Search Results for Tag: sea ice
Arctic climate: positive narrative?
As 2015 draws to a close, the NOAA report card on the state of the Arctic and a substantial new study on the Greenland ice sheet belie the myth that the Paris climate conference has put us on track for averting the worst climate change impacts. NOAA confirms that the Arctic experienced record air temperatures and a new low in peak ice extent during 2015, and the scientists warn that climate change is having “profound effects” on the entire marine ecosystem and the indigenous communities that rely on it.
![]() read more
read more
Paris: A COP-out for Arctic Peoples?
As I write, the climate negotiations have been extended into Saturday. Same procedure as every year? While I still hope the seemingly never-ending bickering will result in a document which will at least signal the end of the fossil fuels era, I cannot help feeling a sense of sadness and regret, that this is all way too late for the Arctic, as I discussed in the last blog post. And I wonder how all this feels to indigenous folk living in the High North, as they see their traditional lifestyles melting away.
On a recent edition of DW’s Living Planet programme, Lakeidra Chavis reported on the effect of melting permafrost on indigenous communities in Alaska. Chatting to a colleague in between times about the story, she told me how moved she was to hear how skulls had been washed up in a river as the permafrost at a burial site thawed.
Climate change impacts the present, future – and past
I had a kind of déjà vu feeling. Back in 2008, in those early days of the Ice Blog, I travelled out to Point Barrow, the northernmost point in the USA, with archaeologist Anne Jensen. We visited the site where a village had had to be re-located because of coastal erosion, with melting permafrost and dwinding sea ice. She told me how she was called up by distraught locals in the middle of the night and asked to help recover the remains of their ancestors before they were washed into the ocean. My colleague here in Bonn was surprised to hear that I had conducted that interview back in 2008. How could this have been known at that time already, yet so little publicized?
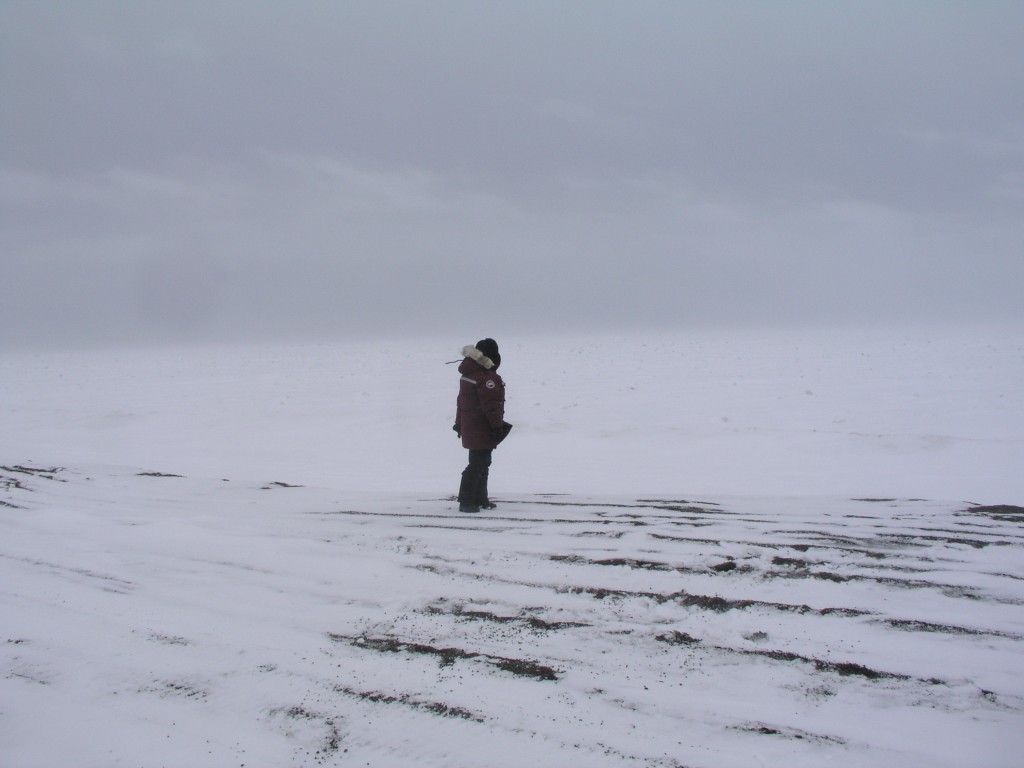

Climate change impacts: Jensen at the site of a lost Inupiat village at Point Barrow, 2008 (Pic.: I.Quaile)
Victims or culprits?
While a lot of attention is focused (and rightly so) on the impacts on developing countries, Asia, Africa, rising sea levels, this is an issue a lot of people know very little about. In an article for Cryopolitics Mia Bennet puts her finger on an interesting aspect of all this. The Arctic indigenous peoples are living in industrialized, developed states. That gives them an interesting status, somewhere between being victims and perpetrators of climate warming.
“A discourse of victimization pervades much Western reporting on the Arctic”, she writes. A lot of people in the region tend to blame countries outside the region for climate change. She quotes a study in Nature Climate Change in which researchers found that emissions from Asian countries are the largest single contributor to Arctic warming. But she notes that gas flaring emissions in Russia and forest fires and gas flaring emissions in the Nordic countries are the second two biggest contributors. And these industries are often supported by locals, not least because of the jobs and prosperity they bring.
This brings me back to some encounters I had during that trip to Alaska in 2008 – and others since, with Inuit people employed in the oil sector. They were reluctant to accept that the industries that provided their livelihoods could ultimately be literally eroding the basis of their cultures. Russia, the USA, Canada, Norway – are all countries involved in oil and gas exploitation. Some northern regions are highly dependent on the industries which are warming the climate.
“And for their part, Arctic countries must realize that reducing emissions begins at home on the region’s heavily polluting oil platforms and gas flaring stacks – not in Paris”, says Mia Bennet.
All up to Paris?
The sad truth is that even the two-degree target – or the 1.5 currently being debated – will not have much of an impact on Arctic warming.
Mia Bennet puts it bluntly. “Regardless of whether a positive or negative outcome is reached in Paris at COP 21, it will not dramatically affect the Arctic.”
A delegation of indigenous leaders from the Arctic countries is in Paris at the talks. Both the Inuit Circumpolar Council and the Saami Council have sent delegates, with the aim of highlighting the consequences of a warming climate for the polar regions.
Council representatives are from three distinct Inuit regions: Canada, the USA and Greenland. The Chukotka region of Russia also has a substantial Inuit population, who are not directly represented in Paris, but belong to the Council. The Saami Council has representatives from Finland, Russia, Norway and Sweden. Both sets of delegates are attending as observers, without voting rights.
In a position paper, Inuit Circumpolar Council Chair Okalik Eegeesiak of Canada stresses the Inuit’s deep concern about the impacts of climate change on their cultural, social and economic health.
She describes the Arctic’s sensitive ecosystem as a “canary in the coal mine for global change”. Following that metaphor, the canary must be close to suffocating.
The Inuit representatives in Paris are appealing for stronger measures to keep global temperature rise below 1.5 degrees C. They stress that the land and sea sustain their culture and wildlife, “on which we depend for food security, daily nutrition and overall cultural integrity”.
But ultimately, in a world where altruism seldom plays a part, it may be their other argument – the role of the Arctic in influencing the global climate system – that convinces negotiators of the need to work against global warming. With increasing knowledge and awareness of the extent to which the Arctic influences global processes and thus weather and climate all over the globe, the willingness to take measures to prevent further deterioration of the cryosphere is likely to increase. Whether it will be in time is another question. Any negotiator in Paris who has taken a brief moment off to read this – remember, we are not talking about a remote region with a small population. We are all in this together.
Arctic residents in hot water
At the swimming club last weekend, one of my fellow swimmers complained the water was too warm. She said she couldn’t swim at her usual speed when the temperature in the pool rose even a little bit. It left her feeling tired and lethargic. So how much more dramatic must it be for the tiny creatures at home in cold Arctic waters, when a warm influx changes their surroundings and living conditions.?
The warming of Arctic waters with climate change is likely to produce radical changes in the marine habitats of the High North. Data from long-term observations in the Fram Strait, which researchers from the Alfred Wegener Institute (AWI) have now analysed and published in the journal “Ecological Indicators”, confirms that even a short-term influx of warm water into the Arctic Ocean would suffice to fundamentally impact the local symbiotic communities, from the water’s surface down to the deep seas. They found that this happened between 2005 and 2008.
The deep sea observatory
Over the past 15 years, researchers from Germany’s Alfred Wegener Institute for polar and marine science (AWI) have been keeping an eye on the sensitive marine ecosystem in the Fram Strait, the sea lane between Greenland and Svalbard .The institute operates a deep-sea observatory there, known as “HAUSGARTEN”, which translates literally as house garden. It is actually a network of 21 individual mini research stations. Every summer, scientists pay them a visit and collect water and soil samples. Some of the stations have anchored systems that operate year-round, recording the water temperature and tides, collecting water and soil samples at regular intervals, and capturing the sediments that drift down to the seafloor from the upper water layers.
“This is the only observatory of its kind in the world. There’s no other project in which readings from the surface down to the ocean floor were taken in fixed positions over such a long time – let alone in the polar regions,” says AWI biologist Thomas Soltwedel.
For the current publication, the AWI researcher and his team analysed the first 15 years of the HAUSGARTEN dataset. The Fram Strait is especially interesting for Soltwedel and his colleagues because it represents the only deep juncture in the Arctic Ocean, allowing water masses from the Atlantic to flow into the Arctic to the west of Svalbard. In turn, water and ice floes find their way back out of the Arctic Ocean on the strait’s Greenland side.
Too warm for comfort
Until now, the scientists say it was unclear just how polar marine organisms were responding to the warming of the ocean and shrinking sea-ice cover. Now, the long-term observations show that arctic marine habitats could change radically if subjected to a sustained rise in temperature. The AWI researchers say their most surprising finding is that the thermally induced changes at the ocean surface can rapidly spread to affect life in the deep seas.
Normally the water near the surface, which flows north out of the Atlantic through the Fram Strait, has an average temperature of three degrees Celsius. With the help of their observatory, the AWI researchers were able to establish that from 2005 to 2008 the average temperature of the inflowing water was one to two degrees higher: “In that time, large quantities of warmer water poured into the Arctic Ocean. Since polar organisms have adapted to living in constant cold, this extra heat input hit them like a temperature shock,” Soltwedel explains.
He says the reactions in the ecosystem were correspondingly extreme: “We were able to identify serious changes in various symbiotic communities, from microorganisms and algae to zooplankton.”
Migrating sea creatures
One major change described in the article was the increase in free-swimming conchs and amphipods, which are normally found in the more temperate and subpolar regions of the Atlantic. In contrast, the number of conchs and amphipods in the Arctic dropped significantly.
The researchers also noted a decline in small, hard-shelled diatoms. Prior to the unexpected influx of warm water, they made up roughly 70 per cent of the vegetable plankton in the Fram Strait. But during the warm phase, the foam algae Phaeocystis took their place. A change with consequences, Soltweder explains: “Unlike diatoms, foam algae tend to clump and sink to the ocean floor, where they become a food source. But the sudden rise in available food led to major changes in deep-sea life, including a noticeable increase in the settlement density of benthic organisms.”
If you are not a marine biologist, you may be wondering what that means for the future of the Arctic and why we should be concerned about it. The problem is that all of this affects the Arctic food web.
The scientists can’t say exactly how at this point. But, as with so many other aspects of climate change: “Above all, we’re troubled by the simple fact that the changes have been so rapid, and so far-reaching.”
New residents here to stay
Since the flow of warm water has subsided, the water temperature in the Fram Strait has stabilised – though it is still slightly above the average value from before 2005. Yet some of the changes appear to be there to stay. The conchs from the lower latitudes seem to have made a home for themselves in the Fram Strait.
As usual, the scientists are reluctant to say whether the warm-water influx they monitored is due to climate change or could be part of natural climate fluctuations. They say they need data covering several decades to be more certain.
But either way, the results of the ecological long-term studies clearly show that even short-term changes in ocean temperature can drastically impact life in the Arctic. So it looks like there will certainly be more to come, as the world continues to heat up.
Farewell to ‘Last Ice’ victims in a rapidly warming world
Ice Blog readers may remember the story of the two ice researchers and polar explorers who died when they broke through unexpectedly thin ice in the Canadian Arctic earlier this year. This week I had the chance to join friends and admirers of Marc Cornelissen and Philip de Roo at a ceremony held in their home country, the Netherlands. The unusually warm November weather, with people sitting out eating ice cream, seemed oddly apt for a tribute to two people who died doing climate research.
![]() read more
read more
Arctic plastic “garbage patches”
There are a lot of things you might want to discover on a research cruise in the Arctic. Chunks of plastic floating around are not amongst them. But that is just what biologist Melanie Bergmann and her colleagues from the Alfred-Wegener-Institute and the Belgian Laboratory for Polar Ecology repeatedly did find while they were cruising through the Fram Strait, between Greenland and Svalbard.
They have just published a study documenting that plastic garbage has even reached the far north of the planet. In the online portal of the magazine Polar Biology, they describe how they found plastic waste floating on the surface of the ocean.
Plastic pollution – a fact of life?
In 2012, Bergmann and her colleagues took the opportunity of joining a cruise on the German research ship Polarstern to the Fram Strait to measure the extent of plastic pollution there. They monitored the ocean surface from the boat and a helicopter. Over 5,600 kilometres they found 31 pieces of plastic rubbish. But that will only be the tip of the “garbage-berg”.
“Since we were counting from the bridge of the ship, which is 18 metres above the sea surface, or from the helicopter, we primarily found large pieces of flotsam”, Bergmann told journalists. “So our figures very probably under-estimate the actual amount of garbage”, she added.
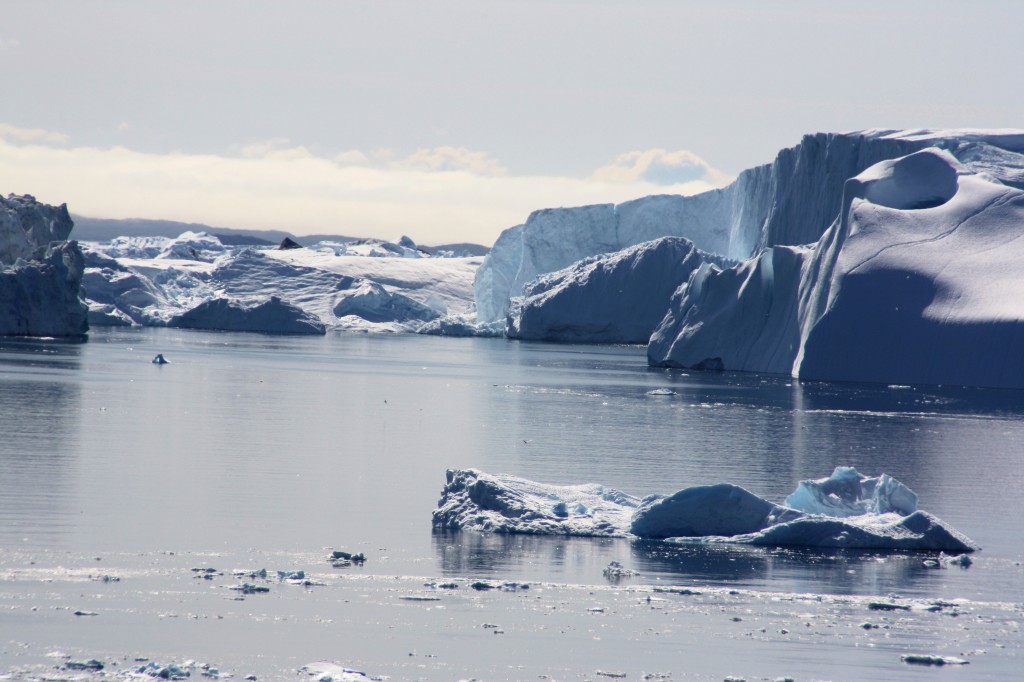

Too beautiful to “waste”? The team even found plastic waste in Greenland’s Ice Fjord (Pic: I. Quaile, Ilulissat)
Plastic waste tends to disintegrate into small pieces, just one or two centimeters in size, if they float in the sea for any length of time.
Somehow, the results of this study did not really surprise me. That, I think, is a very sad state of affairs. There have been so many reports of plastic particles being found in animals and birds and so in our human food chain that there is a danger we take this serious form of pollution for granted. The ngo Ocean Care estimates that around nine million tons of plastic waste finds its way into the oceans every year.
The seabed as a waste dump?
The AWI scientists say this is actually the first study to show that plastic waste is floating around on the surface of Arctic waters. For an earlier study, the German biologist searched for plastic, glass and other waste on photos taken of the Arctic seabed. She found that even in deep sea areas, the amount of garbage has increased in recent years. The concentration is 10 to 100 times higher than on the surface. The experts deduce from this that garbage ultimately sinks to the bottom and collects there.

Plastic bag at the HAUSGARTEN, the deepsea observatory of the Alfred Wegener Institute in the Fram Strait. This image was taken by the OFOS camera system in a depth of 2500 m. Photo: Alfred-Wegener-Institut/Melanie Bergmann/OFOS
The question is: how does this waste get up into the Arctic? It could, it seems be part of what, is described as a “garbage patch”, created when plastic waste gets caught up in ocean currents and concentrated into a kind of whirlpool.
Scientists have already identified five of these patches around the globe. The waste in the Arctic appears to be part of a new, sixth “patch” developing in the Barents Sea. What a depressing development! Scientist Melanie Bergman thinks it probably contains waste from the densely populated coastal regions of northern Europe.
“It is thinkable, that some of this garbage drifts north and northwest, as far as the Fram Strait”, she says. Another theory, she says, it that the garbage being found in the Arctic is caused by the retreat of sea ice.
“More and more fish trawlers are following cod further north. Presumably, rubbish from the ships ends up in Arctic waters, either deliberately or by accident. We are assuming that this trend will continue”, says Bergmann.
Climate change and pollution threat
So while here in Bonn, just across the road from my office, the UN climate secretariat is struggling to come up with a draft text for the Paris COP21 summit, which will be acceptable to all parties (and so subject to so many compromises and loopholes?), we have yet another sign of a climate change impact on the no-longer-pristine Arctic. And at the same time, it indicates the effects our unsustainable lifestyles are having on the environment of the planet. I have been witness to many arguments over whether governments should put more effort into combating climate change or environmental degradation and pollution. Ultimately, once more I come to the conclusion that it is virtually impossible to separate the two.
Last week I interviewed two experts on different aspects of ocean protection for a Living Planet special: Oceans under Pressure. They expressed similar views on the intrinsic connections between climate change, humans’ maltreatment of the environment and the health of the oceans on which we rely for survival. Not only are we causing climate change. The other pressures we put on the oceans make it less able to cope.
Tony Long is in charge of work against illegal fishing with Pew Charitable Trusts:
“I think climate change, over-fishing and illegal fishing are all linked in one way or another. The bad practices that occur from illegal fishing can damage the ecosystem, whether it be trawling and ripping up corals, or fishing the wrong species at the wrong time. It all has an effect on the broader ecosystem. And with ocean acidification and the changes that are taking place now scientifically proven, that’s going to reduce the amount of fish people can catch, if we don’t start to look after it. So actually it should all be seen as one”. (Read the interview here).
Ove Hoegh-Guldberg is Director of the Global Change Institute at the University of Queensland, Australian, and chief scientist with the XL Catlin Seaview Survey, which has been monitoring the state of the world’s coral reefs, including the current global bleaching event:
“On our current track where we’re polluting local water, we’re overfishing coral reefs and now we’re rapidly changing the temperature and acidity of the ocean, we won’t have coral reefs and it will be a very long time before they come back – probably well after our exit from the climate. We are the first generation to see these types of impact and we are going to be the last that has the chance to do something. We must get to very low CO2 emission rates as soon as possible, hopefully over the next 20 to 30 years. Because if we don’t – it won’t just be coral reefs. It will be a large number of other ecosystems that go, and humanity will be in trouble.” (Read the interview here.)
I rest my case.





























Feedback