Search Results for Tag: sea ice
Finland courts US rivals Russia and China in bid for key role in Arctic power game

China has its own Arctic research station on Svalbard. (Pic. I.Quaile)
Finland does not often make its way onto the international news agenda, but as the country prepares to take over the presidency of the Arctic council from the USA next month, it succeeded twice over the past week. Firstly, the country’s President offered to host a meeting between Russian President Putin and US President Trump. Then Chinese President Xi Jinping flew in on a state visit on his way to a meeting with Trump.
Tackling the summit
At a forum in the northern Russian city of Arkhangelsk last Thursday entitled “The Arctic: Territory of Dialogue”, Finland said it was willing to host a high-level summit meeting during its two-year presidency and would be happy to receive the Russian and US Presidents in Finland.
In his statement, the Finnish leader stressed that “the geopolitical tensions in other parts of the world should not be allowed to spill over to the Arctic. Cool heads are needed to keep the Arctic an area of low tensions also in the future.”
Under the chairmanship slogan “Exploring Common Solutions”, he said “we want to highlight the need for constructive cooperation between all Arctic stakeholders. Also, we believe it is time to take the Arctic cooperation to a new level. Finland proposes the convening of an Arctic Summit to discuss a wide range of issues pertaining to the region and beyond. This would provide an opportunity to ensure that the Arctic indeed remains a territory of dialogue”.
Heather Exner-Pirot, Managing Editor of the Arctic Yearbook, was scathing about the Finnish move in a blog post for Eye on the Arctic. She says Finland has been floating the idea of such a summit at least since 2010.
“But after meeting with Barack Obama in May 2016, Niniistö seemed to abandon such plans, calling the timing “inappropriate” given the international political situation. That was short-lived. Niniistö once again revived the idea in his first telephone call with now President Trump, in December 2016.”

Go for the summit or work from base camp? (Greenland, Pic. I.Quaile)
Stick to base camp?
Exner-Pirot finds it “bewildering” that the current situation could be considered more appropriate than they were a year ago.
“Niniistö may not have noticed, but the Trump Presidency is in crisis, a political dumpster fire, not least because it is under investigation for inappropriate ties to Russia during its 2016 Presidential campaign. Any meeting of Trump and Putin under the current political climate would be a circus.”
She says Finland has not put forward any convincing reasons to host such a Summit, and that the usual biannual Arctic Council Ministerial, which will take place next month, is an adequate regular platform to address high level Arctic issues amongst the Arctic states’ Foreign Ministers.
“The Trump Administration has proffered no position on Arctic affairs except, tangentially, to cast doubt on the anthropogenic contributions to climate change; it is hard to imagine more sophisticated or constructive discussions arising from an Arctic Summit.”
She argues for continuing “compartmentalization” as a guiding principle in regional Arctic politics, keeping environmental issues and development “insulated from the destabilising fluctuations that occur within the broader international system.”
Cooperation with Russia is “rational and necessary”, Exner-Pirot concludes, but “inviting Trump and Putin together for an Arctic Summit flagrantly violates this strategy. Instead, it invites drama and uncertainty into Arctic politics at a time when multilateral efforts are progressing quite smoothly; an all-risk-and-no-reward scenario. This is not the Arctic way. Cooperation with Russia in the Arctic must continue. But the proposal for an Arctic Summit should be shelved.”

Easier access necessitates close cooperation to cope with more traffic in the High North (I.Quaile)
Nice try?
While there is much to be said for tackling issues at lower levels – can you blame Finland for making the most of its central role at the helm of the Arctic Council? It is surely natural for a country in this position to offer a stage for a high-profile meeting of these two world leaders – perhaps especially when it seems unlikely in the present circumstances.
At any rate, it will only happen if the two key players feel it could be to their advantage. The very prospect certainly ensured considerable news and public attention for the incomimg Arctic Council Presidency.
Finnish President Sauli Niinisto back-pedaled a little later, saying the nation was unlikely to hold an Arctic summit at short notice, cooling media excitement at the prospect of an early meeting between US President Trump and Putin.
For his part, President Putin said he was willing to meet Trump in Finland, but “he would wait longer if needed”, the news agency AP reported: “We are waiting for the situation to normalize and become more stable. And we aren’t interfering in any way.”
With a US congressional investigation of possible links between the Trump election campaign and Russia underway, the jury, presumably, can said to be “still out” on that one.
Ultimately, insulating the Arctic from the tensions of international politics as Exner-Pirot suggests, seems like wishful thinking.
There is evidence enough that Russia has been moving to increase its military presence in the region. In a feature for Reuters published January 30th, Andrew Osborn wrote Russia was “again on the march in the Arctic and building new nuclear icebreakers.”
Osborn describes this as “part of a push to firm Moscow’s hand in the High North as it vies for dominance with traditional rivals Canada, the United States and Norway as well as newcomer China.”

The Chinese lion is claiming its space in the Arctic. (Svalbard, Pic. I.Quaile)
Based on interviews with officials and military analysts and reviews of government documents, Osborn concludes that Russia’s build-up is the biggest since the fall of the Soviet Union and that it will “in some areas, give Moscow more military capabilities than the Soviet Union once had.”
He continues “under President Vladimir Putin, Moscow is rushing to re-open abandoned soviet military, air and radar bases on remote Arctic islands and to build new ones, as it pushes ahead with a claim to almost half a million square miles of the Arctic.”
The article was written after a tour of the Lenin, a Russian icebreaker now functioning as a museum in Murmansk. This week that name popped up again in a story in the Barents Observer by Thomas Nilsen entitled “FSB fears terror at nuclear installations in Murmansk region”.
The topic was on the agenda at a conference on board that same museum icebreaker in Murmansk the day after the metro attack in St. Petersburg.
The conference was entitled “Improving antiterrorist protection of civilian and military nuclear power facilities, preventing acts of nuclear terrorism”.
Nilsen points out that there are few places in the world with more operational nuclear reactors than the Murmansk region.
So is there a link between the Arctic and possible terrorist attacks by “Islamic State”, suspected by Moscow of being behind the St. Petersburg attacks?
Nilsen quotes Oleg Gerasin, head of the Russian intelligence bureau FSB in Murmansk region, explaining that ships from Russia’s Northern Fleet have been taking part in “antiterrorist operations in Syria.”
This demonstrates once more the inter-connectedness of the world today. With all due respect for essential multilateral cooperation on a wide range of issues at lower levels, across the board, ultimately the nature of politics in a globalized world can necessitate participation at the highest leadership level and lend symbolic significance to top-level summits. And that can apply especially if they can be brought about in times of strained relations and global risks.

The view from above can be useful (Greenland, Pic. I.Quaile)
Chinese ties
This week also saw Chinese leader Xi Jinping pay a visit to Helsinki, on the way to his tensely awaited meeting with US President Trump. This was only the second ever visit to Finland by a Chinese leader, although Xi himself visited in 2010 when he was vice-president. Niinistö made an official visit to China in 2013 .
Finland opened political ties with China in 1950 and Chinese state media were keen to stress that Finland was the first western country to sign a governmental bilateral trade agreement with Beijing.
Xi said in a statement there was “great potential” for future bilateral trade ties. He stressed that “over the past 67 years of diplomatic ties, the China-Finland relationship has enjoyed steady and sound growth despite the changing international landscape”. China is Finland’s fifth largest trading partner and Xi said he saw “great space and potential for further economic cooperation and trade”.
During the visit, Finland became the latest to benefit from what the news agency AFT describes as “Beijings famed panda diplomacy”. A pair of giant pandas will be leased to Ahtari zoo in central Finland, where a new panda cage costing more than eight million euros is being constructed.
So while President Trump warned talks with Xi would be “very difficult” – the US deficit with China rose to 31.7 billion $US in February – Finland was stepping up its game, cultivating non-Arctic nation China. China has observer status at the Arctic Council and a strong economic interest in making use of shorter sea routes from Asia to Europe and the USA through the Arctic, with climate change making access easier, although relatively high transit costs and unpredictable ice cover still limit its attractiveness. Beijing is keen to gain footholds in a region it sees as key for the future.

The Russian Peter 1 was the first sailing boat to cross the North Pole unaided in 2010 http://www.rusarc.ru/
China is starting to build its own icebreakers. New icebreakers could allow year-round navigation in the 2020s, Grigory Stratiy, deputy governor of Murmansk Region told Reuters.
China is leading a “Belt and Road Initiative” (BRI), a $5trillion plan to upgrade infrastructure between Asia and Europe. So far, Russia is the only one of the eight Arctic nation states to be a BRI partner. China, which has partnered heavily with Iceland in recent years, is keen to get the Nordic nations on board.
In the statement issued after the visit, China and Finland stressed two key over-arching issues:
“Both sides are committed to working together to reduce or limit greenhouse gas emissions, promote sustainable development and strengthen climate change adaptation and mitigation efforts.”
The two partners “shared the view that economic activities in the Arctic area should take into full consideration the protection and sustainable use of its natural resources. The two countries will intensify economic and technological cooperation in the fields of arctic marine industry, arctic geology, marine and polar research (including polar weather and sea ice monitoring and forecast), environmental protection technology, shipping and maritime safety, including vessel monitoring and reporting, ICT and tourism.”
A wide-ranging and ambitious spectrum.

Get rid of those emissions (Arctic Tromsö, Pic. I.Quaile)
Meanwhile, on the global climate action stage, China seems set to benefit from the backward-looking policies of the Trump administration, positioning itself as a new world leader. At home pollution, drought and desertification are causing increasing problems for Beijing. To ensure peace and food security and avert unrest, a switch to renewable energies is essential. Beijing has also recognized their economic potential. At the same time the country can polish up its international image by taking on the role of climate leader while Donald Trump advances to environment and climate public enemy number one.
While it leads the global move to halt climate change, China is positioning itself to exploit the impacts global warming has already had on the Arctic. Given the current state of the global climate and the slow progress towards keeping to the two-degree let alone 1.5 degree upper limit for global warming, the Arctic is unlikely to re-freeze in the near future. Full speed ahead for Arctic development?
The Arctic Council has to be the body that controls what is happening in the High North and coordinates protection of the fragile Arctic environment.
As President of the body for the next two years, Finland has the opportunity – and the responsibility – to make its influence felt.
As far as the first meeting between the Russian and US-American “big men” is concerned, Finland just might have to pass. Finnish leader Niinistö had to admit to a news conference:
“The G20 meeting in Germany will likely be the first meeting for presidents Trump and Putin”, (July 7 and 8.)
Watch this space.
Arctic sea ice: is the minimum maximum the new normal?

Even the winter sea ice is waning (Off Svalbard, pic. I.Quaile)
If you blinked, you might have missed it. The confirmation came this week that the Arctic sea ice reached yet another all-time low this past winter. It came and went, without too much ado.
Maybe the excitement was just past. The maximum extent was actually reached on March 7th, but of course you can only be sure it is really not going to spread any further once it has definitely been retreating for some time with the onset of spring.
I was waiting for the NSIDC confirmation, but not with any doubt in my mind that it would tell us officially the maximum for this season would be a minimum.
The danger is a “so what?” kind of reaction, or resignation, with the feeling that nothing short of some kind of unprecedented experimental geo-engineering could save the Arctic summer sea ice in the coming years, as the world continues to warm.
Lowest on record
The National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC), part of the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder, and NASA confirmed this week that Arctic sea ice was at a record low maximum extent for the third straight year.
It reached the maximum on March 7, at 14.42 million square kilometers (5.57 milion square miles). Since then, it has started its annual decline with the start of the melt season. Some time in September it will reach its minimum.
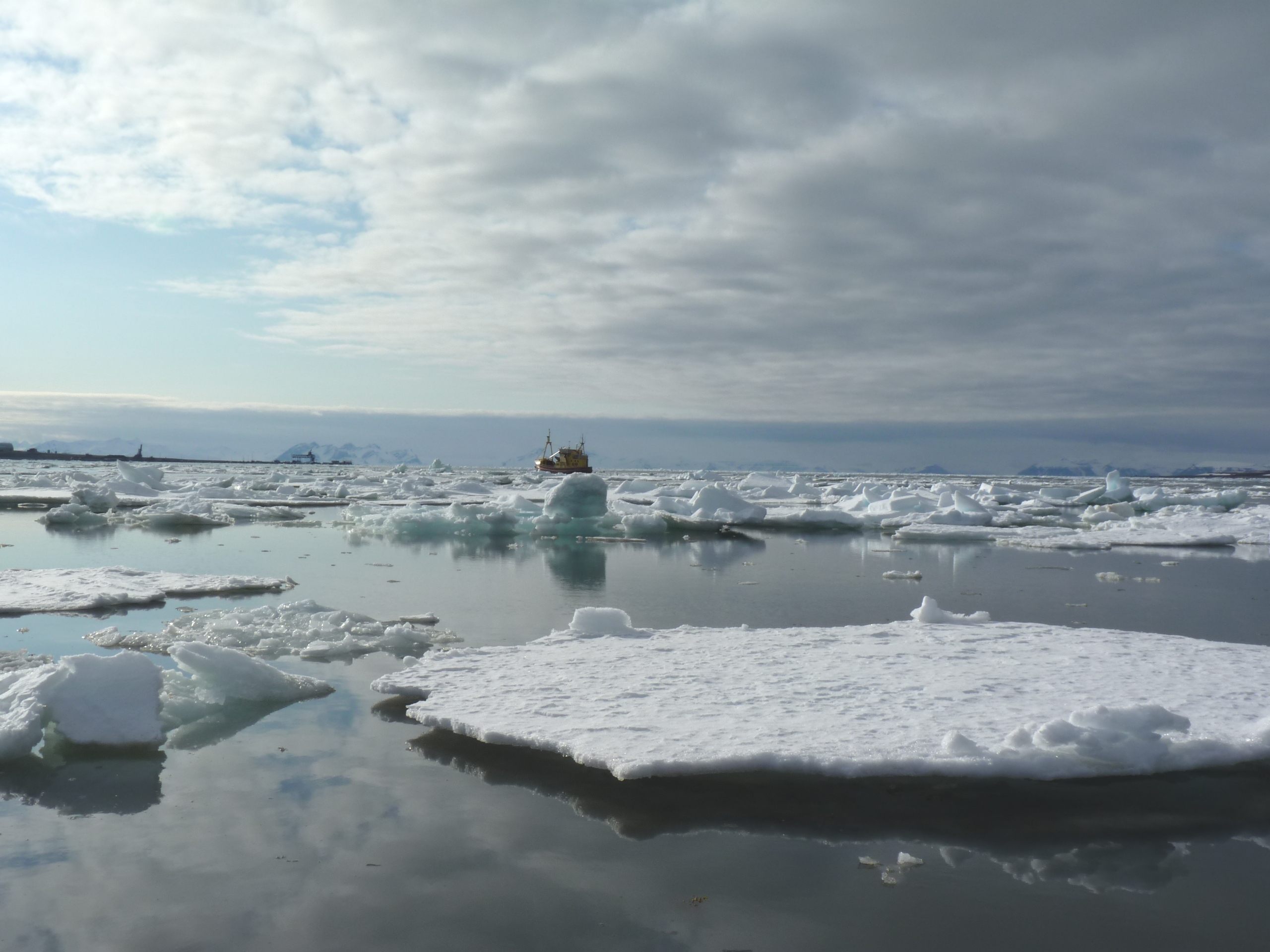

Sea ice going, going, gone? (Photo: I Quaile, off Svalbard)
This year’s maximum is the lowest in the 38-year satellite record. NSIDC scientists said a very warm autumn and winter had contributed to the record low maximum. Air temperatures were 2.5 degrees Celsius (4.5 degrees Fahrenheit) above average over the Arctic Ocean. Against the background of overall warmth came a series of “extreme winter heat waves over the Arctic Ocean, continuing the pattern also seen in the winter of 2015”, NISDC said in a statement.
The air over the Chukchi Sea northwest of Alaska and the Barents Sea north of Scandinavia was even warmer, averaging around 9 degrees Fahrenheit (five degrees C) above the norm.
NSIDC director Mark Serreze said in his statement: “I have been looking at Arctic weather patterns for 35 years and have never seen anything close to what we’ve experienced these past two winters.”
The winter ice cover was also slightly thinner than that of the past four years, according to data from the European Space Agency’s CryoSat-2 satellite. Data from the University of Washington’s Pan-Arctic Ice Ocean Modeling and Assimiliation System also showed that the ice volume was unusually low for this time of year.
Record summer melt ahead?
“Thin ice and beset by warm weather – not a good way to begin the melt season,”, said NSIDC lead scientist Ted Scambos.
A low maximum does not necessarily mean the minimum to be measured in September will also be a record low, as it depends on summer weather patterns. But Julienne Stroeve from NSIDC and professor of polar observation and modeling at the University College London said “Such thin ice going into the melt season sets us up for the possibility of record low sea ice conditions this September”.
“While the Arctic maximum is not as important as the seasonal minimum, the long-term decline is a clear indicator of climate change”, said Walt Meier, a scientist at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Cryospheric Sciences Laboratory and an affiliate scientist at NSIDC. Iceblog readers might wonder if that is stating the obvious, but given the attitudes of the US administration, you can’t take anything for granted.

Data from satellites is key. Reception centre at KSAT in Tromso, Norway, Pic. I Quaile)
The September sea ice measurements began to attract attention in 2005, when the ice extent first shrank to a record low over the period of satellite observations. It broke the record again in 2007 and in 2012. There used to be little interest in the maximum extent of the Arctic sea ice at the end of winter. I can remember reading with concern and writing a piece about the maximum extent also reaching a record low in 2015.
NOAA (climate.gov, “science & information for a climate-smart nation”!) said in its statement:
“Arctic sea ice extents have followed a steady downward trajectory since the start of the 21st century – at the same time global temperatures have reached new record highs. Betides setting multiple record low summertime minimum extents, Arctic sea ice began to exhibit a pattern of poor winter recovery starting around 2004.”
Living on thin ice
I remember an expedition to Alaska in 2008, when locals at Barrow told me about their personal experiences of the sea ice becoming thinner and less dependable. Some years later I heard similar reports from people in Greenland, who were selling their sled dogs and buying boats in preparation for changing from ice to open water fishing. The data backs them up.

Sled dog – out of work? (I.Quaile, Greenland)
Yereth Rosen, writing for Alaska Dispatch News, draws attention to the problems of continuing to collect that data. She quotes NSIDC’s Serreze:
“Just how well the center will be able to track sea ice in the future remains unclear. No new satellite is expected to be in place until 2020, and there are concerns about potential interruptions in the record that goes back to 1979… We’re at a situation where the remaining passive microwave instruments up there are kind of elderly. If we have satellite failures, we could lose that eye in the sky”.
Now there is a worrying thought.
Against the background of budget cuts proposed by the Trump administration, that – to put it mildly – does not regard tracking climate change as a high priority – scientists are understandably worried about the future of scientific research on climate and environment related issues.
Method in the madness?
Without reliable continuous satellite data, it would be much harder to track how climate change is affecting the polar regions, the ocean and our planet in general. This may well be the intention of climate-change deniers behind the scenes. But climate change itself will not go away – and the impacts will be increasingly evident.
Tim Ellis, writing for Alaska Public media, quotes Serreze as saying the polar ice cap will not last long if the region continues to warm at this rate.
“We are on course sometime in the next few decades, maybe even earlier, to have summers in the Arctic where, you go up there at the end of August, say, and there’s no ice at all.”
“The view from space in the fall of around 2040” , he went on – assuming we still have satellites to take the pictures – “will be of a blue Arctic Ocean, aside from some scattered icebergs and clusters of pack ice”.
I don’t know about you, but I find that a rather depressing thought.

My kind of sea ice – frozen Chukchi Sea (Pic: I.Quaile)
Implications for the rest of the globe
Andrea Thompson, for Climate Central, writes “even in the context of the decades of greenhouse gas-driven warming, and subsequent ice loss in the Arctic, this winter’s weather stood out.”
She also reminds us of the global impacts of a warming Arctic and decline in sea ice:
“The Arctic was one of the clear global hotspots that helped drive global temperatures to the second- hottest February on record and the third-hottest January, despite the demise of a global heat-boosting El Nino last summer.”
This week the UN’s World Meteorological Organisation (WMO) said 2016 had been the hottest year ever recorded, and that the record-breaking heat had continued into 2017, sending the world into “truly uncharted territory”.
“The dramatic melting of Arctic ice is already driving extreme weather that affects hundreds of millions of people across North America, Europe and Asia, according to emerging research”, Damian Carrington writes in the Guardian.
On March 15th, Carrington published an article entitled “Airpocalypse smog events linked to global warming”, referring to extreme smog occurrences in China.
Optimism – the only way to go?
This week I interviewed German oceanologist and climatologist Mojib Latif. I wanted to find out whether the highly unusual extreme rainfall and flooding happening in Peru could be explained by natural cycles or was likely to be a climate change impact which could reoccur. You can read the interview here or listen to it on my Living Planet show this week online or on soundcloud.

Professor Latif on a visit to Bonn. (Pic. I.Quaile)
The professor stressed that the scientists are baffled, because it is not really the time for an el Nino, although this seems to be a “coastal el Nino”, driven by exceptionally warm water off the coast. Of course he is reluctant to attribute any single event to climate change. He stated unequivocally, though, that the warming of the ocean worldwide was absolutely inexplicable without anthropogenic CO2 emissions, that this is all in line with climate models and that we should all be preparing for an increasing number of increasingly extreme weather events, as the world warms.
He says the governments of the world (apart perhaps from the new US administration) are in no doubt that climate change is happening and they need to halt it. But they have so far failed in their attempts.
When I asked Professor Latif if he still felt optimistic, he told me we really had no other choice. While critical of the lack of government action, he is convinced the world will realize that renewables are ultimately far superior to fossil fuels and will ultimately prevail. The question is whether that will happen in time. As far as the Arctic summer sea ice is concerned, I have to go with a Scots expression: “A hae ma doots”.
Arctic summer sea ice cover could disappear with 2C temperature rise

The sea ice has been dwindling for decades (Photo: I Quaile)
The Arctic sea ice may disappear completely in summers this century, even if the world keeps to the Paris Agreement. That is the worrying message of a report published on Monday in the journal Nature Climate Change.
The 2015 Paris Agreement set a goal of limiting the rise in global temperature to well below two degrees Celsius (3.6 Fahrenheit) above pre-industrial times. Ideally, 1.5C (2.7F) was agreed to be the “aspirational” target. James Screen and Daniel Williamson of Exeter University in the UK, wrote, after a statistical review of ice projections, that a two degree Celsius rise would still mean a 39 percent risk that ice would disappear from the Arctic Ocean in summers. If warming is kept to 1.5 degrees Celsius, the ice was virtually certain to survive, they calculated.
Current emissions targets way too low

Looking to an uncertain future. Svalbard polar bear. (Pic. I.Quaile)
If you take the old “glass being half-full rather than half-empty” metaphor, you could see that as a positive option to hang on to. However, the scientists estimated that if we continue along current trends, temperatures will rise by three degrees C (5.4 F.). That would give a 73 percent probability that the ice would disappear in summer. To prevent it, governments would have to up their targets and make considerably larger cuts in emissions than presently planned.
The sea ice will reach its maximum winter extent some time soon. So far, the March figures rival 2016 and 2015 as the smallest for the time of year since satellite records began in the late 1970s.
“In less than 40 years, we have almost halved the summer sea ice cover”, Tor Eldevik, a professor at the Bjerknes Centre for Climate Research at the University of Bergen in Norway, told Reuters. Eldevik was not involved in the study.
He predicted that sea ice would vanish in the Arctic Ocean in about another 40 years, on current trends.
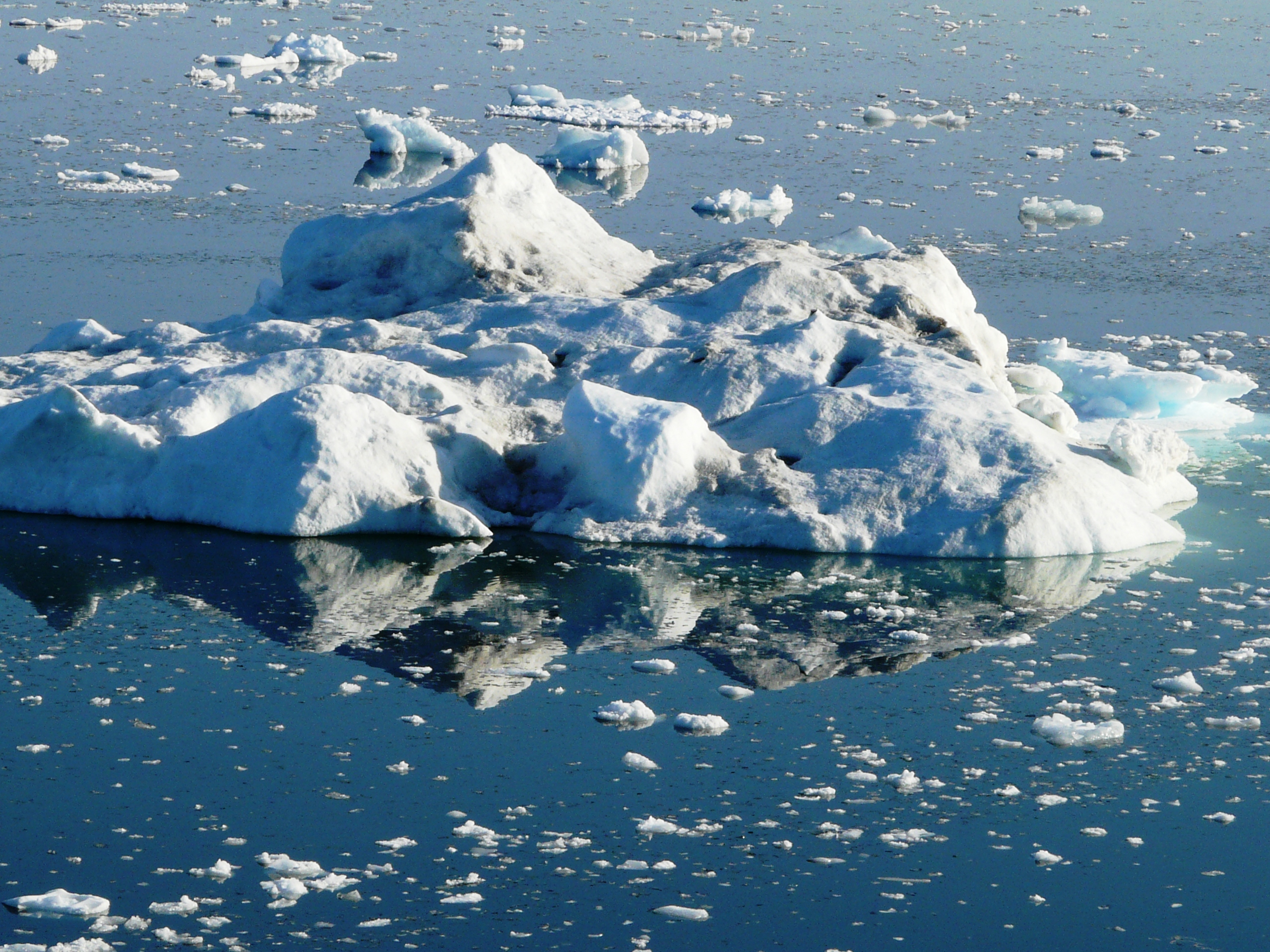

… And the ice just keeps on melting. (Pic: I. Quaile,) Greenland)
Steady melting trend
Scientists define an ice-free Arctic Ocean as one with less than one million square kilometers (386,000 square miles) of ice, because they say some sea ice will linger in bays, for instance off northern Greenland, even after the ocean is ice-free.
Despite fluctuations from year to year, long-term trends in the Arctic clearly show a decline in sea ice. The ten lowest ice extents since 1979 have all occurred since 2007.
According to the latest figures from the NSIDC (March 6), high air temperatures observed over the Barents and Kara Seas for much of this past winter moderated in February. Still, overall, the Arctic remained warmer than average and sea ice extent remained at record low levels.
Arctic sea ice extent for February 2017 averaged 14.28 million square kilometers (5.51 million square miles), the lowest February extent in the 38-year satellite record. This is 40,000 square kilometers (15,400 square miles) below February 2016, the previous lowest extent for the month, and 1.18 million square kilometers (455,600 square miles) below the February 1981 to 2010 long term average.
Good times ahead for Arctic shipping, trade and tourism? Not much of a future for polar bears struggling for survival, or for people whose livelihood and way of life depends on reliable ice cover.
Can environmentalists trump Trump’s climate plans?
When it comes to the latest data on the state of the Arctic sea ice, the Greenland ice sheet or other key features of the cryosphere, the chances are NASA will have been involved in providing it. For those of us interested in protecting our icy regions against climate change, US President-elect Donald Trump’s plan to scrap NASA’s climate research and shift the funding to space exploration is alarming, to say the least.
Why the world needs NASA – not just for space
Two of my colleagues at DW talked to leading scientists about Why Trump scrapping NASA climate funding is bad news for our planet. Thomas Hollands from the German polar agency the Alfred Wegener Institute explains the essential role played by NASA’s network of satellites in providing data for climate researchers the world over.
“Scientists around the world depend on NASA for a variety of information – from measuring the state of the Earth’s atmosphere and the shape of its gravity field, to observations on glacier melting, sea ice formation, forest loss and urban growth”, the article says. It goes on to explain how important it is to have continuous measurements over time to be able to establish trends and changes.
Presumably, of course, if the Trump administration makes good on election promises to revive the US coal industry, there are those who would find it advantageous to get rid of any technology that can measure the extent of the impact of fossil fuel emissions on the world’s climate. A scenario to be avoided at all costs.
Fighting back
So I was interested to read a piece on the news agency AP this week headlined “Trump rollback of Obama climate agenda may prove challenging”. I hope “challenging” will turn out to be an understatement.
The story, by Michael Biesecker, says a President Trump would be in a strong position to dismantle some of President Obama’s efforts to reduce carbon emissions:
“But experts say delivering on campaign pledges to abolish the Environmental Protection Agency and bring back tens of thousands of long-gone coal mining jobs will likely prove far more difficult for the new president”, Biesecker writes.
Environmental groups are gearing up to defend Obama’s environmental legacy in court. Sierra Club Executive Director Michal Brune is quoted as saying “we intend challenging every single attempt to roll back regulations on air, water and climate”, and that his group is already hiring additional lawyers. It does not surprise me that fundraising for environmental causes has also spiked since Donald Trump’s victory.
The question is just how much the President is able to do and what tools are available to opponents to stop him.
The powers of the President
Many legal experts believe Mr. Trump would be able to cancel the Paris Climate Treaty, as he threatened to do when he was campaigning (although his stance has shifted slightly in the meantime). It is not a treaty and was not approved by the (Republican-controlled) Senate. The future president could also order the EPA – where the transition team is being led by a climate skeptic leading a think-tank funded by the fossil fuel industry – not to take the action required to meet the US commitment to cut emissions.
It seems, though, that it is not that easy to dismantle EPA regulations which have already been finalized and implemented. Jody Freeman, director of the environmental law program at Harvard Law School, is quoted as saying “the agency has already built up a very strong record to support those rules”. Ultimately, “it can be very hard to do an about-face.”
From the legal point of view, the President cannot get rid of the EPA without congressional approval – which could be prevented by filibustering. (He could, of course, slash its budget).
When it comes to abolishing NASA’S climate research programme, Mr Trump will also find himself facing some tricky hurdles.
“NASA’s study of earth science is currently mandated by federal law, which means voiding the program would require congressional action”, AP writes. That too means Democrats could block things using a filibuster.
What happened to common sense?
Ideally, common sense and concern for the wellbeing of people and the health of the planet we live on should ensure that Obama’s environmental and climate policies are not turned around. The advances in renewable energy also mean it makes economic sense to shift away from fossil fuels to wind and solar. In fact, it seems the courts will have to tackle the ins- and outs in lengthy and costly investigations.
This past week, in the USA, a group of American youths officially won the right to sue the government of the United States – the world’s second-largest greenhouse gas emitter after China – for failing to curb climate change. The Oregon district court upheld the main argument, that “the government has known for more than 50 years that the carbon dioxide produced by burning fossil fuels was destabilizing the climate system in a way that would significantly endanger plaintiffs, with the damage persisting for millennia.” Yet, the court argues, the government has failed to take action, making it responsible for some of the harm caused by climate change.
Here in Germany, there is also a court case in process, which could set a precedent. A farmer and mountain guide in the Peruvian Andes is suing the German energy giant RWE. Saúl Lliuya from Huaraz says his home is at risk of flooding, as it lies beneath a melting glacier in the Andes mountains. He argues that the company’s coal power emissions contribute to climate change, and so RWE should have to pay a share of measures to protect his home. But RWE says there is no direct link connecting CO2 emissions to the danger of flooding. Lliuya is being supported by the environmental organization Germanwatch. In my Living Planet radio show this week I broadcast an interview with the organisation’s policy director, Christoph Bals.
The plaintiff’s argumentation is that because RWE has produced 0.5 percent of all global emissions since the industrial revolution, the company should at least pay 0.5 percent of the measures to protect the farmer and his home town from flooding as the glacier above it continues to melt. Bals sees it as a major achievement that the case is being dealt with in the German court as one that could set a precedent. Even if the lawyers are not able to prove a direct link and win the case, he says getting to this stage is a demonstration that it is possible to go to court against companies like RWE on climate grounds.
“From now on this is one of the options on the table. I am sure that as soon as we see in the world that we will not stay below two degrees or 1.5 as said in the Paris Agreement, those cases will be much more likely – and it will be much more likely also that the individual court will decide you are right. So for the future this would be one major option if we don’t get a political solution”.
There has to be some food for thought in there for Mr. Trump and his advisors. Interesting times, indeed. And environment and climate advocates have their own trump cards in their hands.
New report sees Arctic melt on course to tip global climate
Scientists say the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard has seen such extreme warmth this year that the average annual temperature could end up above freezing for the first time on record. Ketil Isaksen of the Norwegian Meterological Institute said today the average temperature in Longyearbyen, the main settlement in Svalbard, is expected to be around 0 Celsius with a little over a month left of the year. He called the abnormal warmth “shocking” and beyond anything he could have imagined 10 years ago. The normal yearly average is minus 6.7 C.
And that is not the only shocking thing going on up north. The Arctic sea ice is melting in November. Temperatures in the region are 20 degrees Celsius above usual. Reindeer are dying across Siberia. Polar bears are stranded on land. It’s hard to keep up with the extent and speed of climate change in the far north of the planet. And we in the media have to be aware of the danger that the reports become so commonplace the “new normal” no longer arouses interest.
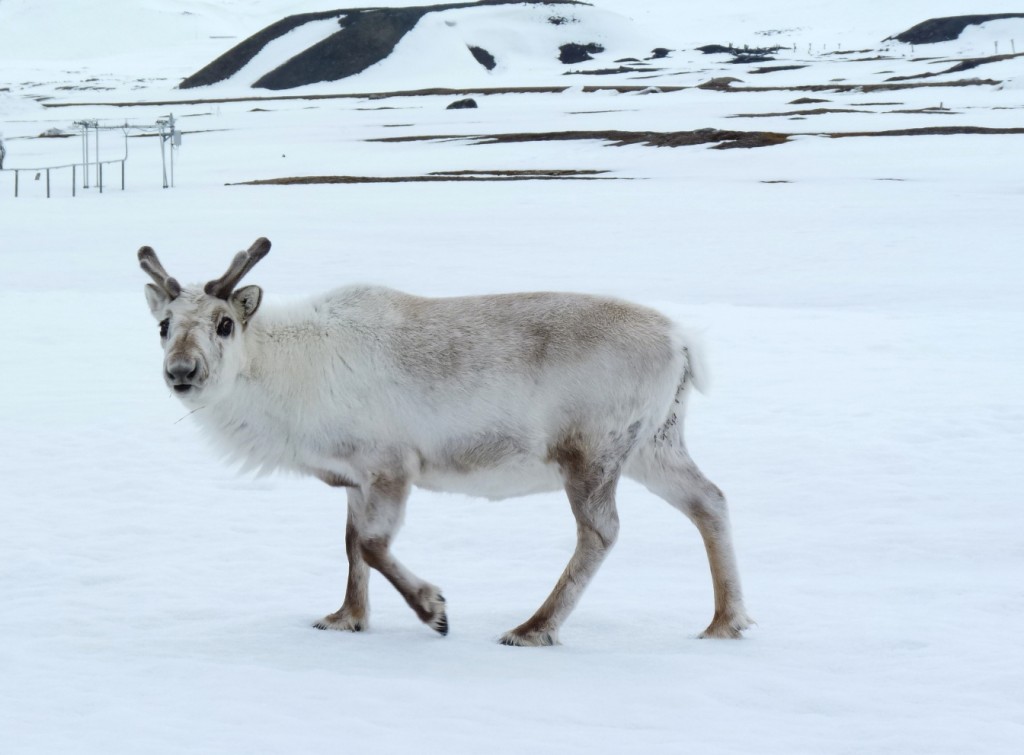

Svalbard’s sturdy reindeer are adapting to climate change. In Siberia, thousands of animals have died of starvation. (Pic: I.Quaile)
Warming, warming, hot
Yet the ever faster melting of our Arctic ice could spell disaster even for distant regions of the planet. What happens in the Arctic doesn’t stay in the Arctic, as discussed here on the Ice Blog many times before. But a new, key report launched today indicates that the effects of increasingly rapid Arctic warming could be set to push global climate change out of control.
The Arctic Resilience Assessment (ARA) is an Arctic Council project led by the Stockholm Environment Institute and the Stockholm Resilience Centre. It is based on collaboration with Arctic countries and Indigenous Peoples in the region, as well as several Arctic scientific organizations. The ARA (previously Arctic Resilience Report) was initiated by the Swedish Ministry of the Environment as a priority for the Swedish Chairmanship of the Arctic Council (May 2011 to May 2013) and is being presented under the US Chairmanship. It aims to synthesize knowledge on Arctic change and how people and the ecosystem are coping with it, bringing the wide range of different factors together.
“Environmental, ecological, and social changes are happening faster than ever in the Arctic, and are accelerating. They are also more extreme, well beyond what has been seen before. This means the integrity of Arctic ecosystems is increasingly challenged, threatening the sustainability of current ways of life in the Arctic and disruption of global climate and ecosystems”, the report says.
Beyond the tipping point
The researchers issue a stark warning: “Some changes are so substantial (and often abrupt), that they fundamentally alter the functioning of the system: an ecological “tipping point” has been crossed. The report examines 19 of these “tipping points” or “regime shifts”, as they are also known: “They affect many ecosystem services that are important to people within and outside the Arctic: from regulating the climate, to providing sustenance (e.g. through fishing)”, the experts tell us.
“The consequences of some of these shifts are likely to be surprising and disruptive – particularly when multiple shifts occur at once. By altering existing patterns of evaporation, heat transfer and winds, the impacts of Arctic regime shifts are likely to be transmitted to neighbouring regions such as Europe, and impact the entire globe through physical, ecological and social connections”, the report says.
The tipping points discussed in the report include the replacement of white ice and snow, which reflect heat back into space, by darker green vegetation or ocean water, which absorbs more heat, higher releases of methane and changes to ocean circulation and so weather patterns around the globe caused by an influx of melting snow and ice.
Major impacts inevitable?
Johan Rockström, director of the Stockholm Resilience Centre and co-chair of the five-year study said in a statement: “If multiple regime shifts reinforce each other, the results could be potentially catastrophic.… The variety of effects that we could see means that Arctic people and policies must prepare for surprise. We also expect that some of those changes will destabilize the regional and global climate, with potentially major impacts”.
The report stresses that many of the changes and feedback effects in process are poorly understood and in need of much more research.
“Arctic ecological protection is now a global concern, and worldwide monitoring is inadequate”, the authors write.
Political “regime shift”?
To reduce the risk of these tipping points, strong action would have to be taken to mitigate climate change, the authors conclude. Aha. Now there’s the rub.
In the Guardian, Fiona Harvey notes the report comes at a critical time in politics, with Donald Trump’s announcement this week that he plans to take away NASA’s budget for climate science and put it into space exploration. She quotes Marcus Carson of the SEI, co-editor of the report:
“That would be a huge mistake…It would be like ripping out the aeroplane’s cockpit instruments while you are in mid-flight”.
If Mr. Trump also makes good his pledge to revive the US coal industry and abandon the Paris Climate Agreement, the chances of halting warming and the climate feedback mechanisms which could spell disaster would seem to be melting away along with that Arctic ice. Not so tasty food for thought this weekend. Well, I could distract myself by getting out the lawnmower. It has been so warm here this week the birds are chirping like spring and the grass has started to grow again.


























Feedback