A good haul for polar night team
The Polar Night cruise will come to an end on Tuesday, when the last of the scientists will leave the ship with their samples. I was able to stay until the end of the week, when I left the ship at Ny Alesund with some of the researchers, who were changing places with colleagues. I have left Svalbard, but not the Arctic. More about my current whereabouts later.
A good haul in the polar night
It was interesting to hear that our scientists were happy with their “catch”. Sören Häfke, the German scientist from the Alfred Wegener Institute in Bremerhaven, had more than enough of the little crustaceans calanus finmarchius. When they get back to Germany, they can start their genetic analysis to find how their biological clock works in the dark, Arctic winter. In summer, it is assumed light tells them when to come to the surface to feed and when to go down deeper to avoid predators. But what happens in winter, when it is dark all day long? I will look forward to hearing what they find out.
The Russian team had plenty of interesting sediment samples to look into. The others on board also seemed to be happy with the plankton, crustaceans and small fish they brought in for further research. Marine Cusa was a bit unhappy about the lack of polar cod in the fjord. There seemed to be no shortage of larger Atlantic cod. This is related to the amount of Atlantic water currently present in the fjord, expedition leader Stig Falk-Petersen explained to me. It looks as if Marine will be changing the subject of her Master’s thesis. But I have the feeling it will be no less interesting.
“Life doesn’t stop when the light goes out”
Paul Renaud, a Professor at the University Centre in Svalbard, coordinated the logistics of the expedition on board as well as conducting his own biological research. He is one of those who came up with this Polar Night project. As he sums it up, there is a need to follow up on the few studies done in the last ten years which indicate that there is much more activity in the Arctic ocean in winter than previously thought. This must be triggered by processes other than light. Light is critical for the functioning of the ecosystem, but “it’s not that when the light goes out, everything stops functioning”, Paul told me.
From the samples I was shown under the microscope, I can confirm that there is indeed plenty of life going on. And many of the creatures were carrying eggs.
Climate paradox: easier access – shifting parameters
I asked Paul what was driving the surge of research into the Arctic winter. Firstly, new technology makes it possible to take measurements under the ice, and all year round, when there is no-one up here, he explains. Buoys tethered to the ice are one example. A series of permanent observatories has also been set up in the fjords here, measuring temperature, salinity, oxygen, light, chlorophyll and the movement of plankton. The number of research stations in the region has also increased.
The other major factor is quite clearly climate change. The absence of ice makes it much easier to sail up here, says Paul. Just 20 years ago, this fjord would have been completely covered with ice at this time. Now the sea ice is only found in the far reaches of the fjord. But Paul confirmed my theory that while warming is making access easier, it is also changing the parameters the scientists want to measure. “We are addressing a moving target”, is how he describes it.
Ice, less ice, no ice?
When it comes to forecasting how the Arctic ocean and its ecosystem will react to climate change in the long term, the scientists here say we desperately need more data. The IPCC gives around ten scenarios for how climate in the Arctic could develop, Paul explains. Clearly, if we can rely on predictions that the Arctic will be ice-free in summer from the middle of the century at the latest, that will have certain effects on ecosystems
Some organisms can be very flexible, says Renaud, not breeding for ten years and still continuing their populations. But short-lived organisms that rely on a certain timing of ice or live in the sea ice may well be more seriously affected. But without more information, it is impossible to tell how they will react in the long term.
Along with climate change, increased development is bringing more changes to this once inaccessible region, as discussed many times here on the Ice Blog and in my articles for dw.de. Paul is involved in developing monitoring practices. He stresses this is new territory for economic activities like oil exploration, fisheries, tourism and shipping, and that we urgently need more data on the effect of these activities on sensitive components of the Arctic ecosystems.
Can science keep pace with development?
One question I seek the answer to when I talk to Arctic experts is: can this research keep pace with the speed of the development? The answer depends partly, of course, on how fast that development will be. The Svalbard expert says there will still be sea ice in the Arctic in winter for the foreseeable future, around 100-150 years. That will slow economic activities like oil and gas exploration. “That buys us a little more time”, says the marine biologist. But he sees a huge challenge to identify and monitor the impacts of rapidly growing activities like tourism and shipping.
As I packed up to prepare to leave the Helmer Hanssen at the Ny Alesund research station, Paul was giving his instructions to the scientific team. Some were leaving with me, others staying on for the next section. Coordinating the cleaning of the laboratory and deck areas still well splattered with mud, then the packing up and labeling of the samples and equipment, is a major operation. I thought it better not to whinge about fitting my cameras, recorders and Arctic gear into their bags, which somehow seemed to have shrunk over the past week.
On our last night in dock at Ny Alesund, we were treated (not for the first time this week) to some northern lights, eerily dancing across the black Arctic sky. A wicked wind bit at our faces as we headed once again for the world’s northernmost marine lab. The researchers brought crates of samples. I myself brought a treasure trove of stories, ready to go online. The Arctic in winter is harsh but has a charm of its own. It was fascinating to experience the Polar Night, but I was looking forward to my next Arctic destination a bit further south, venue for the major Arctic conference: Arctic Frontiers.
I am now in Tromso, Norway’s “Arctic capital”, where the sun will be reappearing above the horizon this week and the magic pink, pale blue, silvery grey and white Arctic light is already in evidence for several hours a day.
Acid Arctic Ocean and Russell Brand?
Is ocean acidification a term you are familiar with? If you are a regular Ice Blog reader, I would like to think you will be. But I am prompted to ask this question because the term came up during a discussion at a weekly evening class I attend, and I was flabbergasted that none of the people there had a clue what it meant. These were all university-educated professionals. That means we in the media have our work cut out for us explaining how climate change is making the seas more acidic, and why this is something we should be worried about.
This incident has reminded me that we journalists have to avoid assuming that everyone is familiar with the terms we use in our coverage on a regular basis. Climate change is the kind of topic where you want to reach a specialist audience, but also the vast majority of the population. We all have to change our habits to reduce CO2 emissions, and we all have to vote for the politicians who have the responsibility for energy and environment policy. That means we need to talk about the problems in a way everybody understands.
I am encouraged to see the BBC website had a longer article on the threat of ocean acidification a few days ago. I don’t think it has made its way into the tabloids though, correct me if I am wrong.
I was made very aware of the issue during a trip to Arctic Spitzbergen in 2010 with a team of scientists monitoring just what happens to the life forms in the sea when it becomes more acidic because it is absorbing so much of the CO2 we emit. The polar regions are suffering more than others, as cold water absorbs CO2 faster.
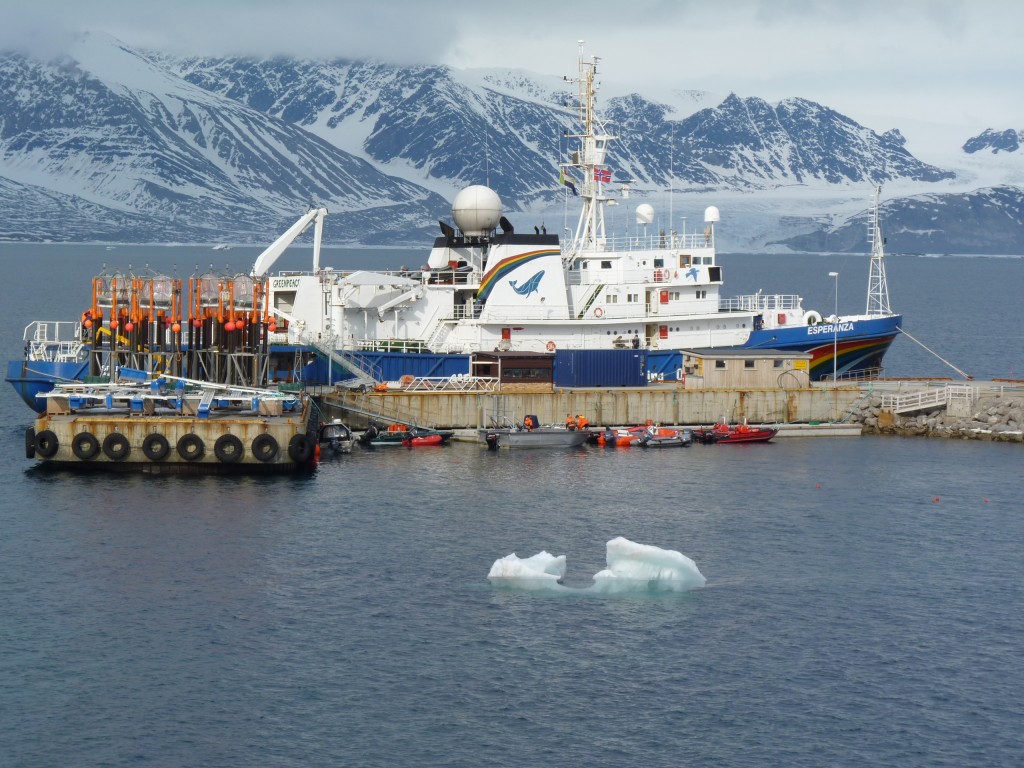

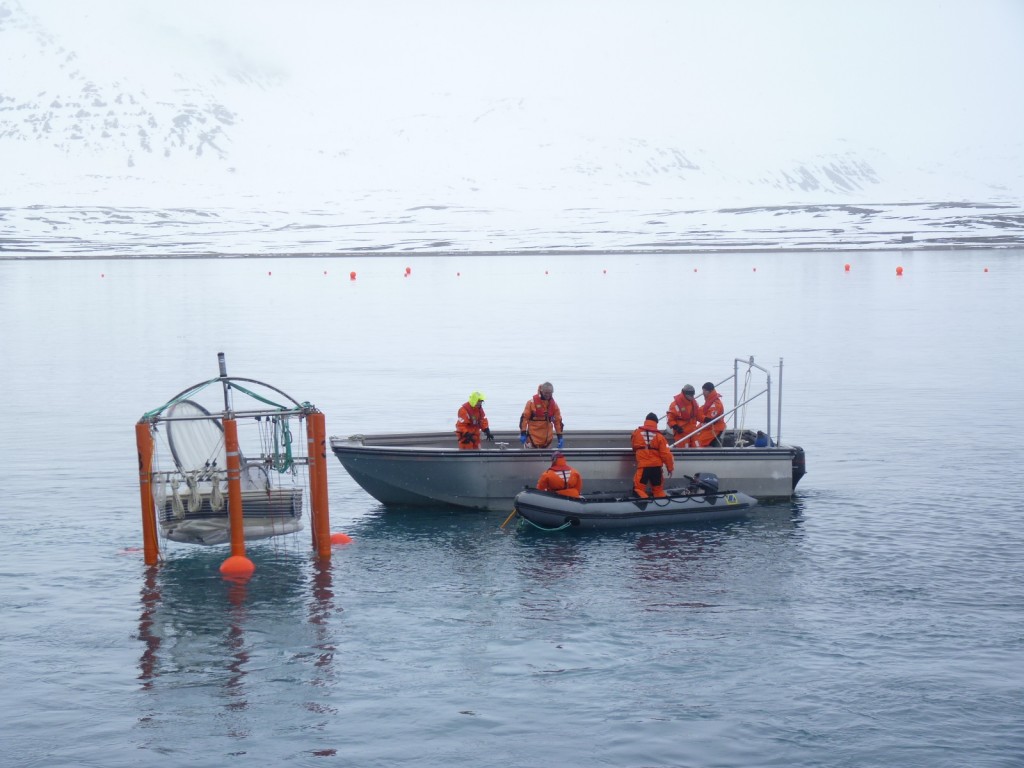
Greenpeace provided scientists with logistic support for the ocean acidification experiments off the coast at Ny Alesund, Spitzbergen. (Pic: Irene Quaile)
Towards the end of last year, I interviewed Professor Alex Rogers from the University of Oxford, who is also the scientific director of the International Programme on the State of the Oceans, which had just published a major study on acidification.
Listen to the interview:
He told me: “The oceans are taking up about a third of the carbon dioxide we’re producing at the moment. While this is slowing the rate of earth temperature rise, it is also changing the chemistry of the ocean in a very profound way.”
Carbon dioxide reacts with sea water to form carbonic acid. Gradually, this makes oceans more acidic.
Threat to marine life
Sea water is already 26 percent more acidic than it was before the onset of the Industrial Revolution. According to the IPSO report, it could be 170 percent more acidic by 2100.
Over the last 20 years, scientists around the world have been conducting laboratory experiments to find out what that would mean for the flora and fauna of the oceans. Ulf Riebesell of the Helmholtz Institute for Ocean Research in Kiel, a lead author of the report, conducted the world’s first experiments in nature, off the coast of the Arctic island of Svalbard in 2010. This was the project I visited.
Giant test-tubes were lowered into the ocean to capture a water column with living organisms inside it. Different amounts of CO2 were added to simulate the effects of different emissions scenarios in the coming decades. The experiments showed that increasing acidification decreases the amount of calcium carbonate in the sea water, making life very difficult for sea creatures that use it to form their skeletons or shells. This will affect coral, mussels, snails, sea urchins, starfish as well as fish and other organisms. Scientists say some of these species will simply not be able to compete with others in the ocean of the future.
Hard times for coastal residents
All this will have severe economic and social consequences. Ultimately, acidification will affect the food chain. Tropical and sub-tropical areas with warm-water corals are going to suffer. Coral reefs are home to numerous species, serve as nurseries for fish and are a valuable tourist attraction. They also protect coastlines against waves and storms.
At the same time, the polar regions are suffering more than others, as cold water absorbs CO2 faster. Riebesell told me the experiments in the Arctic indicate that the sea water there could become corrosive within a few decades. “That means the shells and skeletons of some sea creatures would simply dissolve.” What a horrific prospect.
The Antarctic is already affected. IPSO’s Alex Rogers told me: “We’re seeing instances where we’re finding tiny shelled molluscs, tiny snails that swim in the surface of the oceans, with corroded shells.”
These creatures play a key role in the marine food chain, supporting everything from tiny fish to whales. “One of our primary sources of marine-derived protein is in rapid decline,” says Monty Halls, manager of the UK-based Shark and Coral Conservation Trust. He describes ocean acidification as the “most serious threat to our children’s welfare.” Monty is working to produce video and cartoon material to interest the younger generation in the need to change our behavior to protect marine life.
Two German scientists Antje Funcke and Konstantin Mewes have written and illustrated a children’s story called Tipo and Tessi to make kids aware of the need to protect the ocean. So far, it has only been published in German. The English translation is available, but so far there is a lack of funding for publication.
Vicious circle of climate change
Scientists are also concerned about a feedback effect that will further exacerbate global warming. In the long run, the ocean will become the biggest sink for human-produced CO2, but it will absorb it at a slower rate. That means the more acidic the ocean becomes, the less capacity is has to act as a buffer.
Alex Rogers sees a further problem: “Carbonate structures actually weigh down particular organic carbon. In other words, they help carbon to sink out of the surface layers of the ocean into the deep sea. Anything that interferes in that process can potentially accelerate the rate of CO2 increase in the atmosphere.”
And that would be very dangerous. “The rates of CO2 increase we are seeing at the moment are probably as high as they’ve been for the last 300 million years,” says Rogers.
The IPSO scientists draw an unsettling comparison between conditions today and climate change events in the past that have resulted in mass extinctions. They say a lot of these major extinction events occurred in connection with high temperatures and acidification, similar effects to the ones that we are experiencing today.
The BBC article I mentioned earlier also mentions new research by scientists at Exeter University, indicating that increasing acidity creates conditions for animals to take up more coastal pollution, like copper. That would mean not only creatures with calcium-based shells would be endangered.
Find a celebrity champion?
The experts stress that it is not too late to halt the acidification process, although the CO2 will remain in the oceans for thousands of years. This brings me back to the topics of recent Ice Blog posts: the UN climate negotiations and the need for urgent action. And of course, to the mention in the title above of the British comedian Russell Brand. This relates to another issue I have been writing about recently: the question of celebrity involvement and whether that can help inform people about and interest them in topics like climate change and the acidification of our oceans. My commentary on this, with regard to Leonardo di Caprio at Ban Ki-moon’s September summit in New York, sparked some interesting discussions.
Just this morning I was reading about Russell Brand and how his new book calling for a revolution on all kinds of issues is attracting huge interest. I have noticed that people otherwise completely uninterested in politics and social issues are at least paying some attention because their favourite comedian is talking about them. Maybe we have to get Russell Brand on board. I’m not sure what kind of action he would advocate, but there would certainly be a lot fewer people who could say they’d never heard of ocean acidification.
Polar ice tipping points
As I get ready to head up to Tromso for the Arctic Frontiers conference and prepare my accreditation for the next routine round of climate talks here in Bonn in March, I find myself with plenty of food for thought.
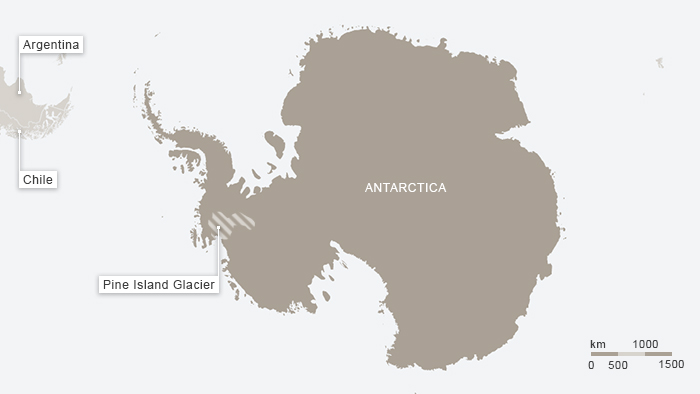
It seems like not that long ago that scientists were telling us that although the Arctic is clearly melting fast, there was no need to worry about the Antarctic ice melting. But for the past 15 years or so, scientists have been observing that glaciers in West Antarctica are out of balance. Ice shelves have been breaking off and the calving fronts of glaciers have been retreating, draining huge amounts of ice into the ocean. This week I was interested and concerned to read about the results of a modelling effort, using 3 different types of model, indicating a key Antarctic glacier was melting irreversibly.
(Map courtesy of Deutsche Welle)
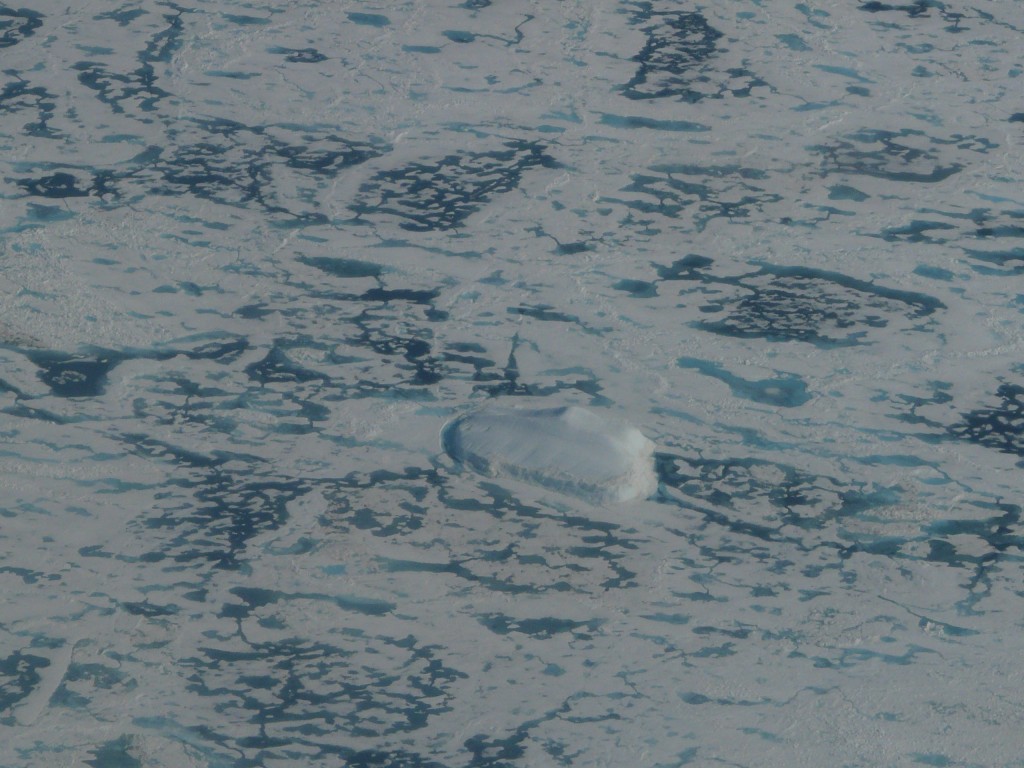
The Pine Island Glacier in the Antarctic hit the headlines last year when a giant iceberg broke off it. It is a key glacier because it is actually responsible for some 20 percent of the total ice loss from the region. Now scientists have found the glacier is melting irreversibly – with dramatic consequences for global sea levels. For an article for DW entitled Antarctic’s glacier retreat unstoppable, I interviewed Gael Durand of the French University of Grenoble, one of a team of scientists who have just published the new study: “We show that the Pine Island Glacier will continue to retreat and that this retreat is self-sustaining. That means it is no longer dictated by changes in the ocean or the atmosphere, but is an internal, dynamic process”, Durand told me. This will mean an increasing discharge of ice and a greater contribution to global sea level rise. “It was estimated at around 20 gigatons per year during the last decade, and that will probably increase by a factor of three or five in the coming decade. That means this glacier alone should contribute to the sea level by 3.5 to 10 millimetres a year, accumulating to up to one centimetre sea rise over the next 20 years. For one glacier, that is colossal”, says Durand.
I called up Angelika Humbert from Germany’s Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research (AWI) to get an expert opinion on the significance of the new research. She told me 1cm over 20 years would be an “extremely high” amount. The glaciologist, who is also working on models for the Pine Island Glacier, stresses that all models include a degree of abstraction and uncertainty. However, her work also indicates that the glacier will make an increasing contribution to sea level rise in the coming years and describes the new study as a “considerable advance on the results of research to date.” Humbert says the results could well be applied to other glaciers of the same type.
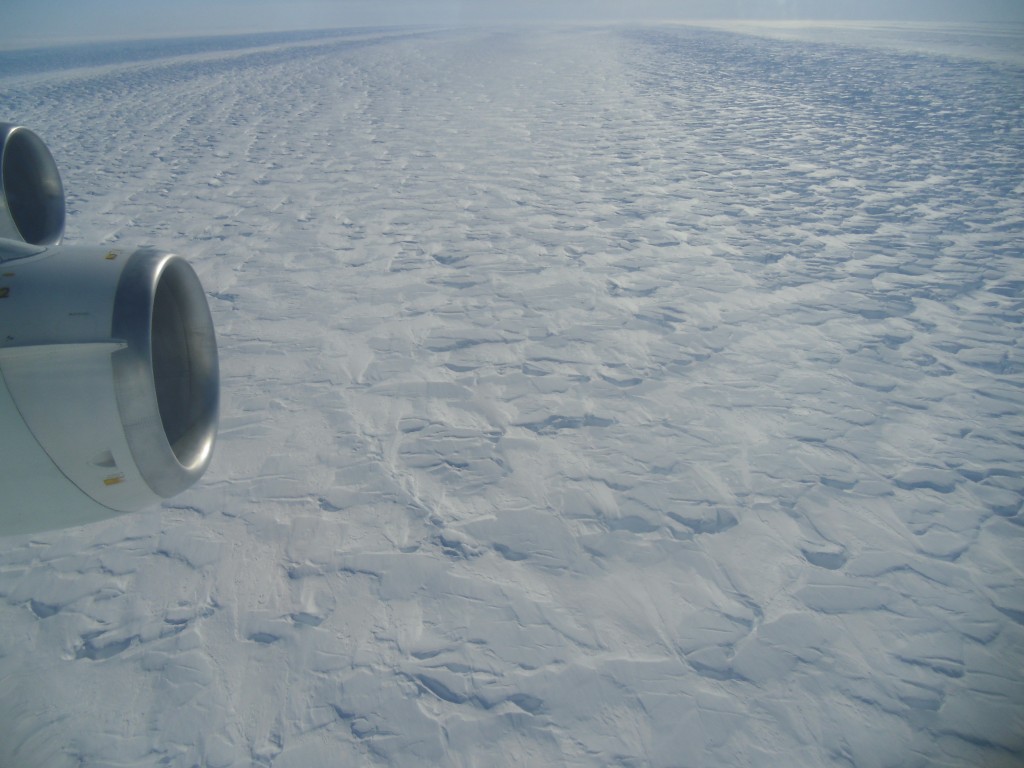

Angelika Humbert from AWI took this picture flying over the Pine Island Glacier in a NASA DC8 as part of the IceBridge campaign in 2011
Durand’s new study shows that the glacier is now flowing at a rate and in a way that makes the process irreversible. Even if the air and ocean temperatures cooled off to what they were a hundred years ago – which is in no way likely – Durand is convinced the glacier would not recover. Durand says the study should arouse concern because the glacier has passed a “tipping point”, a much discussed concept in climate science. “That means because of our behaviour, our climate is changing and will continue to change a lot. I think it is one of the first times we are passing these tipping points.”
The scientist compares the situation to that of a cyclist coming down from the top of a mountain and unable to brake: “We have to fear that the retreat will continue, that other glaciers in the region will start to do the same, and that we will have a collapse of this part of the ice shelf. That would take centuries, but it would mean a rise of several metres in sea level.”
The last report by the Intergovernmental Panel on climate Change (IPCC) warned of the implications if the glaciers of West Antarctica were to become unstable. “Here,” says Durand, “we have proof that that is already happening with this one.”
At the Arctic Frontiers conference two years back, I heard a lot of interesting discussions about climate tipping points. Professor Carlos Duarte Directorof the Oceans Institute at The University of Western Australia and Research Professor with the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) talked to me at length about tipping points. Let me quote him briefly:
“Tipping Points – or thresholds – are levels of pressures beyond which small response of a property of interest becomes abrupt. Once a system or ecosystem or earth system crosses beyond a threshold, the changes, e.g. in the extent of ice or rate of warming, accelerate greatly, and once the threshold is crossed, it is sometimes very difficult to return to the original state even if pressure is released or reduced.”
We discussed the possible tipping points and warning signs outlined in a key piece of research by Timothy Lenton and others. Some would argue that tipping points have already been crossed in the Arctic region, which is known to be warming at least twice as fast as the rest of the earth. One of Lenton’s other key factors is the West Antarctic ice sheet becoming unstable. Now the “eternal ice” down south could be reaching a kind of “tipping point” in places. Yes, I know this only applies to a particular region of the West Antarctic, but the implications of irreversible glacier melt there are already huge. Greenland and that West Anarctic ice sheet play a key role in storing masses of fresh water, which would have huge implications if they melted. With marine glaciers, like the Pine Island Glaciers, the melt of white ice to expose more dark ocean surface underneath would further increase warming by absorbing solar heat instead of reflecting it back.
With the EU in the news today for considering moving away from binding climate targets, and little progress in sight towards an effective new climate agreement scheduled to be agreed in Paris in 2015, this all puts me in a pensive mood, as I get ready to head north and focus on the implications of the changing climate for “Humans in the Arctic”.
Climate change and the polar vortex
If you live in one of the North American areas hit by the latest big freeze, you may well have been hearing someone say “so much for global warming” over the last week or so. If you live on this side of the Atlantic, you might have been tempted to worry more about climate change if you were being battered by storms or gales. Then there are those here in Germany saying “give me more of this warming”, with the birds tweeting and the bushes blooming as if we were already in the middle of spring.
![]() read more
read more
Polar regions hit by ocean acidification

In 2010 I watched the start of the first in situ ocean acidification experiments off the coast at Ny Alesund, Spitsbergen, as part of the EU’s EPOCA project. Mesocosms, or giant test-tubes, were being taken out to sea by the Greenpeace ship the Esperanza. (Pic: Irene Quaile)
Did you notice much about the problem of CO2 in the oceans in the (already minimal in most places) coverage of the Warsaw climate conference? A summary of the report published recently by the International Programme on the State of the Oceans (IPSO) was presented at the meeting to draw attention to the dangers posed by acidification for ecosystems, humankind and, in form of a feedback effect, for the climate warming which is causing it in the first place. If that sounds complicated, but intriguing enough to warrant further interest, you might want to listen to an interview I recorded this week with Alex Rogers. He is a Professor of Conservation Biology at the Dept. of Zoology and a Fellow of Somerville College, University of Oxford. Amongst his many other titles, he’s the Scientific Director of IPSO. He told me it was a “fascinating coincidence” that the report was published just after the latest IPCC report, which noted, amongst other things, that atmospheric temperatures hadn’t risen as much over the last ten years or so as had been expected. One main reason suggested is that the excess heat is being taken up by the ocean, especially the deep ocean. And that fits perfectly with the findings of the big ocean survey and collation of data, says Prof. Rogers.
I also talked to Ulf Riebesell from the Helmholtz Institute for Ocean Research in Kiel, Germany, a lead author of the report and the scientist who has been in charge of the in situ acidification experiments in the Arctic .You might also enjoy in my report from that venture.
That interview is in German, so I’m not putting it up here, but the content will be flowing into an article for the DW website very soon. Meanwhile, here’s Professor Rogers:































Feedback