Search Results for Tag: EU
Polar ice tipping points
As I get ready to head up to Tromso for the Arctic Frontiers conference and prepare my accreditation for the next routine round of climate talks here in Bonn in March, I find myself with plenty of food for thought.
It seems like not that long ago that scientists were telling us that although the Arctic is clearly melting fast, there was no need to worry about the Antarctic ice melting. But for the past 15 years or so, scientists have been observing that glaciers in West Antarctica are out of balance. Ice shelves have been breaking off and the calving fronts of glaciers have been retreating, draining huge amounts of ice into the ocean. This week I was interested and concerned to read about the results of a modelling effort, using 3 different types of model, indicating a key Antarctic glacier was melting irreversibly.
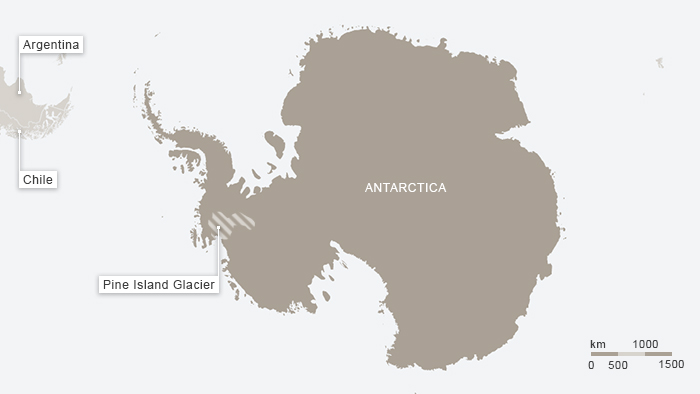
(Map courtesy of Deutsche Welle)
The Pine Island Glacier in the Antarctic hit the headlines last year when a giant iceberg broke off it. It is a key glacier because it is actually responsible for some 20 percent of the total ice loss from the region. Now scientists have found the glacier is melting irreversibly – with dramatic consequences for global sea levels. For an article for DW entitled Antarctic’s glacier retreat unstoppable, I interviewed Gael Durand of the French University of Grenoble, one of a team of scientists who have just published the new study: “We show that the Pine Island Glacier will continue to retreat and that this retreat is self-sustaining. That means it is no longer dictated by changes in the ocean or the atmosphere, but is an internal, dynamic process”, Durand told me. This will mean an increasing discharge of ice and a greater contribution to global sea level rise. “It was estimated at around 20 gigatons per year during the last decade, and that will probably increase by a factor of three or five in the coming decade. That means this glacier alone should contribute to the sea level by 3.5 to 10 millimetres a year, accumulating to up to one centimetre sea rise over the next 20 years. For one glacier, that is colossal”, says Durand.
I called up Angelika Humbert from Germany’s Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research (AWI) to get an expert opinion on the significance of the new research. She told me 1cm over 20 years would be an “extremely high” amount. The glaciologist, who is also working on models for the Pine Island Glacier, stresses that all models include a degree of abstraction and uncertainty. However, her work also indicates that the glacier will make an increasing contribution to sea level rise in the coming years and describes the new study as a “considerable advance on the results of research to date.” Humbert says the results could well be applied to other glaciers of the same type.
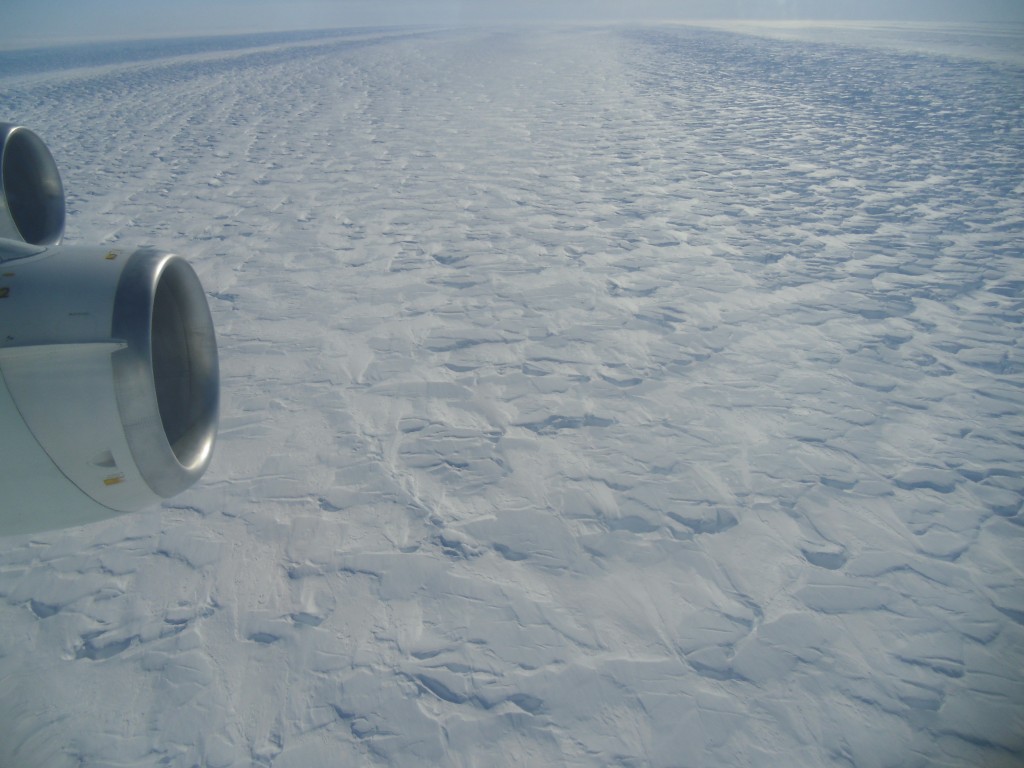

Angelika Humbert from AWI took this picture flying over the Pine Island Glacier in a NASA DC8 as part of the IceBridge campaign in 2011
Durand’s new study shows that the glacier is now flowing at a rate and in a way that makes the process irreversible. Even if the air and ocean temperatures cooled off to what they were a hundred years ago – which is in no way likely – Durand is convinced the glacier would not recover. Durand says the study should arouse concern because the glacier has passed a “tipping point”, a much discussed concept in climate science. “That means because of our behaviour, our climate is changing and will continue to change a lot. I think it is one of the first times we are passing these tipping points.”
The scientist compares the situation to that of a cyclist coming down from the top of a mountain and unable to brake: “We have to fear that the retreat will continue, that other glaciers in the region will start to do the same, and that we will have a collapse of this part of the ice shelf. That would take centuries, but it would mean a rise of several metres in sea level.”
The last report by the Intergovernmental Panel on climate Change (IPCC) warned of the implications if the glaciers of West Antarctica were to become unstable. “Here,” says Durand, “we have proof that that is already happening with this one.”
At the Arctic Frontiers conference two years back, I heard a lot of interesting discussions about climate tipping points. Professor Carlos Duarte Directorof the Oceans Institute at The University of Western Australia and Research Professor with the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) talked to me at length about tipping points. Let me quote him briefly:
“Tipping Points – or thresholds – are levels of pressures beyond which small response of a property of interest becomes abrupt. Once a system or ecosystem or earth system crosses beyond a threshold, the changes, e.g. in the extent of ice or rate of warming, accelerate greatly, and once the threshold is crossed, it is sometimes very difficult to return to the original state even if pressure is released or reduced.”
We discussed the possible tipping points and warning signs outlined in a key piece of research by Timothy Lenton and others. Some would argue that tipping points have already been crossed in the Arctic region, which is known to be warming at least twice as fast as the rest of the earth. One of Lenton’s other key factors is the West Antarctic ice sheet becoming unstable. Now the “eternal ice” down south could be reaching a kind of “tipping point” in places. Yes, I know this only applies to a particular region of the West Antarctic, but the implications of irreversible glacier melt there are already huge. Greenland and that West Anarctic ice sheet play a key role in storing masses of fresh water, which would have huge implications if they melted. With marine glaciers, like the Pine Island Glaciers, the melt of white ice to expose more dark ocean surface underneath would further increase warming by absorbing solar heat instead of reflecting it back.
With the EU in the news today for considering moving away from binding climate targets, and little progress in sight towards an effective new climate agreement scheduled to be agreed in Paris in 2015, this all puts me in a pensive mood, as I get ready to head north and focus on the implications of the changing climate for “Humans in the Arctic”.
Rovaniemi: Finland and the Arctic
Rovaniemi is where I would like to have spent the last few days. From Dec. 2nd to 4th, the first of a series of Arctic conferences was held there, organized by the city of Rovaniemi and the Arctic Centre of the University of Lapland.
Rovaniemi, a Finnish town right on the edge of the Arctic circle, is known to “Arctic buffs” because of the “Rovaniemi Process”, a Finnish initiative for Arctic environmental co-operation, which ultimately led to the adoption of the “Arctic Environmental Protection Strategy”, signed in Rovaniemi in 1991. This in turn played an important role in the establishment of the Arctic Council
In the spirit of that “Rovaniemi Process”, the city and the University’s Arctic Centre decided to organize a series of conferences, this being the first one. Finland, like all the northern states, is trying to assert its position in the region against the background of climate change and growing international interest.
Earlier this year, I received a copy of a very useful booklet produced by the Arctic Centre of the University of Lapland. It’s entitled “The Arctic Calls. Finland, the European Union and the Arctic Region“. The authors are Markku Heikkilä and Marjo Laukkanen, both based at the Arctic Centre. Its aim is to “put a human face on the Arctic Region”, and it does that very well, looking across the whole region. President Sauli Niinistö wrote the foreword to the publication. He mentions Finland’s initiative to establish an EU Arctic Information Centre in Rovaniemi, which I am following with interest.

Useful maps and info on the Arctic and its peoples
The European Union Arctic Information Centre (EUAIC) initiative is an international network of 19 leading Arctic research and outreach institutions from the various European Union Members States, and the EEA countries. It was started in 2009 as a professional network of European institutions aiming to provide information, outreach and insight into Arctic issues. The network’s objective is to provide the European Union, its citizens, institutions, companies and member states with a reliable source of information on what is happening in and concerning the Arctic. The EUAIC initiative network aims to “facilitate two-way communication between experts, decision makers, stakeholders and the public”, according to its website.
The initiative is organized as a network, making use of existing expertise and the infrastructures of its members. Its headquarters are located at the Arctic Centre in Rovaniemi. Currently there are nineteen partners. The European Commission selected the consortium to carry out a key one million euro project to produce a “Strategic Environmental Impact Assessment of development of the Arctic”. The project should be completed in 2014 and should make for interesting reading.
Bearing all this in mind, it’s worth keeping an eye on what comes out of the Rovaniemi conference. And I’d recommend the publication, “The Arctic Calls”, ISBN 978-952-281-065-6. It has interesting interview, maps, photos and insight. You can also get it from the Arctic Centre or download an online version.
Let me just finish by quoting from the final pages:
“The images of icebergs drifting out to sea have turned from symbols of freshness to symbols of disappearance. They have become images of a unique world that is undergoing drastic change and is about to lose many of its characteristics.” How right you are.
10 years French-German Arctic Station
Congratulations to the team of the joint French-German Arctic research station in Ny Alesund, Svalbard. It is ten years since the German polar authority AWI (Alfred-Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research) and its French counterpart IPEV (Institut Polaire Paul Emile Victor) joined forces at the world’s northernmost research base.
The station was my first Arctic destination in 2007, so it has a special significance for me. During the IPY, I was involved in an international radio cooperation to report on polar science, which was how the Ice Blog was born.
Photo gallery from Ny Alesund, “From Pole to Pole”.
AWIPEV is the biggest of the research stations in Ny Alesund, and takes up to 150 scientists from France and Germany in the course of a year.
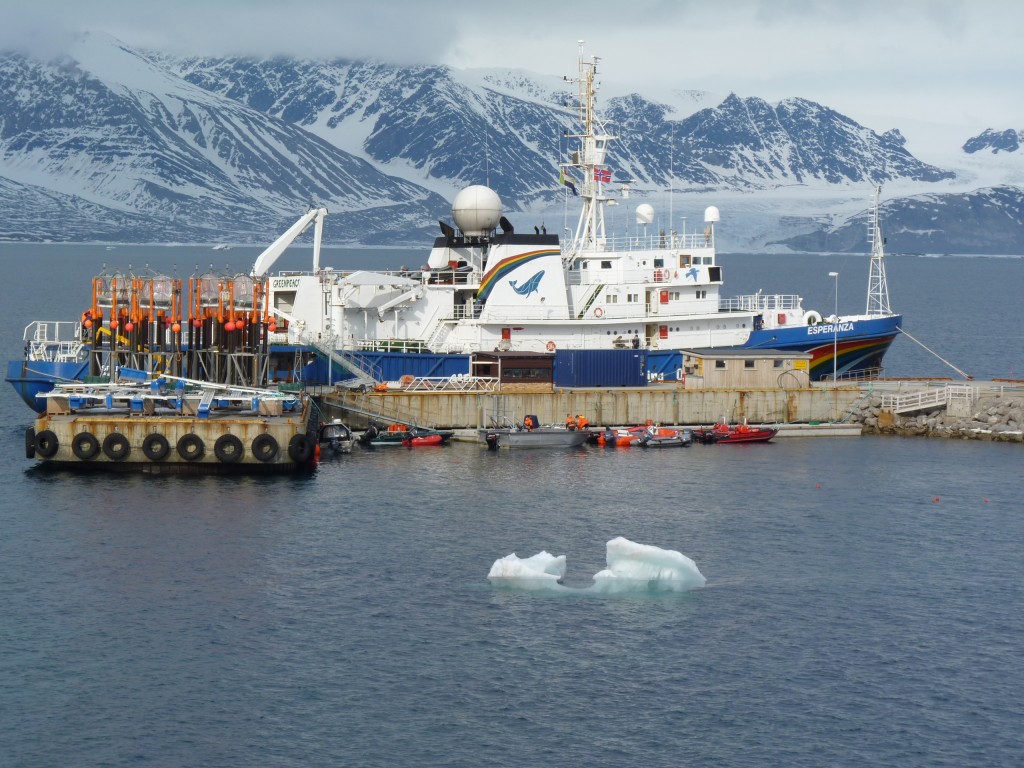
I visited again in 2010 with a team looking at ocean acidification. Their equipment was transported up by the Greenpeace ship Esperanza, a “first” in terms of cooperation between scientists funded by the EU’s EPOCA programme and the environment group. Greenpeace offered the ship to help out when none of the scientific research vessels was available for the project.
The station has also just been the first to be officially approved by the climate data network GRUAN. Not a terribly attractive acronym, but definitely easier to say/write than the whole title: Global Climate Observing System Reference Upper Air Network. Basically, the idea is to standardize and the measurement of climate parameters around the world so that the figures are really comparable. It was initiated by the World Meteorological Organization, the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, UNESCO, UNEP and the International Council for Science.
Keep up the good work everyone up there at AWIPEV.
EU stepping up campaign to join Arctic Council
When the Arctic Council meets in Sweden in May before chairmanship is handed over to Canada, one of the items on the agenda will be applications from the EU and China amongst others for observer status of the Arctic Council.
With climate change making access easier, the chances of keeping the Arctic free of economic activities like oil and gas exploration and increased sipping are dwindling. (I wrote a story about this just very recently: Business opportunities boom in the Arctic).
Some EU members are already on the Council, but the organisation wants its own observer seat. The reasons for this interest are not hard to find: to “wield greater influence over a region thought to hold huge undiscovered oil and gas reserves”, according to the publication EurActiv.com
EU member countries have different interests in the Arctic, so this is an interesting development to watch.
Climate talks too slow for Antarctic sea snails

The pteropod, (marine snail) Limacina hilicina antarctica, Photo: Nina Bednarsek
While the climate negotiations continue at a snail’s pace in Doha, marine snails or pteropods in the Antarctic are losing their shells because of ocean acidification. Researchers from the British Antarctic Survey (BAS) and partners have published the first evidence of ocean acidification affecting live marine creatures in the Southern Ocean. Ocean acidification is caused by the uptake of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere emitted as a result of fossil fuel burning.
![]() read more
read more

























Feedback