to me there is no arguing with that.
Related stories:
Antarctic melt could raise sea levels faster
West Antarctic ice sheet collapse unstoppable
Climate change risk to icy East Antarctica
Antarctic Glacier’s retreat unstoppable
Human action speeds glacial melting
It might sound like stating the obvious, but in fact it is not easy to find clear evidence that human behavior is behind the retreat of glaciers being monitored in different parts of the world. Hence my interest in a study just published in the journal Science.
The main problem is that it usually takes decades or even centuries for glaciers to adjust to climate change, says climate researcher Ben Marzeion from the Institute of Meteorology and Geophysics of the University of Innsbruck. He and his team of researchers have just published the results of a study for which they simulated glacier changes during the period from 1851 to 2010 in a model of glacier evolution. They used the recently established “Randolph Glacier Inventory” (RGI) of almost all glaciers worldwide to run the model, which included all glaciers outside Antarctica.
“Melting glaciers are an icon of anthropogenic climate change”, the authors say. However, they stress that the present-day glacier retreat is a mixed response to past and current natural climate variability and “current anthropogenic forcing”. Their modeling shows though that whereas only 25% of global glacier mass loss between 1851 and 2010 can be attributed to human-related causes, the fraction increases to around 69% looking at the period between 1991 and 2010. So human contribution to glacier mass loss is on the increase, the experts write.
Marzeion says the global retreat of glaciers observed today started around the middle of the 19th century at the end of the Little Ice Age, responding both to naturally caused climate change of past centuries (like solar variability), and to human-induced changes. Until now, the real extent of human contribution was unclear. The authors say their latest piece of work provides clear evidence of the human contribution.
Once more I am happy to refer to the Climate News Network, in this case to Tim Radford, for an easy-to-read summary of the main research results and the background. There is no doubt that glaciers are losing mass, retreating uphill and melting at a faster rate, says Radford. He refers to some Andes glaciers and the the Jakobshavn glacier in Greenland, or Sermeq Kujualleq as I prefer to call it, using the indigenous name. Ice Blog followers may remember my own trip to Greenland and that particular glacier. I have also written on the speeding of the melt there on the Ice Blog and on the DW website.
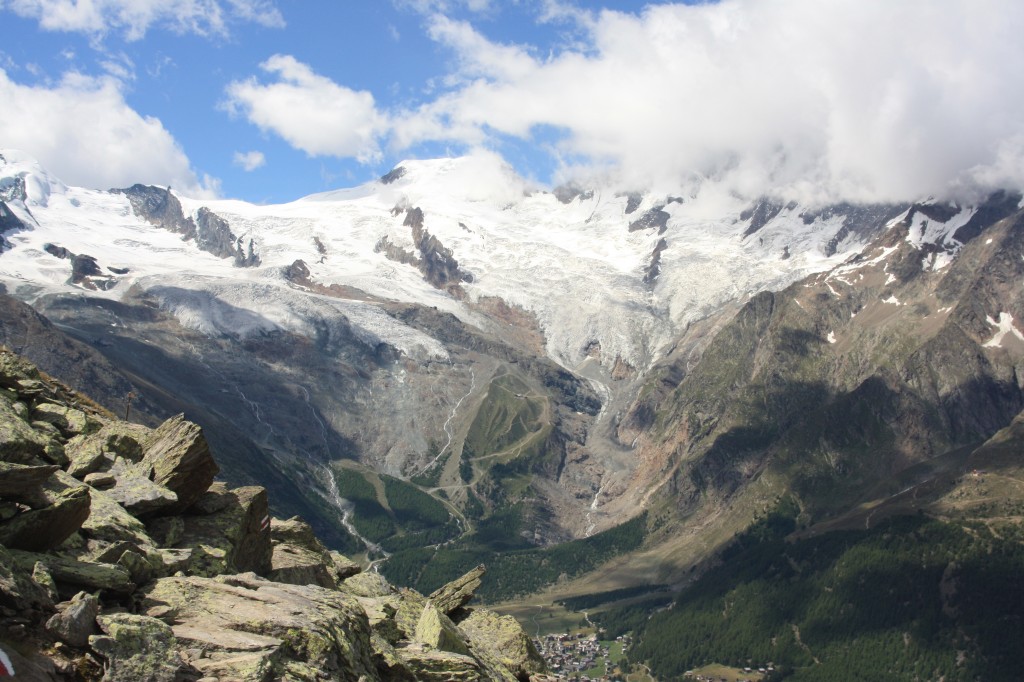

Alpine glacier like these in Saas-Fee, Switzerland, have declined dramatically in recent decades. (I.Quaile)
Radford also refers to ascertaining the melting of alpine glaciers by comparing historic paintings and other documentation with the current ice mass. That decline is something I have observed at first hand in Valais in Switzerland during regular visits over the past 30 years. Look out for a comparative photo gallery of my own pics, when I get time to put it together. Since most of the shots are from the pre-digital era, that will be a time-consuming task.
I also remember a trip to the Visitor Centre of the Begich Boggs glacier in Alaska in 2008. The glacier has already retreated so far you can’t see it at all from the Centre built specially for the purpose of viewing it.
The question until now was how much of all this was caused by natural developments and how much to changes in land use and the emission of greenhouse gases? The latest study supported, among others, by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) and the research area Scientific Computing at the University of Innsbruck, has come up with some answers. Since the climate researchers were able to include different factors contributing to climate change in their model, they can differentiate between natural and anthropogenic influences on glacier mass loss
“While we keep factors such as solar variability and volcanic eruptions unchanged, we are able to modify land use changes and greenhouse gas emissions in our models,” says Ben Marzeion, who sums up the study: “In our data we find unambiguous evidence of anthropogenic contribution to glacier mass loss.”
As always, there is still need for further research – and a lot more monitoring. The scientists say the current observation data is insufficient in general to derive any clear results for specific regions, even though anthropogenic influence is detectable in a few regions such as North America and the Alps, where glaciers changes are particularly well documented.
With global glacier retreat contributing to rising sea-levels, changing seasonal water availability and increasing geo-hazards, the study’s conclusions should help put a little more pressure on the world’s decision-makers to get serious about emissions reductions.
Arctic thaw – carry on regardless?
When a colleague who has a lot of sympathy for those who do NOT accept that humans are responsible for global warming drew attention to the fact that this had been the hottest June on record, following hard on the hottest May, I must admit I was temporarily put of my guard. Aha, I thought. Is he finally getting the message? Alas, the answer is no. There is a small minority of people that still argues – for whatever reason – that natural variation could be responsible for all this, while acknowledging the record concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere. “And all that stuff”. Hm.
![]() read more
read more
Arctic birds breeding earlier
Migratory birds that breed in the Arctic are starting to nest earlier in spring because the snow melt is occurring earlier in the season. This is confirmed by a new collaborative study,”Phenological advancement in arctic bird species: relative importance of snow melt and ecological factors” published in the current online edition of the journal Polar Biology. The scientists, including Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) biologists, looked at the nests of four shorebird species and one songbird in Alaska, recording when the first eggs were laid in the nests. The work was undertaken across four sites ranging from the oilfields of Prudhoe bay to the remote National Petroleum Reserve of western Arctic Alaska.
The scientists looked at nesting plots at different intervals in the early spring. Other variables, like the abundance of nest predators (which is thought to affect the timing of breeding) and satellite measurements of “greenup” (the seasonal flush of the new growth of vegetation) in the tundra were also assessed as potential drivers, but were found to be less important than snow melt.
Lead author Joe Liebezeit from the Audubon Society of Portland says “it seems clear that the timing of the snow melt in Arctic Alaska is the most important mechanism driving the earlier and earlier breeding dates we observed in the Arctic. The rates of advancement in earlier breeding are higher in Arctic birds than in other temperate bird species, and this accords with the fact that the Arctic climate is changing at twice the rate.”
Over nine years, the birds advanced their nesting by an average of 4-7 days. The researcher says this fits with the general observation of 0.5 days per year observed in other studies of nest initiation in the Arctic, of which, they say, there are not very many. The rates of change are much higher than those of observed in studies of temperate birds south of the Arctic.
Co-author Steve Zack from WCS says “Migratory birds are nesting earlier in the changing Arctic, presumably to track the earlier springs and abundance of insect prey. Many of these birds winter in the tropics and might be compromising their complicated calendar of movements to accommodate this change. We’re concerned that there will be a threshold where they will no longer be able to track the emergence of these earlier springs which may impact breeding success or even population viability”.
WCS Beringia Program Coordinator Martin Robards says “Everything is a moving target in the Arctic because of the changing climate. Studies like these are valuable in helping us understand how wildlife is responding to the dramatic changes in the Arctic ecosystem. The Arctic is so dramatically shaped by ice, and it is impressive how these long-distance migrants are breeding in response to the changes in the timing of melting ice.”
In connection with Migratory Bird Day some time ago, I talked to Ferdinand Spina, head of Science at Italy’s National Institute for Wildlife Protection and Research ISPRA, in Bologna, Italy. He is also in charge of the Italian bird ringing centre, and Chair of the Scientific Council of the UN Convention on Migratory Species, CMS. In the interview, he stressed that climate change is becoming one of the greatest threats to birds that breed in the Arctic.
“Birds are a very important component of wildlife in the Arctic. There are different species breeding in the Arctic. The Arctic is subject to huge risks due to global warming. It is crucially important that we conserve such a unique ecosystem in the world. Birds have adapted to living in the Arctic over millions of years of evolution, and it’s a unique physiological and feeding adaptation. And it is our duty to conserve the Arctic as one of the few if not the only ecosystems which is still relatively intact in the world. This is a major duty we have from all possible perspectives, including an ethical and moral duty, ” he says. We talked about the seasonal mismatch, when birds arrive too early or too late to find the insects they expect to encounter and need to feed their young.
This reminds me of a visit to Zackenberg station in eastern Greenland in 2009. At that time, Lars Holst Hansen, the deputy station leader, told me the long-tailed skuas were not breeding because they rely on lemmings as prey. The lemmings were scarce because of changes in the snow cover.
Jeroen Reneerkens is another regular visitor to Zackenberg, as he tracks the migration of sanderlings between Africa and Greenland. A great project and an informative website!
Morten Rasch from the Arctic Environment Dept of Aarhus University in Denmark is the coordinator of one of the most ambitious ecological monitoring programmes in the Arctic. The Greenland Environment Monitoring Programme includes 2 stations, Zackenberg, which is in the High Arctic region and Nuuk, Greenland’s capital, in the “Lower” Arctic. Hansen and other members of Rasch’s teams monitor 3,500 different parameters in a cross-disciplinary project, combining biology, geology, glaciology, all aspects of research into the fragile eco-systems of the Arctic. At that time, he told me during an interview, ten years of monitoring had already come up with worrying results:
“We have experienced that temperature is increasing, we have experienced an increasing amount of extreme flooding events in the river, we have experienced that phenology of different species at the start-up of their growing season or the appearance of different insects for instance now comes at least 14 days earlier than when we started. And for some species, even one month earlier. And that’s a lot. You have to realise the entire growing season in these areas is only 3 months. When we start up at Zackenberg in late May, or the beginning of June, the ecosystem is completely covered in snow and more or less frozen, and when we leave, in normal years – or BEFORE climate change took over – then we left around 1st September and the ecosystem actually started to freeze up. So the entire biological ecosystem only has 3 months to reproduce and so on. And in relation to that, a movement in the start of the system between 14 days and one month – that’s a lot.”
Listen to my radio feature: Changing Arctic, Changing World
I can’t write about birds and climate change in the Arctic without finishing off with a mention of George Divoky, an ornithologist whose bird-monitoring has actually turned into climate-change monitoring on Cooper Island, off the coast of Barrow, Alaska. George looks after a colony of Black Guillemots and spends his summer on the island. In recent years, he has taken to putting up bear-proof nest boxes for the birds, because polar bears increasingly come to visit, as the melting of the sea ice has reduced their hunting options. He has also observed the presence of new types of birds which die not previously come this far north.




























Feedback