Search Results for Tag: glaciers
Melting glacier risk to seabed ecosystem
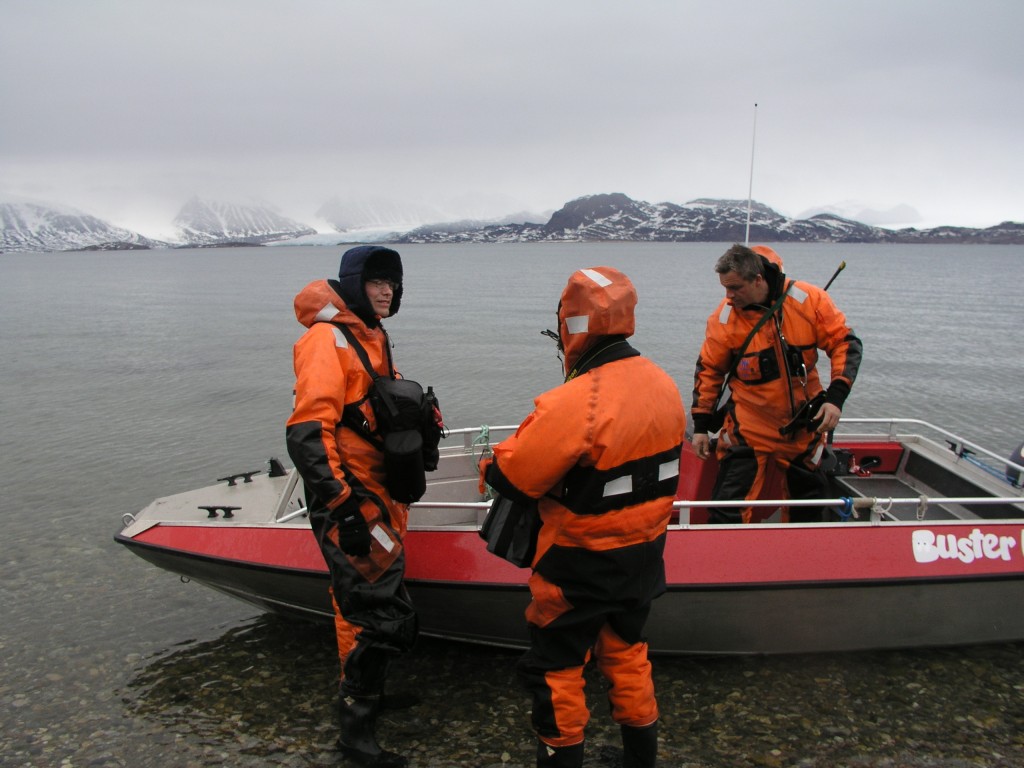
On my first visit to the Arctic in 2007, I went out into the Kongsfjord at Ny Alesund, Spitsbergen, with some marine biologists working out of Koldewey station, run jointly by France and Germany. It was June, and the glaciers at the end of the fjord were just starting to thaw. While I was enjoying the blues, whites and greys of the sea, ice and sky, the researchers in the small boat got very excited when they saw the water turned brown, where sediment was flowing into the fjord from the retreating glacier.
“Who turned off the light up there”?
They had been waiting impatiently for the thaw to set in, because their research focus was on what that means for the life forms on the seabed, or benthos. Clearly, if you live down on the sea floor, the intrusion of brown mud and other sediment changes your surroundings. Not least, it means less light coming down from above. Now while a certain amount of that is going to happen naturally every year with the changing seasons, the question is: what happens if there is a big increase in sediment coming in because of increasing melt through climate change?
I was interested to hear about a study published this week in Science Advances, dealing with that same question in the Antarctic. The findings indicate that melting coastal glaciers are having an impact on the entire ecosystem on the seafloor, leading to a loss of biodiversity through sedimentation. The scientists were looking at the West Antarctic peninsula, where the temperature has risen almost five times faster than the global average in the last fifty years.
Global warming changes seafloor communities
The study, published by experts from Argentina, Germany and Great Britain, including the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (AWI,) is based on repeated research dives. The scientists believe increased levels of suspended sediment in the water caused the dwindling biodiversity registered in the coastal region. They say it occurs when the effects of global warming lead glaciers near the coast to begin melting, discharging large quantities of sediment into the seawater.
To find out exactly how and to what extent the retreat of glaciers is affecting bottom-dwelling organisms, researchers at the Dallmann Laboratory are now mapping and analysing the benthos in Potter Cove, located on King George Island off the western Antarctic Peninsula. The lab is operated by the Alfred Wegener Institute and the Argentine Antarctic Institute (IAA) as part of the Argentinian Carlini Station. Researchers have been monitoring benthic flora and fauna there for more than two decades.
In 1998, 2004 and 2010, divers photographed the species communities at three different points and at different water depths: the first, near the glacier’s edge; the second, an area less directly influenced by the glacier; and the third, in the cove’s minimally affected outer edge. They also recorded the sedimentation rates, water temperatures and other oceanographic parameters at the respective stations, so that they could correlate the biological data with these values. Their findings: some species are extremely sensitive to higher sedimentation rates.
Short sea squirts adapt better
Sea squirts are small invertebrate creatures that live on the sea floor and feed by filtering the water through their anatomies.
“Particularly tall-growing ascidians like some previously dominant sea squirt species can’t adapt to the changed conditions and die out, while their shorter relatives can readily accommodate the cloudy water and sediment cover,” says Dr Doris Abele, an AWI biologist and co-author of the study. She is worried that “the loss of important species is changing the coastal ecosystems and their highly productive food webs, and we still can’t predict the long-term consequences.”
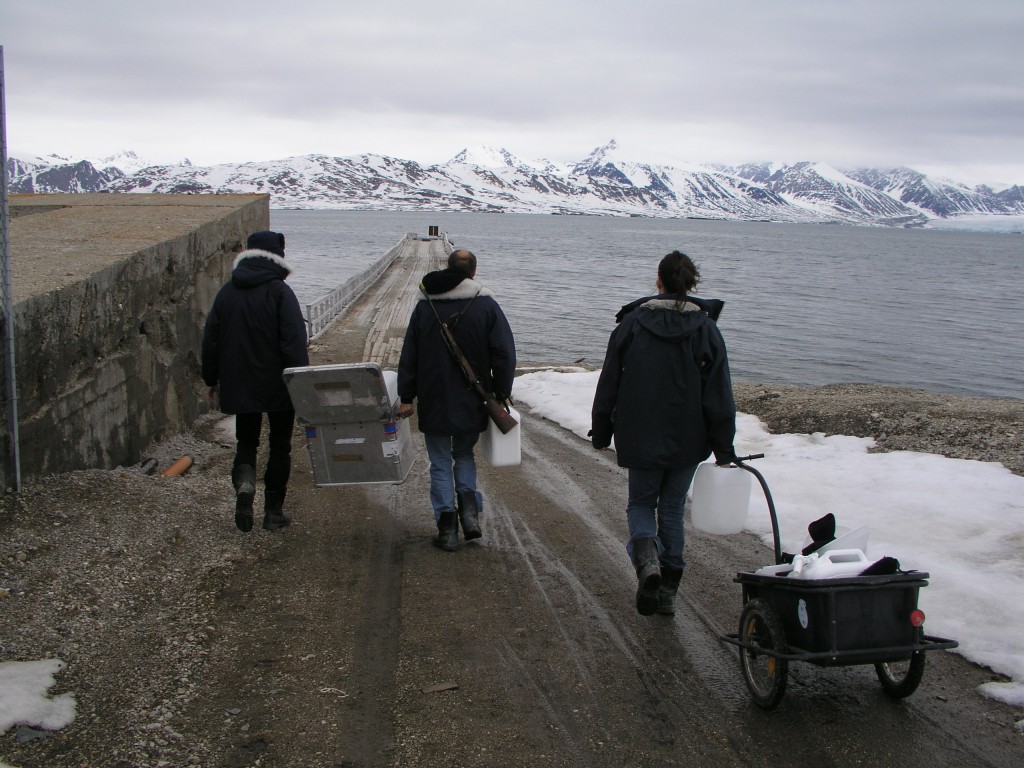

Can Arctic marine biologists work fast enough to keep up with climate change? (Ny Alesund, Pic: I.Quaile)
As with so many aspects of our oceans, there is a lack of base data on how sediment from melting glaciers affects the numerous life forms on the seabed.
“It was essential to have a basis of initial data, which we could use for comparison with the changes. In the Southern Ocean we began this work comparatively late,” says the study’s first author, marine ecologist Ricardo Sahade from the University of Cordoba and Argentina’s National Scientific and Technical Research Council CONICET, who is leading the benthic long-term series. “Combining this series of observations, accompanying ecological research on important Antarctic species, and mathematical modelling allows us to forecast the changes to the ecosystem in future scenarios,” says co-author Fernando Momo from Argentina’s National University of General Sarmiento.
With scientists telling us the ice of the West Antarctic peninsula has already passed a tipping point, the question is whether scientific monitoring and research will be able to keep pace with the rapid rate at which climate warming is already having major impacts on our oceans. For many species of our seabottom-dwelling creatures, the slow pace of greenhouse gas emissions reductions may well come far too late.
See also: Antarctic glaciers retreat unstoppable
Polar melt confirmed from space
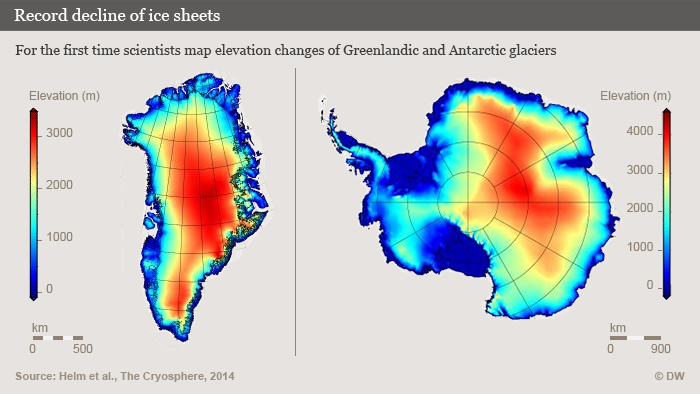
I am disappointed that there was so little mainstream media coverage (please correct me if I am wrong) of a report from a team of scientists from Germany’s Alfred Wegener Institute (AWI) in Bremerhaven who have analysed just over two years of data from the CryoSat-2 satellite. Their conclusion that the Greenland ice sheet and Antarctica’s glaciers are melting at record pace, dumping some 500 cubic kilometers of ice into the oceans every year, twice as much in the case of Greenland and three times as much in the case of Antarctica, by comparison with 2009 – yes, you read right, we are talking about a very short period for such a dramatic increase in ice loss – should have made more news headlines and not just the science pages.
To understand the scale of that, the researchers say it would be the equivalent of an ice sheet that’s 600 meters thick and covers an area as big as the German city of Hamburg – or, my colleagues here at DW calculate, as big as Singapore.
The research team headed by Veit Helm used around two years’ worth of data from the ESA CryoSat-2 satellite to create digital elevation models of Greenland and Antarctica. The results were published in the online magazine of the European Geoscience Union (EGU) The Cryosphere.
“The new elevation maps are snapshots of the current state of the ice sheets,” Helm says. “The elevations are very accurate, to just a few meters in height, and cover close to 16 million square kilometers of the area of the ice sheets.” He says this includes an additional 500,000 square kilometers that weren’t covered in previous elevation models from altimetry.
Space technology shows declining ice mass
Helm and his team analyzed all data from the CryoSat-2 radar altimeter SIRAL in order to come up with the detailed maps. The satellite with this new radar equipment was launched in 2010. Satellite altimeters measure the height of an ice sheet by sending radar or laser pulses which are then reflected by the surface of the glaciers or surrounding areas of water and recorded by the satellite.
The researchers used other satellite data as well to document how elevation has changed between 2011 and 2014.
Rapid ice loss over a short period of time
The team used more than 200 million SIRAL data points for Antarctica and some 14 million data points for Greenland to create the elevation maps. The results show that Greenland alone is losing around 375 cubic kilometers of ice per year.
Compared to data which was collected in 2009, the loss of mass from the Greenland ice sheet has doubled. The rate of ice discharge from the West Antarctic ice sheet tripled during the same period.
I think this is definitely worth talking about. We know the huge implications of polar ice melt for global sea levels. Other research from this year also tells us that, at least in the case of parts of Antarctica, the ice melt is probably irreversible.
We cannot afford to ignore what is happening to the ice sheets. The extent of ice loss in Greenland is particularly dramatic. I am losing patience with those people who respond to studies like this and our reporting on it by saying “but the East Antarctic is gaining volume” and “the Antarctic sea ice has grown”. It is so easy to take things out of context and mix different factors up when trying to understand a very complex system.
I will give the last word here to AWI glaciologist Angelika Humbert, who co-authored the study: “If you combine the two ice sheets (Greenland and Antarctic), they are thinning at a rate of 500 cubic kilometers per year. That is the highest rate observed since altimetry satellite records began about 20 years ago.” It seems to me there is no arguing with that.
Related stories:
Antarctic melt could raise sea levels faster
West Antarctic ice sheet collapse unstoppable
Climate change risk to icy East Antarctica
Antarctic Glacier’s retreat unstoppable
Human action speeds glacial melting
It might sound like stating the obvious, but in fact it is not easy to find clear evidence that human behavior is behind the retreat of glaciers being monitored in different parts of the world. Hence my interest in a study just published in the journal Science.
The main problem is that it usually takes decades or even centuries for glaciers to adjust to climate change, says climate researcher Ben Marzeion from the Institute of Meteorology and Geophysics of the University of Innsbruck. He and his team of researchers have just published the results of a study for which they simulated glacier changes during the period from 1851 to 2010 in a model of glacier evolution. They used the recently established “Randolph Glacier Inventory” (RGI) of almost all glaciers worldwide to run the model, which included all glaciers outside Antarctica.
“Melting glaciers are an icon of anthropogenic climate change”, the authors say. However, they stress that the present-day glacier retreat is a mixed response to past and current natural climate variability and “current anthropogenic forcing”. Their modeling shows though that whereas only 25% of global glacier mass loss between 1851 and 2010 can be attributed to human-related causes, the fraction increases to around 69% looking at the period between 1991 and 2010. So human contribution to glacier mass loss is on the increase, the experts write.
Marzeion says the global retreat of glaciers observed today started around the middle of the 19th century at the end of the Little Ice Age, responding both to naturally caused climate change of past centuries (like solar variability), and to human-induced changes. Until now, the real extent of human contribution was unclear. The authors say their latest piece of work provides clear evidence of the human contribution.
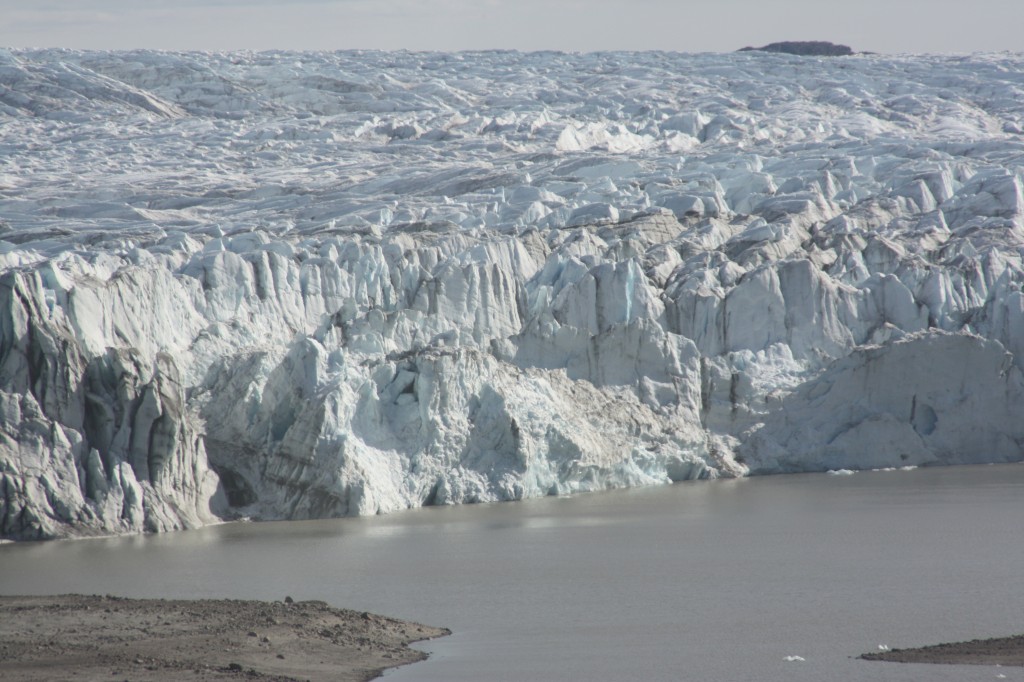
Once more I am happy to refer to the Climate News Network, in this case to Tim Radford, for an easy-to-read summary of the main research results and the background. There is no doubt that glaciers are losing mass, retreating uphill and melting at a faster rate, says Radford. He refers to some Andes glaciers and the the Jakobshavn glacier in Greenland, or Sermeq Kujualleq as I prefer to call it, using the indigenous name. Ice Blog followers may remember my own trip to Greenland and that particular glacier. I have also written on the speeding of the melt there on the Ice Blog and on the DW website.
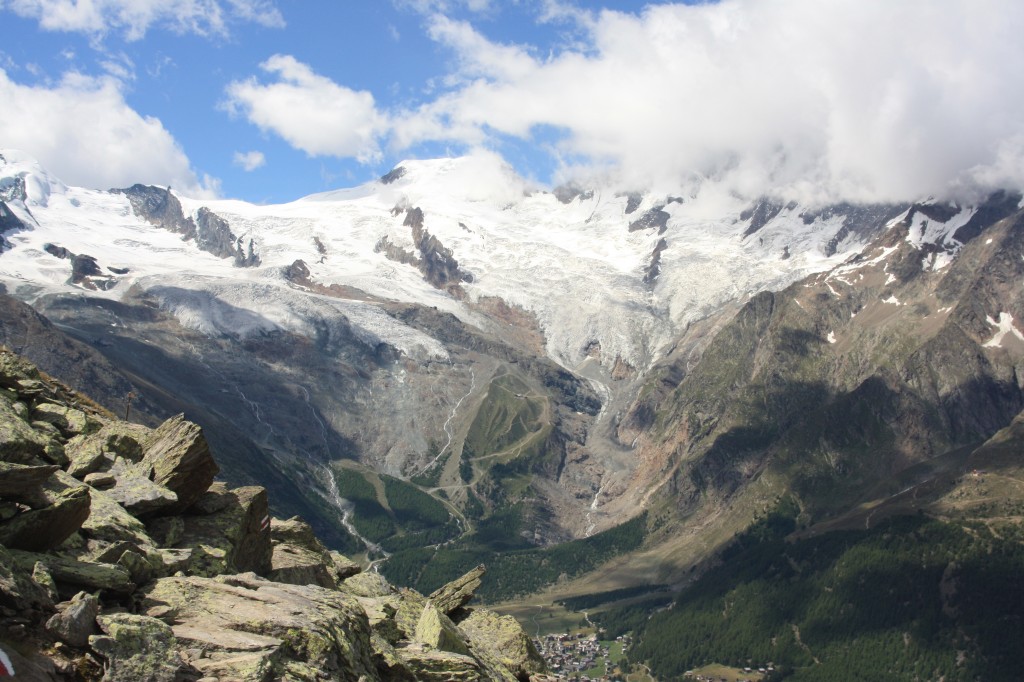

Alpine glacier like these in Saas-Fee, Switzerland, have declined dramatically in recent decades. (I.Quaile)
Radford also refers to ascertaining the melting of alpine glaciers by comparing historic paintings and other documentation with the current ice mass. That decline is something I have observed at first hand in Valais in Switzerland during regular visits over the past 30 years. Look out for a comparative photo gallery of my own pics, when I get time to put it together. Since most of the shots are from the pre-digital era, that will be a time-consuming task.
I also remember a trip to the Visitor Centre of the Begich Boggs glacier in Alaska in 2008. The glacier has already retreated so far you can’t see it at all from the Centre built specially for the purpose of viewing it.
The question until now was how much of all this was caused by natural developments and how much to changes in land use and the emission of greenhouse gases? The latest study supported, among others, by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) and the research area Scientific Computing at the University of Innsbruck, has come up with some answers. Since the climate researchers were able to include different factors contributing to climate change in their model, they can differentiate between natural and anthropogenic influences on glacier mass loss
“While we keep factors such as solar variability and volcanic eruptions unchanged, we are able to modify land use changes and greenhouse gas emissions in our models,” says Ben Marzeion, who sums up the study: “In our data we find unambiguous evidence of anthropogenic contribution to glacier mass loss.”
As always, there is still need for further research – and a lot more monitoring. The scientists say the current observation data is insufficient in general to derive any clear results for specific regions, even though anthropogenic influence is detectable in a few regions such as North America and the Alps, where glaciers changes are particularly well documented.
With global glacier retreat contributing to rising sea-levels, changing seasonal water availability and increasing geo-hazards, the study’s conclusions should help put a little more pressure on the world’s decision-makers to get serious about emissions reductions.
Cryosphere in Crisis?
You can’t say the latest research results on the thinning of the West Antarctic ice sheet didn’t make the media. From the news agencies through the quality media and even publications not known for their detailed science or environment coverage – nearly all reported that two separate studies each independently come to the conclusion that parts of the West Antarctic ice sheet are already “collapsing”. They say this could result in a considerable sea level rise within the next century or two. This would have devastating consequences for low-lying coastal areas around the globe.
No-one can really say they didn’t know about this. For once, the Antarctic ice has made into the headlines of the mainstream media. This is the region people tend to think of as having “eternal ice”, where global warming will “not make much difference”. There are those who criticize the media for sensationalism or exaggeration by taking over the term “collapse” for a process which will still take hundreds to thousands of years. See for example Andrew Revkin’s post on Dot Earth (New York Times), (and an excellent response by Tom Yulsman in ImaGeo: (Discover Magazine). But, semantic discussions apart – as Yulsman puts it:
“On a human timescale, 200 years or more for the start of rapid disintegration is a very long time indeed. But on a geologic timescale, it is the blink of an eye. And that’s important to keep in mind too — that in a blazing flash, geologically speaking, we humans are managing to remake the life support systems of our entire planet. This is why I think today’s news may eventually be seen as having historic significance”. At any rate, he concludes “it is yet another clear sign that human-caused changes to the planet once regarded as theoretical are now very real”.
Indeed Tom. The question is: what are we going to do about it? Has it set the alarm bells ringing? Did anybody see a rash of reactions promising quick action on reducing emissions to mitigate climate change? If so, please point me in the right direction. So far, I haven’t seen any indication of anything other than business as usual.
The West Antarctic ice sheet contains so much ice that it would raise global sea level by three to four meters if it melted completely. As it sits on bedrock that is below sea level, it is considered particularly vulnerable to warming sea water. Until now, scientists assumed it would take thousands of years for the ice sheet to collapse completely. The two new studies indicate that could happen much faster – as early as 200 years from now or, at the most, 900. Both research teams, using different methods and looking at different parts of the ice sheet, conclude that the trend is probably unstoppable.
The NASA study published in “Geophysical Research Letters” uses data from satellites, planes, ships and measurements from the shelf ice to examine six large glaciers in the Amundsen Sea over the last 20 years. The second report, from the University of Washington published in the journal “Science,” uses computer models to study the Thwaites glacier. It is considered of particular importance because it acts as a type of “lynch pin”, holding back the rest of the ice sheet.
According to NASA researcher Eric Rignot, the glaciers in the Amundsen Sea sector of West Antarctica have “passed the point of no return.” He told journalists this would mean a sea level rise of at least 1.2 meters (3.93 feet) within the next 200 years.The University of Washington scientists worked out, using topographical maps, computer simulations and airborne radar, that the Thwaites glacier is also in an early stage of collapse. They expect it to disappear within several hundred years. That would raise sea levels by around 60 centimeters (23.62 inches). The NASA study showed that sea level rises of 1.2 meters are possible
The good news, according to author Ian Joughlin, is that while the word “collapse” implies a sudden change, the fastest scenario is 200 years, and the longest more than 1,000 years. The bad news, he adds, is that such a collapse may be inevitable: “Previously, when we saw thinning we didn’t necessarily know whether the glacier could slow down later, spontaneously or through some feedback,” Joughlin says. “In our model simulations it looks like all the feedbacks tend to point toward it actually accelerating over time. There’s no real stabilizing mechanism we can see.”
The latest IPCC report does not adequately factor ice loss from the West Antarctic ice sheet into its projections for global sea level rise, on account of a lack of data. These “will almost certainly be revised upwards,” according to Sridar Anandakrishnan from Pennsylvania State University at the presentation of the University of Washington study. The scientist was not involved in the research.
NASA glaciologist Rignot said he was taken aback by the speed of the changes. “We feel this is at the point where … the system is in a sort of chain reaction that is unstoppable,” he said.
Rignot also makes the key point that this development tells us not only about the area down at the South Pole, but about the whole climate system: “This system, whether Greenland or Antarctica, is changing on a faster time scale than we anticipated. We are discovering that every day.”
My last two blog posts have been about melting of the Greenland ice sheet and melting even in the East Antarctic, which is usually cited as the last bastion against ice-destroying climate change. We are subjecting our cryosphere to huge pressures and have set a “snowball” rolling, which is picking up momentum and will ultimately carry masses of ice into a rising ocean.
Rignot says even drastic measures to cut greenhouse gas emissions could not prevent the collapse of the West Antarctic ice sheet. That is a terribly depressing thought. I would like to think this will prove wrong. But if there is any chance to avert that disaster and preserve our polar ice for thousands of years rather than just a few hundred, surely the time for action is now?
Greenland melt natural or man-made?
And does it ultimately make any difference? Scientists from the University of Washington (UW) have published a paper in Nature estimating that up to half of the recent warming in Greenland and surrounding areas may be due to climate variations that originate in the tropical Pacific and are not connected with the overall warming of the planet. You can just hear the “I told you so”, from the climate skeptics. “Still”, the UW scientists add, “at least half the warming remains attributable to global warming caused by rising carbon dioxide emissions”.
With all due respect to the scientists who do this essential research – I repeatedly find myself wondering how we can talk about “natural” climate variations at all any more, given that we have changed the parameters so much you could argue none of it is really without human impacts. Does natural fluctuation not act differently if you are starting from completely different base data, brought about by man-made warming through greenhouse gas emissions?
Greenland and parts of neighboring Canada have experienced some of the most extreme warming since 1979, at a rate of about 1 degree Celsius per decade, or twice the global average, the scientists say. “We need to understand why in the last 30 years global warming is not uniform”, says first author Qinghua Ding, a UW atmospheric research scientist. “Superimposed on this global average warming are some regional features that need to be explained”.
The study uses both observations and advanced computer models. It comes to the conclusion that a warmer western tropical Pacific Ocean has caused atmospheric changes over the North Atlantic that have warmed the surface by about half a degree per decade since 1970. “The pattern of the changes in the tropical Pacific that are responsible for remarkable atmospheric circulation changes and warming in Greenland and the Canadian Arctic are consistent with what we would call natural variability”, says co-author David Battisti, a UW professor of atmospheric sciences.
Of course there will always be natural variability in the course of the seasons and changing meteorological conditions. But in many of the fastest—warming areas on earth, co—author of the new study John “Mike” Wallace, also professor at UW, says global warming and natural variations combine to create a “perfect storm” for warming.
The scientists attribute the natural variations in their study to an “unusually warm western tropical Pacific, near Papua New Guinea. Sind the mid-1990s the water surface there has been about 0.3 degrees hotter than normal. Computer models show this affects the regional air pressure, setting off a stationary wave in the atmosphere that arcs in a great circle from the tropical Pacific toward Greenland before turning back over the Atlantic”. Wallace says there are warm spots where the air has been pushed down, and cold spots where the air has been pulled up. And Greenland, he explains, is in one of the warm spots”.
This and other research by these scientists has documented the existence of decades-long climate variations in the Pacific Ocean which resemble the better known shorter-range El Nino variations. Other studies have indicated that waves starting in the same place in the tropical Pacific but radiating southward are warming West Antarctica and melting the Pine Island Glacier, which has been the subject here on the Ice Blog before.
The experts describe this natural variation as “unpredictable”, whereas the half of the warming in Greenland from the “forcing of climate by anthropogenic greenhouse gases” is “predictable”.
So what do we learn from all of this? One thing is clear. It does NOT change the threat to Greenland’s ice from our man-made warming: “Nothing we have found challenges the idea that globally, glaciers are reatreating, says Battisti. “Ice appears to be exquisitely sensitive to the buildup of greenhouse gases, more than we ever would have thought”, says his colleague Wallace.
Ultimately, the researchers say, natural variations could either accelerate or decelerate the melting rate of Greenland’s glaciers in coming decades. But, “in the long run, the human induced component is likely to prevail”.
So don’t let anybody use this as an excuse to talk down the need to cut emissions in a big way asap.





























Feedback