Search Results for Tag: Greenpeace
Arctic sea ice low as UN delegates talk climate in a sweltering Bonn.

Blue skies, temperature rising at UN climate headquarters in Bonn
It’s been a scorcher of a week here in Bonn. Delegates to the UNFCCC climate talks (one of the interim meetings to prepare the big COP24 which will take place in Katowice, Poland, in December) have been experiencing non-stop sunshine and temperatures up to 30 degrees Celsius. It feels like the height of summer here, although we are only at the beginning of May.
How appropriate as a backdrop to a meeting that is trying to work out the nitty gritty of actually fulfilling the Paris Agreement commitment to limiting global warming to 2 or preferably 1.5 degrees C warming.
“Currently we’re heading for 3 degrees C of warming rather than the 1.5 degrees C agreed in Paris, and the window of opportunity to reverse this is swiftly closing,” was the comment from Jens Mattias Clausen from Greenpeace Nordic.
Sea ice on the wane (again)
Coming back to work after a long break, a catch-up look at twitter, #Arctic drew my attention first to a tweet from @ArthurWyns telling me “next week it will be 20°C warmer than usual on the #Arctic!!!”
Then came one from @ketil_Isaksen, about one of my own favourite Arctic places:
“Unusually early, extensive and rapid snow melt on #Svalbard releasing extreme melt water discharges in the valleys. +6°C and strong breeze today in #Longyearbyen (78°N)”
In Arctic Today, Yereth Rosen has an article telling us this year’s Arctic sea ice melt season is “off to an unusually fast start”, and provides some worrying data from the NSIDC.

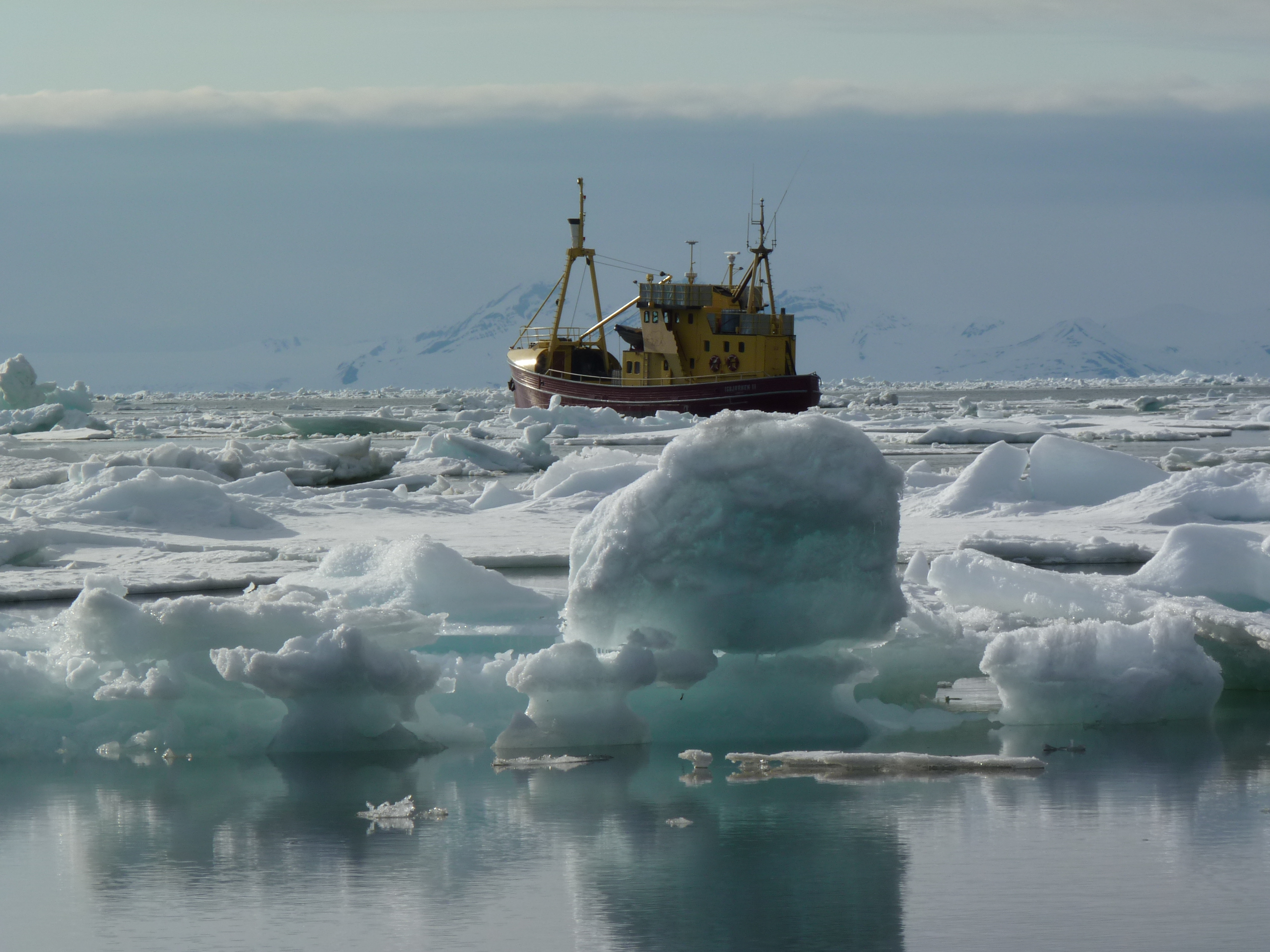
Melting ice off Svalbard (Pic I.Quaile)
Still working out the rules
Given all this, I can well understand why a lot of people involved in the talks in Bonn are feeling frustrated at the slow progress being made.
The delegates are charged with finalizing the rules for the actual implementation of the Paris Agreement. You can be forgiven if you thought things had already moved beyond that stage.
Yes, the wheels of international climate diplomacy move very slowly.
At a press briefing organized by the Climate Action Network (CAN), Li Shuo, a Senior Climate & Energy Policy Officer with Greenpeace stressed: “This is a mini Paris here. We really are trying to finalize all the detailed rules for the Paris Agreement. That’s a daunting task.”

Climate-friendly electric lorry in Bonn (assuming it’s not running on coal-powered electricity?) (I.Quaile)
The Polish dilemma
The next COP at the end of this year will be held in Katowice, the heartland of Poland’s coal industry. Wouldn’t it be fantastic if that turned out to be a turning point in the transition away from fossil fuels to renewable, climate-friendly forms of energy? The city itself says it wants to go green, as one of our correspondents reported in the latest edition of my radio show Living Planet. But, alas. There are absolutely no signs that the Polish government is planning to change its policy any time soon.
“We have seen worrying signs that the Polish presidency thinks that it will sufficient just to get some kind of rulebook,” said Alden Meyer, Director of strategy and policy for the Union of Concerned Scientists, also at the event organized by CAN.
He went on: “We don’t have to wait for the IPCC special report in October to know that what’s on the table and being implemented falls far short of what’s needed to reach the temperature goals countries agreed to in Paris.”
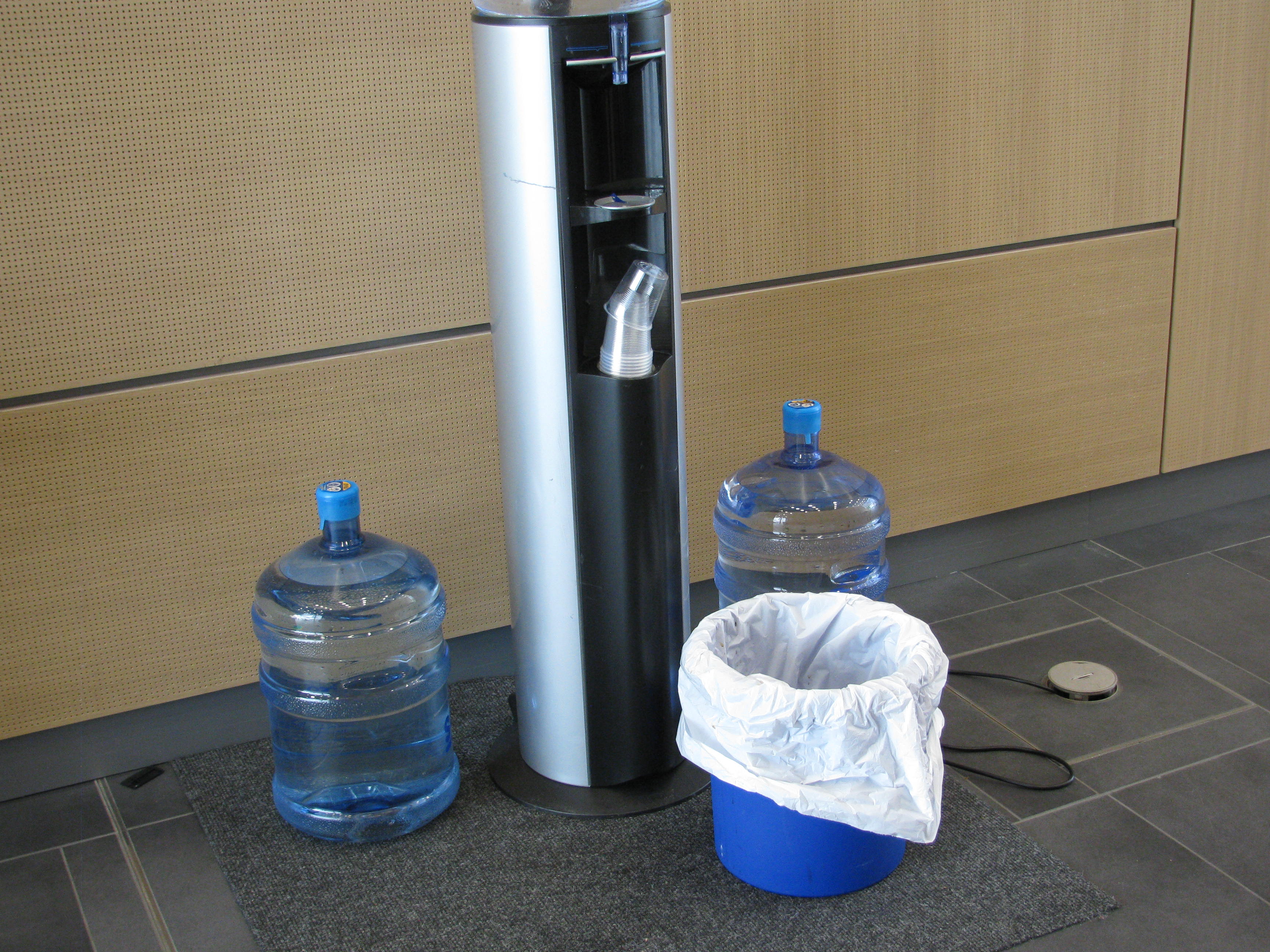

PLASTIC bottles, plastic cups for water? Yes, at the UN climate conference. (I.Quaile)
Coal and climate
I asked him how he saw Poland’s stance on all this at the moment. In spite of the government’s support for coal and reluctance to see to see the EU step up its goals, he stressed that “the role of the presidency is to put their domestic considerations aside and operate on behalf of the entire world community”.
Well, we can try to be optimistic.
“We retain some hope that Poland in its role as the presidency will be different from Poland in its role within the European Union and in its domestic energy policies”, said Meyer, they have to ensure that “the first review of the Paris Agreement, actually triggers much stronger climate commitments”.
Li Shuo noted that Poland was rather late in “shaping up their team” for the climate conference.
“There’s really no clarity from the incoming Polish presidency on how they plan to deal with the political process at Katowice. So we need to hear more from Poland”, he told me at our meeting.
The state of play
When I hear after a week and a half of a two-week working meeting that some progress has been made on technical issues of implementing the rules of the climate agreement, it does not make me feel confident that the international community is going to meet the emissions targets on time. “Other discussions are really stuck because of political differences”, said Li Shuo – mostly relating to the INDCs, or “nationally determined contributions”.
Concerned scientists’ representative Meyer reiterated the urgent need for progress on adaptation, with a lot of climate impacts already being felt: “No matter how successful we are on meeting the Paris temperature limitation goals, those impacts are going to continue to mount over the next several decades because of inertia and momentum in the climate system”.

A maze of science! Good to see it at the Bonn gathering. (i.Quaile)
What happens in the Arctic…
That would also apply to the Arctic region, where temperature rise is not only completely altering things for people and nature up there – it is also changing weather patterns and ocean circulation, with severe implications for the whole planet.
“What is missing is leadership and guidance, especially coming from the presidency”, said Li Shuo. And the spectre of another President is also hovering over the Bonn talks.
However, the Polish government has been preparing for the end-of-year climate extravaganza in other ways. It has passed a bill specifically for the UN summit which bans all “spontaneous gatherings” in the southern coal-mining city of Katowice between November 26 and December 16, which covers the entire period of the conference. It also submits registered participants to government surveillance and allows authorities and police to obtain, collect and use personal data of attendees without their consent or judicial oversight.
We’re still trying to get an official UNFCCC statement on that one. Good ground for getting the whole world on board to halt climate change?
Hot, hot, hotter.. can UN talks in Bonn make a difference?
After all the hype surrounding the Paris Climate Agreement in December, there is a real danger of anti-climax, of feeling self-satisfied, of sitting back saying, “Yes, we did”, while the planet continues to break all temperature records and fossil fuel emissions continue to rise.
The first four months of this year were the hottest ever recorded. Even the “ice island” of Greenland has seen temperatures spiking in April, typically a cold month. NOAA says 2016 could be off to a similar start to 2012, when the surface of the ice sheet started melting early and then experienced the most extensive melting since the start of the satellite record in 1978. We have had several reports of islands being submerged by rising seas and devastating forest fires in Canada and now Russia, which experts say will be more common as the planet warms.
Close to my office here in Bonn, Germany’s UN city, the first official working meeting of all the parties to the Paris Agreement started on Monday, going on until next Friday. I have been there, on and off, talking to people, listening in, trying to get a sense of what is happening – or not, as the case may be.
But the atmosphere in Bonn’s new World Conference Centre is definitely low-key compared with the hype surrounding the Paris Climate Conference. Yet the world climate agreement will be worthless if the countries of the world do not succeed in transmitting it into actions in the very near future.
Time to deliver
The President of the Paris COP21, French Environmenent Minister Segolene Royal, and the incoming President of COP22, which will be held in Marrakech, Morocco’s Foreign Minister Salaheddine Mezouar, have made it clear that it is time to shift the focus from negotiation to implementation and rapid action.
The challenge ahead, they say, is to “operationalize the Paris Agreement: to turn intended nationally determined contributions into public policies and investment plans for mitigation and adaptation and to deliver on our promises.”
Indeed. There is no lack of evidence to support the urgent need for faster action on climate change. An increasing number of extreme weather events are being attributed to climate change. The CO2 concentration in the atmosphere is climbing steadily and is likely to cross the critical 400 ppm mark permanently in the not-too-distant future. The global temperature is already one degree Celsius higher than it was at the onset of industrialization. That means very rapid action is needed to keep it to the agreed target of limiting warming to two degrees and preferably keeping it below 1.5 degrees.
Three degrees and more?
The Paris Agreement was hailed widely as a breakthrough, with all parties finally accepting the need to combat climate change by reducing emissions of greenhouse gases. Countries have put pledges on the table, outlining their emissions reduction targets. But so far, the reductions pledged would still take the world closer to a three-degree rise in temperature.
At the Bonn meeting, the International Energy Agency (IEA), issued a warning that governments can only reach their climate goals if they drastically accelerate climate action and make full use of existing technologies and policies.
“The ambition to peak greenhouse gas emissions very soon is anchored in the Paris agreement, but we don’t see the actions right now to make this happen”, said Takashi Hattori, Head of the IEA’s Environment and Climate Change Unit. “At the same time, there are ‘GDP-neutral’ ways and means to get emissions to peak and then fall whilst maintaining economic growth, and that’s what we need to focus on.”
GDP-neutral means that a technology or policy does not negatively impact the economic growth of a country, and can actually contribute to the growth of that country.
In Bonn, Hattori presented what the IEA calls a “bridge scenario” involving the use of five technologies and policies which it says can bridge the gap between what has been pledged by governments so far and what is required to keep the global average temperature to as low as 1.5 degrees Celsius as part of what the agency terms a “well below 2 degrees world”
The five key measures which the IEA say could achieve a peak in emissions around 2020 are energy efficiency, reducing inefficient coal, renewables investment, methane reductions and fossil-fuel subsidy reform. That sounds to me like a very sensible – and practicable set of measures. But that doesn’t mean it will be easy.
Takashi Hattori stressed that “one size does not fit all” when it comes to climate and energy policies. Different measures will be required in different parts of the world. In the Middle East, for example, the greatest potential to reduce emissions is through reducing fossil fuel subsidies, he argued, while energy efficiency would have the greatest potential in Europe and China. He recommended the “massive deployment of renewables” in India and Latin America.
Other solutions outlined include smart grids, hydrogen as fuel that can be generated with renewable sources of energy, and “smart” agriculture.
The IEA says governments should make the energy transition not only because of rising temperatures, but because of other benefits, such as a reduction of air pollution. That makes sense. People in congested cities are more worried about pollution damaging their health than about climate change, the experts say.
I am reminded of an interview I conducted recently with Chinese expert Lina Li, when she told me she thought China’s air pollution problem would speed up the country’s ratification and implementation of the Paris Agreement.
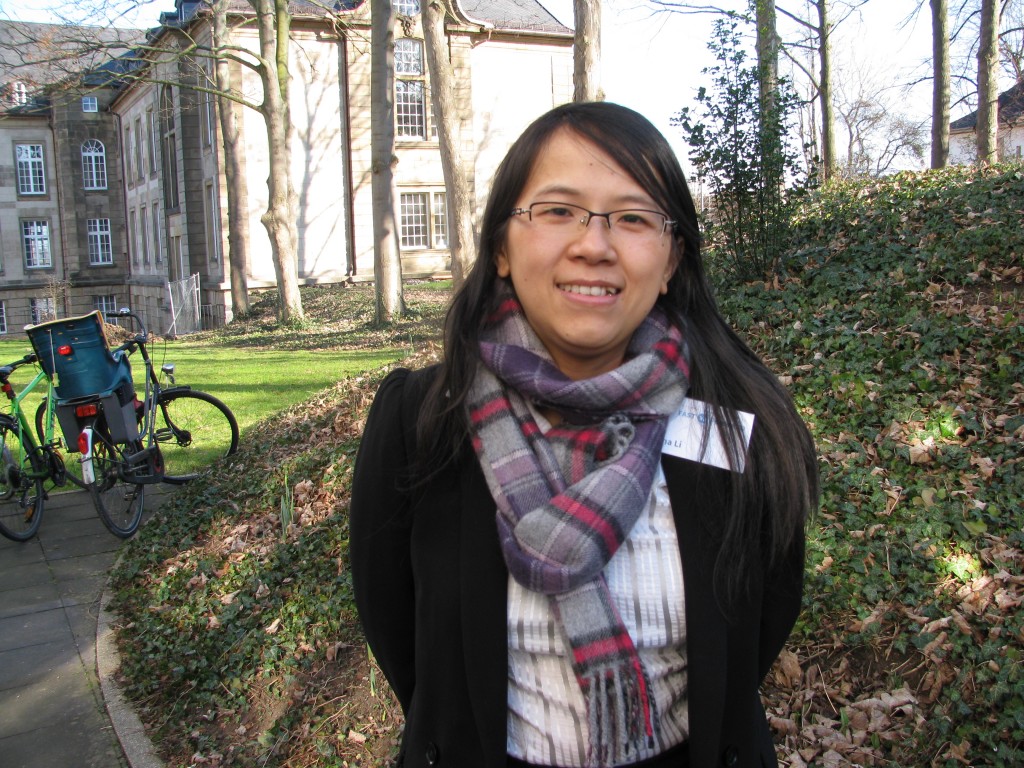

Lina Li from the Adelphi think-tank told me pollution concerns could speed up China’s climate action (Pic. I.Quaile)
The cost argument
Although many scientists are alarmed at the slow pace of emissions reductions, IPCC chief scientist Hoesung Lee told the Guardian in an interview it was still possible to keep to the two-degree target. The current UN climate chief Christina Figueres, who will hand over to Mexican Patricia Espinosa later this year, has said emissions would have to peak by 2020 if that limit is to be kept to. But Lee is keen to keep the options open, saying it would still be possible to keep to the limits if emissions peaked later. But he warned the costs could be “phenomenal”. He believes expensive and controversial geoengineering methods may be necessary to withdraw CO2 from the atmosphere and store it.
A report published this week by UNEP says the cost for assisting developing countries to adapt to climate change could reach up to 500 billion dollars annually by 2050. This is five times higher than previous estimates, the report says.
UNEP urged countries to channel more funds towards adaptation, saying the costs would rise “sharply”, even if countries succeed in limiting global temperature increase to two degrees Celsius.
I asked Mattias Söderberg, Co-Chair of the Climate change advisory group with the climate justice ACT alliance, how he felt about the progress of climate action and the role of the current Bonn meeting. He said the UNEP report, along with the alarming news about islands disappearing under rising seas in the Pacific, highlighted the urgent need for action. “Climate change is not a matter of tomorrow, but a crisis we need to deal with today.”
Time to ratify!
So far, 177 parties have signed the Agreement. But only 16 parties have ratified the treaty. It must be ratified by 55 parties representing 55 percent of total global emissions to enter into force. Söderberg called on wealthy, industrialized countries to move ahead with ratification:
“I am happy to see many of the poor and vulnerable countries moving fast with their ratification, and I hope other countries will follow soon. I am worried about the EU, which seems to be delayed”. Söderberg says the EU, could find itself on the sidelines, overtaken by others.
But the increasing concern over refugees and migration here in Europe could make a lot of countries look more closely at climate change, which is likely to increase the number of people having to leave their homes and look for a better life elsewhere.
“Go, world, go!”
NGO representatives stress that the Bonn talks can only help kick off the series of measures necessary to halt global climate change. Greenpeace climate policy chief Martin Kaiser told me the main work had to be done in the countries themselves, which have to work out their timetables to reach the goals agreed in Paris. That means an early transition to a fossil-free future. Kaiser called on host country Germany in particular, often cited as a model for its shift to renewable energy, to come up with a binding exit strategy for coal by 2030.
“Without an exit from coal, Germany’s signature under the Paris Agreement is worthless”, he told me.
The world’s top emitters, the USA and China, will also have to take major steps to halt climate warming. The delegates meeting in Bonn until May 26 have their work cut out for them. I have always been skeptical about the mass jubilation over the Paris Agreement. Yes, we needed it. But the proof of every pudding is in the eating. All the indications are that 2016 will be the hottest year on record, and probably by the largest margin ever. If the Paris document is to be more than a lot of pieces of paper, we will have to see things happening very soon – and definitely not just in the conference rooms of Bonn and elsewhere.
Earth Day, Climate pact signing – and the Arctic?
How are you feeling this Earth Day? In some ways it could mark a turning point for the planet, with some 165 countries signing the Paris climate treaty at UN headquarters in New York. But, as, always, the proof of the pudding will be in the eating. And so far, I’m not sure it is quite tasty enough.
The trouble is, signing agreements alone is not enough. They have to be turned into action. The world is heating up way too fast, and the transition to an emissions-free world is far too slow. Yes, we can do it, I am convinced. But as well as the political will to sign an agreement, we need the political will to implement measures which will be unpopular with businesses and consumers because they mean major changes to how we work, trade and live.
In the meantime, the Arctic is facing a decline in sea ice that could equal or even beat the negative record of 2012.
Sea ice physicists from the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (AWI), have evaluated current satellite data on the thickness of the ice cover. The data show that the Arctic sea ice was already extraordinarily thin in the summer of 2015 and comparably little new ice formed during the past winter. Speaking at the annual General Assembly of the European Geosciences Union in Vienna, AWI sea ice physicist Marcel Nicolaus said data collected by the CryoSat-2 satellite revealed large amounts of thin ice that are unlikely to survive the summer.
Hard to forecast
Predicting the summer extent of the Arctic sea ice several months in advance still poses a major challenge to scientists and meteorologists. Between now and the end of the melting season, the fate of the ice will ultimately be determined by the wind conditions and air and water temperatures during the summer months. However, conditions during the preceding winter lay the foundations.The AWI scientists say this spring, conditions are as “disheartening as they were in 2012”, when the sea ice surface of the Arctic went on to reach a record low of 3.4 million square kilometres.
At the end of March, the Arctic sea ice was at a record low winter maximum extent for the second straight year, according to scientists at the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) and NASA. Air temperatures over the Arctic Ocean for the months of December, January and February were 2 to 6 degrees Celsius (4 to 11 degrees Fahrenheit) above average in nearly every region.
This year’s maximum winter extent was 1.12 million square kilometers (431,000 square miles) below the 1981 to 2010 average of 15.64 million square kilometers (6.04 million square miles) and 13,000 square kilometers (5,000 square miles) below the previous lowest maximum that occurred last year.
The September Arctic minimum began drawing attention in 2005 when it first shrank to a record low extent over the period of satellite observations. It broke the record again in 2007, and then again in 2012. The March Arctic maximum tended to attract less attention until last year, when it was the lowest ever recorded by satellite.
Ice conditions “catastrophic”
Recently, here on the Ice Blog, I published an account by Larissa Beumer, one of a team of Arctic experts on board the Greenpeace ship the Arctic Sunrise, which has been checking the ice conditions the Arctic archipelago of Spitsbergen. From the ship, she told me the ice conditions were “catastrophic and way outside of normal variations”. She reported transport problems, with many of the usual routes inaccessible by dog sled or snow mobile. She talked of a lack of ice in places where navigation is usually impossibly up to June or July.
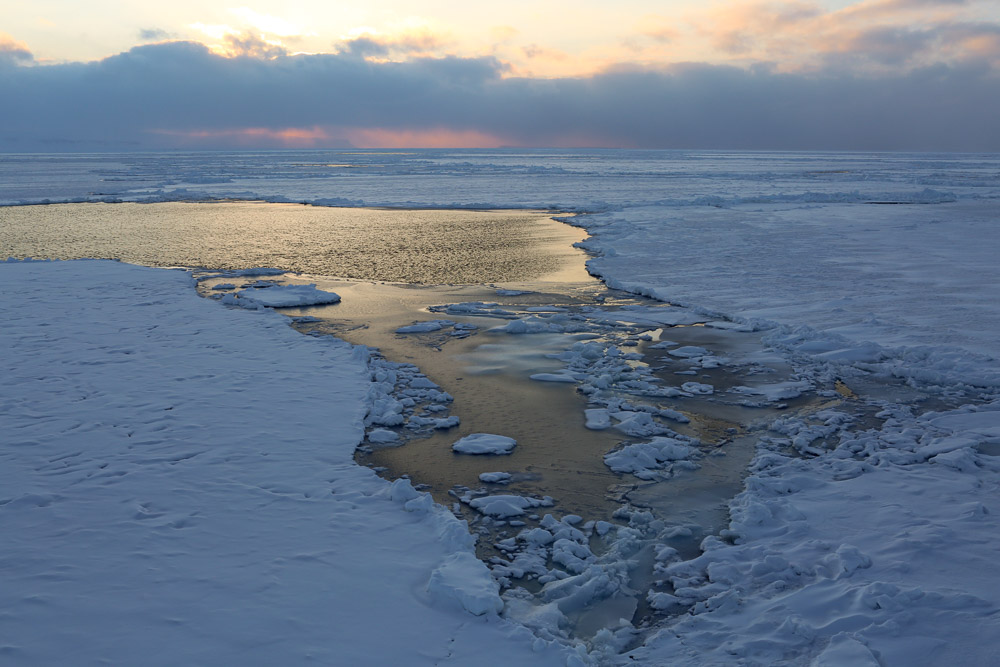

Ice and open water, photographed by Nick Cobbing for Greenpeace, from the Arctic Sunrise, off Spitsbergen.
On thin ice
AWI scientist Marcel Nicolaus says new ice only formed very slowly in many regions of the Arctic, on account of the particularly warm winter.
“If we compare the ice thickness map of the previous winter with that of 2012, we can see that the current ice conditions are similar to those of the spring of 2012 – in some places, the ice is even thinner,” he told journalists at the Vienna Geosciences meeting.
Nicolaus and his colleague Stefan Hendricks evaluated the sea ice thickness measurements taken over the past five winters by the CryoSat-2 satellite for their sea ice projection. They also used data from seven autonomous snow buoys, which they placed on ice floes last autumn. These measure the thickness of the snow cover on top of the sea ice, the air temperature and air pressure. A comparison of their temperature data with AWI long-term measurements taken on Spitsbergen has shown that the temperature in the central Arctic in February 2016 exceeded average temperatures by up to 8 °Celsius.
Breaking ice record
In previously ice-rich areas like the Beaufort Gyre off the Alaskan coast or the region south of Spitsbergen, the sea ice is considerably thinner now than it normally is during the spring. “While the landfast ice north of Alaska usually has a thickness of 1.5 metres, our US colleagues are currently reporting measurements of less than one metre. Such thin ice will not survive the summer sun for long,” Stefan Hendricks said.
The scientists say all the available evidence suggests that the overall volume of the Arctic sea ice will be decreasing considerably over the course of the coming summer. They suspect the extent of the ice loss could be great enough to undo all growth recorded over the relatively cold winters of 2013 and 2014. “If the weather conditions turn out to be unfavourable, we might even be facing a new record low,” Stefan Hendricks said.
So the AWI researchers fear we are going to see a continuation of the dramatic decline of the Arctic sea ice throughout 2016. From that point of view, the signing of Paris climate pact comes way too late. UN Secretary-General Ban ki-Moon is stressing that this can only be the beginning, and that the mammoth task of decarbonising the economy still lies ahead. Here’s hoping the Paris Agreement will not just be a piece of paper which governments use to salve their consciences. Here in Germany, people are concerned that the government will not reach its ambitious climate targets at the present pace. Given that this country has already made remarkable progress in the transition to renewable energy for its electricity production, that is a worrying trend. And other major emitters still have even more to do if that two degree, let alone the 1.5 degrees Celsius limit to global warming is to be more than a very hot piece of pie in the steadily warming sky.
Arctic off limits for giant trawlers?
This past winter, one of the favourite fish dishes being served up here in Germany was skrei, or Arctic cod. I had the feeling this was a new trend in this part of the world, and found myself wondering why there seemed to be more about and whether this could have anything to do with climate change and easier access to fish stocks which were further north before.
My research brought me very quickly to a campaign by Greenpeace, which is tackling this very issue. The website describes the increase in large-scale fishing as a “new threat” to the Arctic:
“Investigations by Greenpeace have shown industrial fishing fleets using destructive bottom trawling are invading previously pristine areas of the Barents Sea in the Norwegian Arctic.”
Greenpeace carried out an investigation focused on part of the Norwegian Barents Sea, including an analysis of vessel movements over three years to September 2015. I called up Frida Bengtsson in Norway, a Greenpeace campaigner and author of the report on the investigation, just published in March, entitled “This Far, no Further. Fishing in the Arctic.”
She told me what she and her fellow conservationists had found out and why they are worried:
“What we’ve seen over the years is that the cod fishery that comes from Norway and provides markets in Europe and also travels to China, North and Latin America, has been expanding further north. So our research shows we are moving further and further north and into the Arctic. These areas have previously been covered by sea ice. Up to half the sea ice cover in the Barents Sea has disappeared since the 1980s”.
Given that the sea ice is disappearing anyway, I wondered whether it wasn’t a natural thing to catch some of the fish in the region:
“Research has just started to look at what’s below the sea ice on the seabed, and we’ve found things they haven’t found in other parts of the Barents Sea where extensive fishing has taken place for longer periods of time. For example, they have found sea pens, up to fifty years of age and up to two metres in height, which is very unique. So we’re calling for a precautionary approach, to not expand into these vulnerable areas but leave them alone and replace the protection the ice once offered with regulation.”
So in fact the problem is not the catching of a limited number of fish, but the effect of the large-scale industry on other species:
“We look at the size of the Barents Sea fishery. It’s very big. There are over 200 factory trawlers licensed to fish in the Barents Sea, and the footprint on the ocean environment is very large. We’re concerned that if this fishery is allowed to move into areas that haven’t been fished before, it will have a very negative impact. We’re mostly concerned about bottom trawling, where you use heavy trawl doors that can weigh several hundred kilos to put the net out and then drag it along the seabed with chains. The creatures on the seabed are very vulnerable and soft, and when they’re hit by these massive trawls they are destroyed.”
I asked what kind of preventive measures Bengtsson and her colleages would like to see?
“We think industry should move out of this area now, and we want to see Norway step up and protect these areas. We think that’s in line with what people generally want when it comes to Arctic protection. It would also mean Norway would meet their commitment towards the 2020 goals the world has set on protecting the world’s oceans.”
Alongside Norway, another major player in the region is Russia. I wondered if Greenpeace was also targeting Russian fishing?
“The Barents Sea fishery is shared between Norway and Russia. But most of the fishing activity actually takes place inside Norway. So we believe that working with the Russian fisheries, the markets that they sell to and the Norwegian government, we will find the right balance. But of course it’s also going to be important to see protection happening all over these vulnerable areas. And the Russians have already acknowledged the vulnerability for their part and have noted these as sensitive areas.
So far, the organization says it has had some interesting reactions both from consumers and the fishing industry to its report:
“It is very clear that people don’t consider that trawling for cod in the Arctic is something that is sustainable. And I think for the industry, it’s important to be at the forefront of sustainability. The indications we have from industry suggest they think it’s important and they want to take preventive measures. That is very encouraging, because I think it’s always good when we can work together. At the moment we’re seeing industry taking initiatives to find some solutions. That is interesting because it’s in line with the same pattern we’ve seen in other places, for example around the soya moratorium in Brazil. There, industry agreed to take preventive measures, to not expand soya production into the Amazon.”
Of course all this relies on pressure from consumers, using their purchasing power to make fishing companies do certain things, like stay out of certain areas. But can ordinary people find out fish is coming from an area of the Arctic it should not be coming from? Not so easy, it seems:
“Unfortunately, today that is very difficult for a consumer. But even so, it’s very important that you ask the question. If more and more consumers start asking where their fish comes from, that will lead to better labeling. We have seen initiatives in Europe where some fish is labeled, with catching area and the fishing boat, but of course that’s only a very small share. We would like to see that happening with the whole of the seafood market”.
Plenty of food for thought there, for anyone who eats fish as well as the industry that brings it from the ocean to the table.
Arctic fish and chips? Listen to my interview with Frida Bengtsson.
A letter from Svalbard’s dwindling sea ice
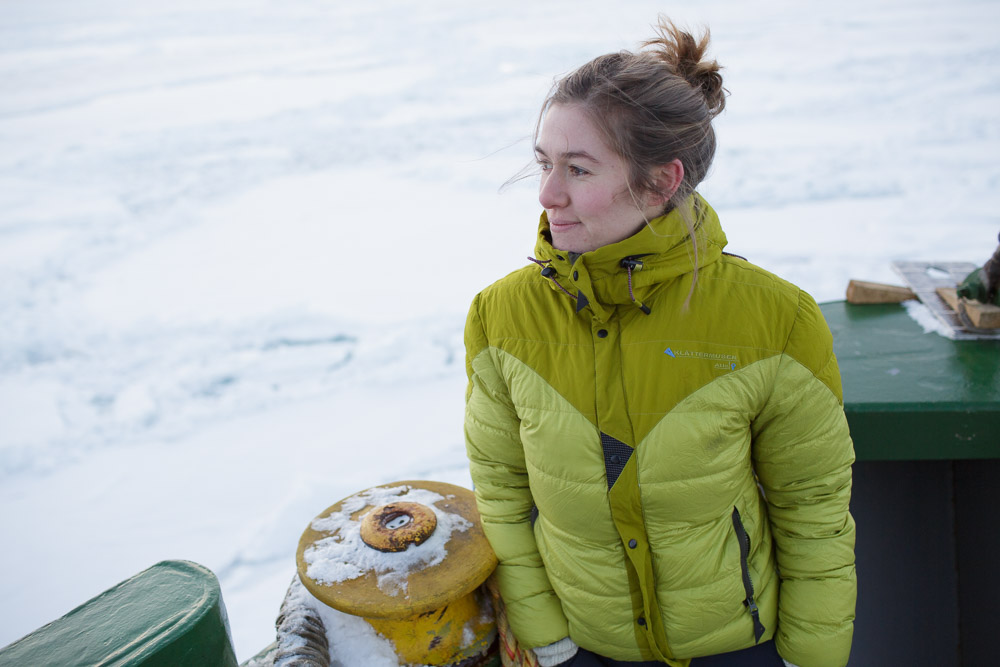

Greenpeace’s Larissa Beumer on board the Arctic Sunrise in the Spitsbergen archipelago. (Pic: Nick Cobbing, courtesy of Greenpeace).
The Arctic sea ice has reached its maximum winter extent for this season, and it was a record low, as reported here on the Iceblog.
The Greenpeace ship the Arctic Sunrise is currently sailing in the Hinlopen Strait in the Arctic archipelago of Spitsbergen, checking out the ice conditions. Larissa Beumer is on board. I wanted to know what the ice situation was like, and she sent me this report. Photographer Nick Cobbing is also on board, so that means we can have a couple of his wonderful pics on the Iceblog. Thanks Nick and Greenpeace.
LARISSA BEUMER: “The ice conditions up here vary considerably from year to year. But this year is really extreme. On the west coast, almost none of the fjords are frozen up. The only exceptions are Dicksonfjord and Van Mijenfjord (and that one isn’t frozen up as far as it “normally” is).
On the east coast, there is no solid, stable ice, frozen through like it normally is. The ice there is moving a lot, it has often broken apart and been blown together again by the wind, so it’s not reliable. (And in general there is less ice there as well).
That means tourists and locals are very severely restricted in their activities. Dog sled and snowmobile tours normally mainly use the frozen-over fjords on the west coast. But this year, a lot of the usual main routes are not usable. That means some of the main destinations like Pyramiden (and Isfjord radio) can only be reached by taking major detours over the glacier systems. The east coast is another of the main destinations for snowmobile excursions. You can still get there quite well, but driving over the ice is more risky than usual. (One tourist group went through the ice this season, but nobody was hurt).
We sailed north along the west coast, then east along the north coast to the Hinlopen strait. We didn’t encounter any large stretches of ice masses anywhere on route. Normally, there is so much ice up there in winter that the route is only navigable from June or July.
Actually, in “normal” years, the pack ice extends down from the north to the northern coast of Spitsbergen right into summer. Now it’s just the bginning of April and the pack ice only starts much further north. Sailing to Nordaustlandet is normally still challenging in August, because of the ice conditions. This year, it’s more or less navigable already. It used to be that expedition cruises billed as “Circumnavigation Cruises” had to change their route because the ice in the north was still so thick they couldn’t get through. I think at the moment you could already do a circumnavigation without any problems.
The ice we can see is mainly fresh ice, one-year ice, with open water here and there and a lot of breaks in it. As I said before, it’s moving about, breaks and is pushed together again. As far as we can see, the thickness is relatively varied, but there is a lot of thin ice amongst it.
The current ice chart from the Norwegian Meteorological Institute shows that a lot of ice from the south has been pushed into the Hinlopen Strait by the wind over the last two days. All this ice just wasn’t there a few days ago. It comes from the pack ice in the north-east, towards Franz-Josef-Land. So it’s not ice that formed here.
So, all in all, it seems fair to say that this year the ice conditions up here around Svalbard are catastrophic and way outside of normal variation. Oscar, our polar-bear guide, says he has never experienced anything as bad as this in the 13 years he has being living here.”
Larissa Beumer, on board the Arctic Sunrise, Spitsbergen.































Feedback