Search Results for Tag: WWF
“Cheers” to a cool Arctic in 2017
As 2016 draws to an end, the shortest day has passed in the northern hemisphere, and it should normally be a “cool” time of the year, in more ways than one, especially in the Arctic. But with temperatures at a record high, sea ice at a record low and feedback loops springing into action, the Arctic is hotting up – and I wish I could say the same for efforts to halt climate change.
Ice expert Jason Box tweeted this morning:
North pole near or at melting, strange given 24 h darkness there now, cold space aloft… is all about heat inflow from south @PolarPortal pic.twitter.com/r5C4i28vKR
— Jason Box (@climate_ice) December 23, 2016
Meteorologist Scott Sutherland writes on Dec. 22nd:
“(…) North Pole temperatures have climbed to 30oC hotter than normal for this time of year.
(…) Now, in late December, in the darkness of the Arctic winter, air temperatures at the North Pole have actually reached the freezing point, as recorded by weather buoys floating within a few degrees of the pole. As of the morning of Thursday, December 22 (3 a.m. EST), the International Arctic Buoy Programme (IABP), operated out of the University of Washington, recorded temperatures from these buoy up to 0oC or slightly higher.”
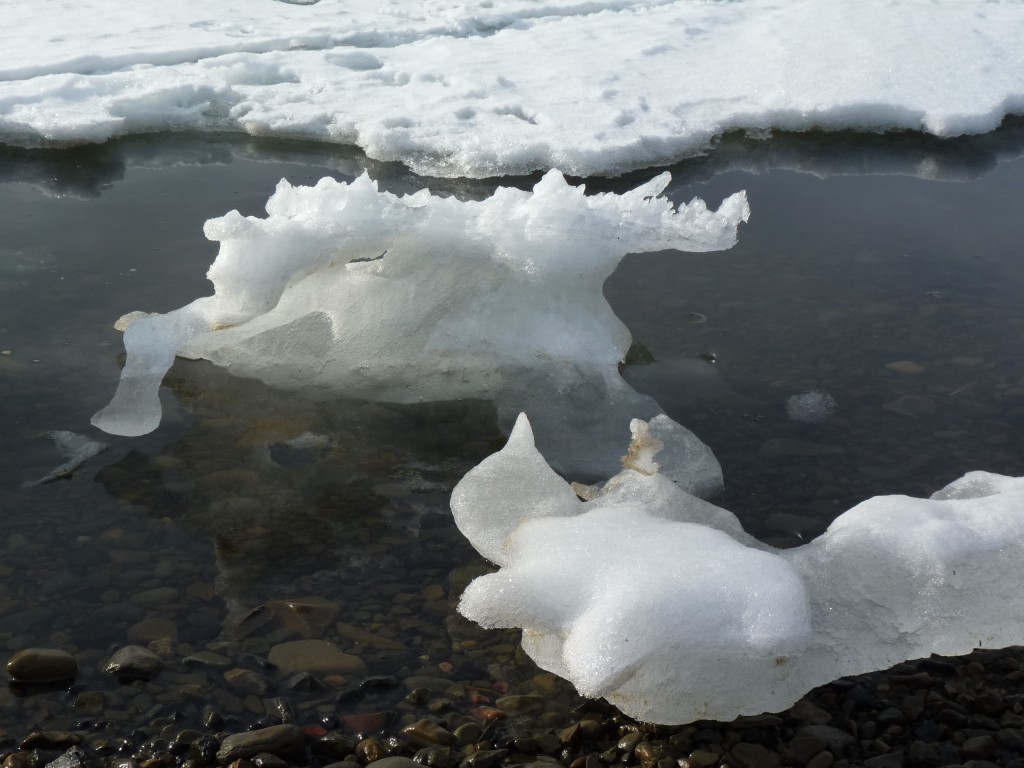
“(…) Right now, Arctic sea ice extent is at the lowest level ever recorded.”
Arctic in need of tlc?
It looks like the Arctic is urgently in need of some tlc – or maybe intensive care would be more fitting.
The Arctic Report Card for 2016 recently published by NOAA should have set alarm bells ringing. Based on environmental observations throughout the Arctic, it notes a 3.5 degree C increase since the beginning of the 20th century. The Arctic sea ice minimum extent tied with 2007 for the second lowest value in the satellite record – 33 percent lower than the 1981-2010 average. That sea ice is relatively young and thin compared to the past.
A “shrew”d indicator of Arctic warming
Let me quote what are described as the “Highlights”:
“The average surface air temperature for the year ending September 2016 is by far the highest since 1900, and new monthly record highs were recorded for January, February, October and November 2016.
After only modest changes from 2013-2015, minimum sea ice extent at the end of summer 2016 tied with 2007 for the second lowest in the satellite record, which started in 1979.
Spring snow cover extent in the North American Arctic was the lowest in the satellite record, which started in 1967.
In 37 years of Greenland ice sheet observations, only one year had earlier onset of spring melting than 2016.
The Arctic Ocean is especially prone to ocean acidification, due to water temperatures that are colder than those further south. The short Arctic food chain leaves Arctic marine ecosystems vulnerable to ocean acidification events.
Thawing permafrost releases carbon into the atmosphere, whereas greening tundra absorbs atmospheric carbon. Overall, tundra is presently releasing net carbon into the atmosphere.
Small Arctic mammals, such as shrews, and their parasites, serve as indicators for present and historical environmental variability. Newly acquired parasites indicate northward shifts of sub-Arctic species and increases in Arctic biodiversity. “
Getting the message across
The NOAA website sums it up in a video, saying:
“…Rapid and unprecedented rates of change mean that the Arctic today is home to and a cause for a global suite of trillion dollar impacts ranging from global trade, increased or impeded access to land and ocean resources, changing ecosystems and fisheries, upheaval in subsistence resources, damaged infrastructure due to fragile coastlines, permafrost melt and sea level rise, and national security concerns.
In summary, new observations indicate that the entire, interconnected Arctic environmental system is continuing to be influenced by long-term upward trends in global carbon dioxide and air temperatures, modulated by regional and seasonal variability.”
Margaret Williams, the managing director for WWF’s US Arctic programme had this to say:
“We are witnessing changes in the Arctic that will impact generations to come. Warmer temperatures and dwindling sea ice not only threaten the future of Arctic wildlife, but also its local cultures and communities. These changes are impacting our entire planet, causing weather patterns to shift and sea levels to rise. Americans from California to Virginia will come to realize the Arctic’s importance in their daily lives.
“The science cannot be clearer. The Arctic is dramatically changing and the culprit is our growing carbon emissions. The report card is a red flashing light, and now the way forward is to turn away from fossil fuels and embrace clean energy solutions. Protecting the future of the top of the world requires us to reduce emissions all around it.”
Sack the teacher, kill the messenger?
That was her response to the Arctic Report Card. In my school days, the report card was a business to be taken seriously. A bad report meant you were in trouble and would have to smarten up your act or you would be in big trouble with mum and dad.
The question is – who gets the report, and who has to smarten up their act?
This one should make the governments of this world speed up action on mitigating climate change and getting ready for the impacts we will not be able to halt.
Then again, they could just try to get rid of the messengers who come up with the bad news. If your kid’s report card is bad, do you try to improve his performance – or get rid of the teacher who came up with the negative assessment – based on collected data?
I am concerned that the administration in the wings of the US political stage could be more likely to do the latter. As I wrote in the last Ice Blog post, the new Trump administration is threatening to cut funding for climate research. The proposed new Cabinet is well stocked with climate skeptics.
Concern about research
Financial support for the Arctic Report Card is provided by the Arctic Research Program in the NOAA Climate Program Office. Its preparation was directed by a “US inter-agency editorial team of representatives from the NOAA Pacific marine Environmental Laboratory, NOAA Arctic Resarch Program and the US Army Corps of Engineers, Cold Regions Research and Engineering laboratory.
Yereth Rosen, writing for Alaska Dispatch News, quotes Jeremy Mathis, the director of NOAA’S Arctic research program and one of the editors of the report card.
“The report card this year clearly shows a stronger and more pronounced signal of persistent warming than in any previous year in our observational record”.
“We hope going into the future that our scientists and researchers still have the opportunity to contribute and make possible the summary that we’re able to present. So we have every intention of continuing to publish the Arctic Report Card as we have in the past and pulling together the resources and the right people that allow us to do that”.
Livid and acrimonious
The debate over President Obama’s announcement that he was making a vast area of the Arctic Ocean off-limits to drilling for oil or gas, shows the dilemma of our times – and .. which could influence the living conditions on our planet for generations to come.
Erica Martinson, writing for the Alaska Dispatch News, provides interesting insights into the debate for those of us who do not live in Alaska.
She quotes Alaska’s Republican Congressman Don Young, saying he used “livid language” in his response. Obama’s move means “locking away our resources and wuffocating our already weakened economy”. He goes on “Alaska is not and shuld not be used as the poster child for a pandering environmental agenda”.
Ooh. Livid indeed.
She also quotes Republican Senator Dan Sullivan as describing the move as “one final Christmas gift to coastal environmental elites”. So would those be the indigenous communities being forced to relocate because climate changes are destroying their homes, Senator?
The administration, on the other hand, says it is protecting the region from the risk of a catastrophic oil spill, Martinson writes.
It seems to me that Obama’s parting gift goes rather to the “Alaska Native communities of the North Slope” who “depend largely on the natural environment, especially the marine environment, for food and materials”, and to the many endangered and protected species in the area, “including bowhead and fin whales, Pacific walrus, polar bear and others”.
What about the Paris Agreement?
But as well as that regional aspect, the decision not to open up new regions to drilling for oil and gas is in line with the global need to cut fossil fuel emissions to halt the warming of the world.
Jamie Rappaport Clark, CEO of “Defenders of Widife”, puts it:
“It marks the important recognition that we cannot achieve the nation’s climate-change goals if we continue to expand oil and gas development into new, protine environments like the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans”.
This is not just about Alaska, not just about the Arctic, but the future of the planet as a whole.
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) says 2016 is on track to be the hottest year on record. According to UN estimates, the global temperature in 2016 was 14.88 degrees C – 1.2 degrees higher than before the industrial revolution began in the mid-19th century.
In an article for the New York Times on December 22, Henry Fountain and John Schwartz quote NOAA’s Arctic Research Program director Jeremy Mathis.
“Warming effects in the Arctic have had a cascading effect through the environment” “We need people to know and understand that the Arctic is going to have an impact on their lives no matter where they live”. That includes the oil-industry-friendly and climate skeptical team that is set to enter the White House in the New Year,
So when I propose a toast to a cool Arctic in 2017, I am not just thinking of my friends in the high north. For all our sakes, we have to kick our fossil fuel habits, save energy and cut the emissions which keep the giant refrigerator that helps make our world a viable place to live well chilled.
Farewell to ‘Last Ice’ victims in a rapidly warming world
Ice Blog readers may remember the story of the two ice researchers and polar explorers who died when they broke through unexpectedly thin ice in the Canadian Arctic earlier this year. This week I had the chance to join friends and admirers of Marc Cornelissen and Philip de Roo at a ceremony held in their home country, the Netherlands. The unusually warm November weather, with people sitting out eating ice cream, seemed oddly apt for a tribute to two people who died doing climate research.
![]() read more
read more
“Last Ice” claims lives of researchers
This post was to be about a trip I just made to St. Petersburg to talk to students and fellow journalists about reporting climate change. Instead, I am shocked and saddened to be writing of the apparent loss of one of the people whose work featured prominently in my talks there. Polar explorer and researcher Marc Cornelissen, who led our Alaskan Arctic expedition in 2008, the first to be documented on the fledgling “Ice Blog”, disappeared in the Canadian Arctic this week and is presumed drowned after breaking through unseasonably thin ice.
In workshops and discussion panels in St. Petersburg, I found myself recounting, as I often seem to do, some of my experiences during that trip. This was the expedition which strengthened my conviction that reporting on climate change in the polar regions and its relevance for the whole world had to be a main focus of my work in coming years. I have been in the Arctic many times, but somehow that trip seems to be the one I always come back to. Dutch polar explorer and researcher Cornelissen was taking a group of young Europeans to Arctic Alaska, to find out how scientists measure sea ice thickness and other parameters – and how climate change was affecting the local indigenous population. In a talk last week, while I told students and environment journalists in St. Petersburg how that group of young Europeans found out about climate change first-hand during the “Climate Change College” project, I was unaware that the charismatic leader of that trip would not be returning from his latest Arctic expedition.
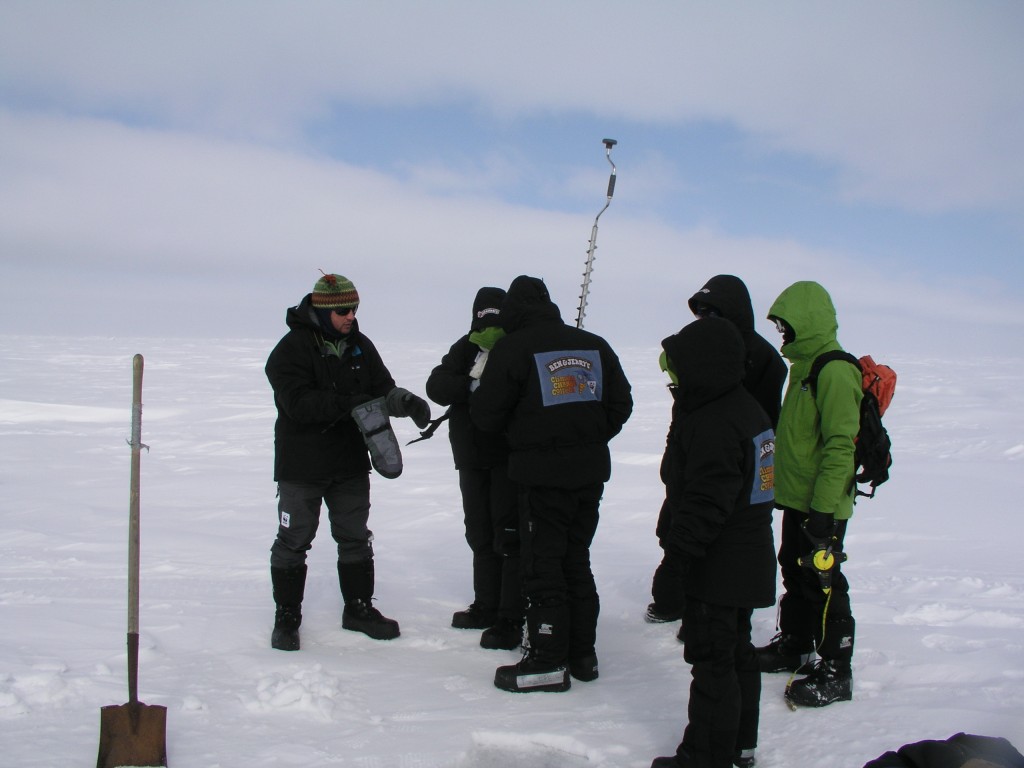

Marc Cornelissen shows climate ambassadors how to drill to measure ice thickness (i.Quaile, Alaska, 2008)
“Search and rescue” becomes “recovery”
Back in Germany I opened my Ipad one morning this week to find urgent messages from two friends I first met during that Alaskan trip – one in the USA, one in Europe – telling me Marc and his colleague Philip de Roo had gone missing on their latest climate fact-finding mission in the Canadian High Arctic. Since then, the search and rescue operation has been called off, the two researchers presumed drowned.
Marc, founder of the organisation Cold Facts, which supports scientific research in polar areas, was travelling on skis with his colleague, for a mission called the “Last Ice Survey“. That title was to become tragically apt in a way they had not anticipated. The two were measuring the thickness of the ice in the “Last Ice Area”,, which is thought to be the place where summer sea ice will continue longest as climate change progresses.
Arctic conditions “tropical”
In his last audio message, sent on April 28th, Marc Cornelissen, always with a great sense of humour, recounts how the weather had been so hot he had to ski in his underpants. He talks of thin ice ahead, and of the likely need to alter course to avoid it.
“We think we see thin ice in front of us, which is quite interesting, and we’re going to research some of that if we can”, Marc said in the last voice mail. Tragically, it seems that research was to prove fatal for the two curious travellers.
Next day the Royal Canadian Mounted Police in Resolute Bay was alerted by a distress signal from the pair, approximately 200 kilometres soiuth of Bathurst Island. The search aircraft sighted one of their sleds, partly unpacked, on the ice with their sled dog, close to a hole in the ice. The other sled was in the water with various bits of equipment.The search and rescue venture was eventually abandoned. The dog has been rescued, but the operation to locate Marc, Philip and their equipment and bring it home, has been halted by bad weather.
The remote, cold, Arctic is a risky place to travel at the best of times. Cornelissen and de Roo were experienced polar explorers. They knew the risks. What they presumably did not know, was just how thin that “last ice” had become.
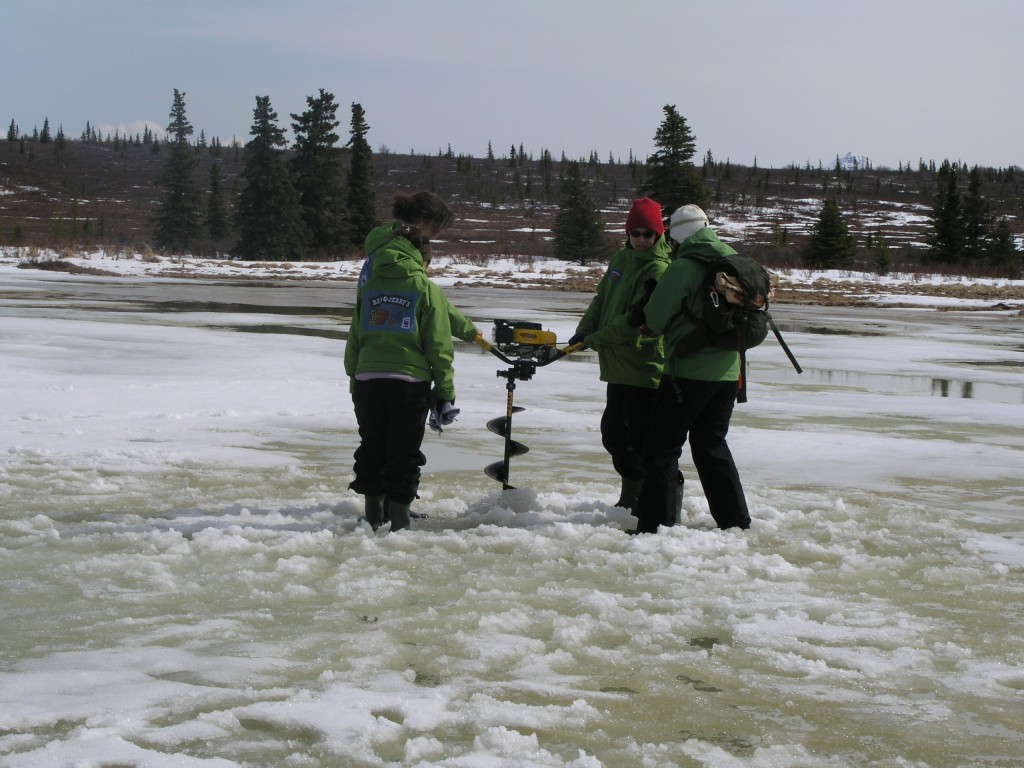

Cornelissen’s team drills to measure methane emissions from melting permafrost (I.Quaile, Denali, 2008)
Climate change is affecting the Arctic faster than any other area of the world. That was the message behind the work of the two researchers . Perhaps it was changing faster than they could have imagined.
Beautiful, fragile, perilous
I am deeply moved by the loss of these two talented and committed fellow Arctic-enthusiasts, who would still have had so much to offer the world. How ironic that the rapid ice melt they were out to document was, it seems, to claim their lives. How sad if these two had to die to underline the point.
A year and a half ago, I narrowly escaped with my life when I slipped off an icy mountain ledge in the alps. Since then, I have been more keenly aware than ever of that ambivalent nature of ice – the attraction of its beauty and the unpredictable dangers. I remember the feeling “this cannot be happening to me”, as I thought the ice I loved was throwing me to my death. I am somehow haunted by images of what Marc and Philip might have sensed in those final, precarious moments in their beloved Arctic.
Marc Cornelissen was a charismatic character, full of stories and enthusiasm for the polar regions. I remember how we laughed as he told us the tale of the “polar bear that caught me with my pants down”, during one of his expeditions. But humour and positive outlook never detracted from his concern for the safety and well-being of his charges, as he guided them onto the sea ice or frozen Arctic lakes. Cornelissen was also a motivating guide and mentor to many who have gone on to make their professions in the fields of climate, environment and sustainability.
He also had an unerring sense of the issues that would emerge ever larger in the polar climate debate in the years to come: sea ice melt, coastal erosion, melting permafrost, methane emissions.
“Everything is connected”.
Why is it I always come back to that particular Arctic trip? It is partly because it was an encounter between commited, idealistic, prosperous young Europeans, with their first climate-saving projects already in the bag, and the “locals” of Barrow, the northernmost – and so very different – settlement in the USA. These were a mixture of Inupiat traditional whale-hunters, who depended on stable sea ice to hunt – and oil workers, who owed their livelihood to the fossil fuels which are helping to melt it.
“Everything is connected” was the conclusion that dawned on the young Danish member of the group, as we stood by a visitors’ centre to look at glaciers further south – which had retreated so far, they were no longer visible from that point.
Irish “climate ambassador” Cara Augustenborg, posted her own moving tribute to Cornelissen earlier this week.
The network that was born during that Alaskan trip is still thriving. The climate ambassadors have gone on to make their ways and play their parts in the effort to understand the workings of the planet and create a low-carbon future.
For all that, you need inspiring leaders, and people who are not afraid to take on the risks of the remote, icy, unpredictable and rapidly changing Arctic. In the last personal message I got from Marc Cornelissen, he had been looking at the Ice Blog and said how pleased he was that I had “stayed with the Arctic”. Me too, Marc. And I am sorry I will never be able to interview him on what seems to have been his final expedition to the “Last Ice”.
Ice paradoxes from pole to pole
Returning after a longish break with little access to news and data, there are several ice and snow stories jumping out of my mailbox at me. I’ve picked out two which those of a skeptical persuasion might say disprove some key climate assumptions, but which actually, in fact, confirm some trends and predictions.
Worrying, but not unexpected, are the latest measurements of the extent of the Arctic sea ice. In February, the experts at the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) based in Boulder, Colorado, noted a record for the lowest observed maximum sea ice extent. Although it seems the sea ice did grow at some points during March, the overall for the month was the lowest recorded since satellite measurements began in 1979. The average extent for the month was 14.39 million square km – some 1.13 million square km below the 1981-2010 long-term average. The previous March low of 14.45 million square km was recorded in 2006.
In the Arctic Journal, Kevin McGwin quotes Andy Mahoney, a geophycisist with the Sea Ice Group at the University of Alaska Fairbanks, as saying the irregular pattern, with a kind of “double dip”, with the ice decreasing, increasing, then decreasing again, is “a pretty unusual event, regardless of the reason”. Normally, the ice levels would increase to the seasonal maximum first in March, then decline.
One reason, Mahoney says, could be the wind blowing ice into the regions where ice growth was observed, according to the NDSIC the Bering Sea, Davis Strait and around Labrador.
No contradiction to climate warming theory
The NSDIC says warm conditions in the Bering Sea and the Russian Sea of Okhotsk contributed to the record low winter ice maximum.
The overall downward trajectory, however, is clear. The brief increase in March is not a sign that the sea ice is recovering. Mahoney told the Arctic Journal parts of Alaska had seen abnormally high temperatures this winter, which was in line with the overall seasonal ice observations.
“What drives the maximum extent is what happens at the margins, and they can grow and retreat due to short-term variants. The conditions in the central Arctic, far from the action, are indicative of the warm year we’ve had in Alaska,” he said. Barrow, on Alaska’s northern coast, far away from the southern margin, for example, saw a lot of broken ice this winter, according to Maloney.
WWF expressed concerned about the latest figures:
“This is not a record to be proud of. Low sea ice can create a series of reactions that further threaten the Arctic and the rest of the globe,” said Alexander Shestakov, Director, WWF Global Arctic Programme.
“This chilling news from the Arctic should be a wakeup call for all of us,” said Samantha Smith, the leader of WWF’s Global Climate and Energy Initiative. She stresses the need to cut global emissions to halt the Arctic melt.
The proportion of thick Arctic ice that lasts multiple years has dwindled over the past two decades. A recent study shows that Arctic sea ice has thinned by 65 per cent since 1975, leaving ice that is more susceptible to melting.
Writing for Alaska Dispatch News (AND), Yereth Rosen notes that the most dramatic changes in the Arctic sea ice extent have been in the melt season, not in the period of maximum winter coverage. He quotes NSIDC scientist Julienne Strove, who led a study published last year in Geophysical Research Letters which showed the open-water season is lengthening, mostly because of extended melt in summer and autumn. So is this additional winter record a sign of more melting to come? Only time will tell, but the signs are not looking good.
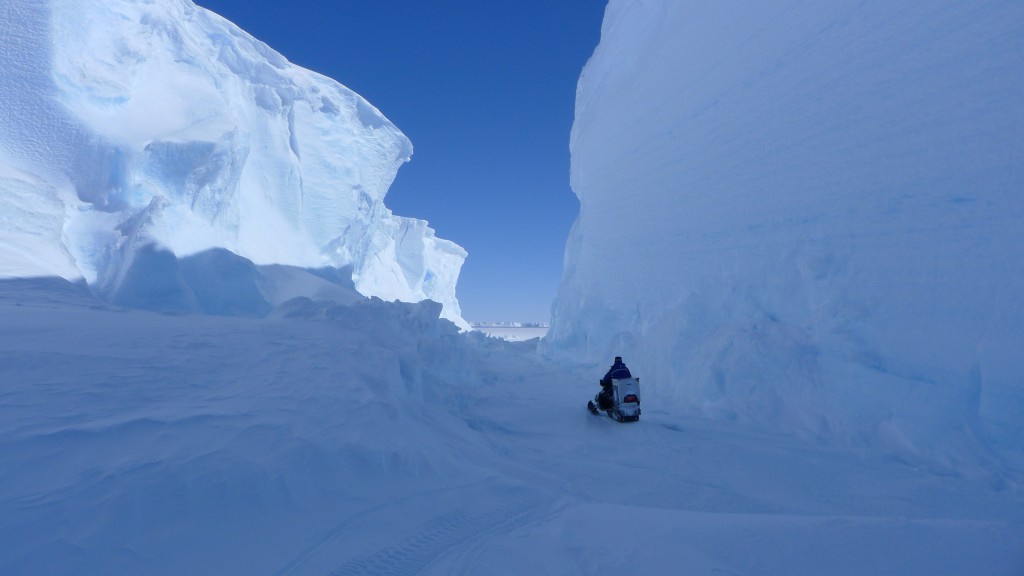

Warmer temperatures, more snow? Belgian International Polar Foundation shot of director and explorer Alain Hubert in the Antarctic.
A story from the opposite pole has also attracted attention. It says climate change is actually increasing the amount of snow in the Antarctic. Puzzling? Not necessarily.
More heat, more snow?
An international study headed by Germany’s Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact research (PIK) comes to the conclusion that every degree of regional warming could increase snowfall there by around five percent. The estimate is based on ice cores and climate modeling.
The information adds a new element to calculations of how much the Antarctic will contribute to global sea level rise. Some people might assume more snow would stop the Antarctic from losing mass. In fact the increasing weight of new snow and ice can make it slide towards the coast and into the ocean faster. In this connection, you might like to read some more stories on these Antarctic issues:
Thicker-ice-in-the-antarctic-good-news-for-the-climate?
Antarctic melt could raise sea levels faster
West Antarctic ice sheet collapse unstoppable
Anders Levermann, one of the new study authors, whom I have spoken to several times on the effects of climate change on the Antarctic and global sea levels, says the latest results back up earlier conclusions that the Antarctic will lose more ice than it will gain and thus have a major influence on global sea level. Levermann, from PIK, is also one of the lead authors of the sea-level chapter of the IPCC report. He stresses that the latest study just provides yet another piece of the “jigsaw puzzle” coming together on how global sea level is likely to develop in the future.
If the world leaders called on to come up with a new world climate agreement at the end of this year need any more motivation, this scientific research from both ends of the world should really give them an extra push.
Arctic oil – still in the picture
Was it too good to be true? The euphoria over the US administration’s moves to protect the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge was dampened somewhat when, just two days later, it released a long-term plan for opening coastal waters to oil and gas exploration, including areas in the Arctic off Alaska. The plan excludes some important ecological and subsistence areas from potential drilling, but it still includes some Arctic areas, including parts of the Beaufort and Chukchi Seas.
Margaret Williams, managing director of WWF US Arctic Programs, told Deutsche Welle, she welcomed in particular the decision to protect the biological hotspot of Hanna Shoal from risky offshore drilling. The Hanna Shoal is a key site for walruses and other animals.
But she stressed other areas of the US Arctic were still subject to oil exploration. The new program will not affect existing leases held by Shell in the Chukchi Sea. The company’s efforts have been the subject of controversy, not least since the grounding of the drill rig Kulluk.
Williams says the problem with the new proposal in general is that it “keeps drilling for oil in the US Arctic offshore in the picture”. With the US poised to take the helm of the Arctic Council, she called for protecting biodiversity to be a top priority for all Arctic nations.
Oil: valuable asset or liability?
It comes as no surprise that Alaskan state politicians and the oil industry promised to fight planned restrictions, saying they were harmful to the economy. But this brings us back to the question of whether the search for new oil in the Arctic makes any sense at all at a time when oil prices are at a record low and the USA is producing plentiful supplies of shale gas.
Bloomberg financial news group quotes financial experts as saying the world’s biggest oil producers do not have “bulletproof business models”, and cites financial cutbacks by BP, Chevrol and Shell:
“The price collapse hobbles a segment of the industry that had already been struggling with years of soaring construction costs, project delays, missed output targets and depressed returns from refining crude into fuels”, analyst Anish Kapadia told Bloomberg.
Climate paradox
Conservation groups stressed the need for a different focus, in the year when the USA has pledged to help create an effective new world climate agreement in Paris in November.
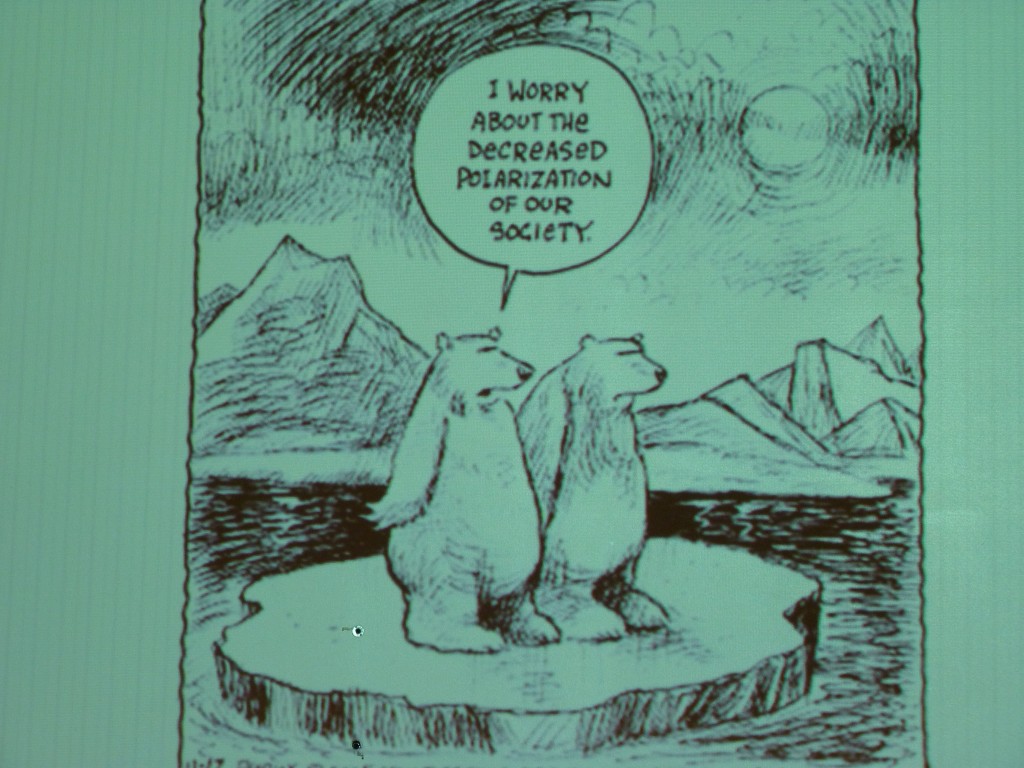

Cartoon by psychologist Per Espen Stoknes, BI Norwegian School of Management.( I photographed it at a workshop on climate change psyschology)
“Rather than opening more of the Arctic and other US coastal waters to drilling for dirty energy, the US needs to ramp-up its transition to a clean energy future. As the Administration works to rally international leaders behind a bold climate pact in 2015, decisions to tap new fossil fuel reserves off our own coasts sends mixed signals about US climate leadership abroad, ” said WWF’s Williams.
We know the Arctic is being hit at least twice as fast as the global average by climate change. The ecosystem is already under huge pressure. The Arctic itself is in turn of key importance to global weather patterns. And burning more oil would exacerbate the situation even further.
“We would like to think that we can shift our energy paradigm to clean energy so that we don’t have to take every last bit of oil out of the earth, especially out of the oceans”, said Jackie Savitz from the Oceana Campaign croup.
Studies by the group and by WWF indicate that developing renewable energy technologies such as offshore wind could create more jobs than hanging on to fossil fuel technologies.
Oil spill concern
In addition to the climate paradox of the hunt for new fossil fuels, environmentalists are concerned about the possible impact of an oil spill. Their opposition is not limited to the Arctic. Proposals to open up large areas of coastal waters including some parts of the Atlantic for the first time have also aroused anxiety about possible pollution. But the Arctic is of particular concern because of its remoteness, harsh weather conditions and seasonal ice cover, which is not likely to disappear soon even with rapid climate change:
“Encouraging further oil exploration in this harsh, unpredictable environment at a time when oil companies have no way of cleaning up spills threatens the health of our oceans and local communities they support. When the Deepwater Horizon spilled 210 million gallons of crude oil five years ago, local wildlife, communities and economies were decimated. We cannot allow that to happen in the Arctic or anywhere else,” said WWF expert Williams.
White House senior counsellor John Podesta justified the ban on oil exploration in the ANWR by saying “unfortunately accidents and spills can still happen, and the environmental impacts can sometimes be felt for many years”. The question is – why should this only be applicable in certain areas? Campaigners say it also applies to the other areas now designated by the administration as “OK” for exploration. For the Arctic in particular, limiting exploration to remote offshore areas does not protect the region against the risk of environmental disaster.
































Feedback