Hot, hot, hotter.. can UN talks in Bonn make a difference?
After all the hype surrounding the Paris Climate Agreement in December, there is a real danger of anti-climax, of feeling self-satisfied, of sitting back saying, “Yes, we did”, while the planet continues to break all temperature records and fossil fuel emissions continue to rise.
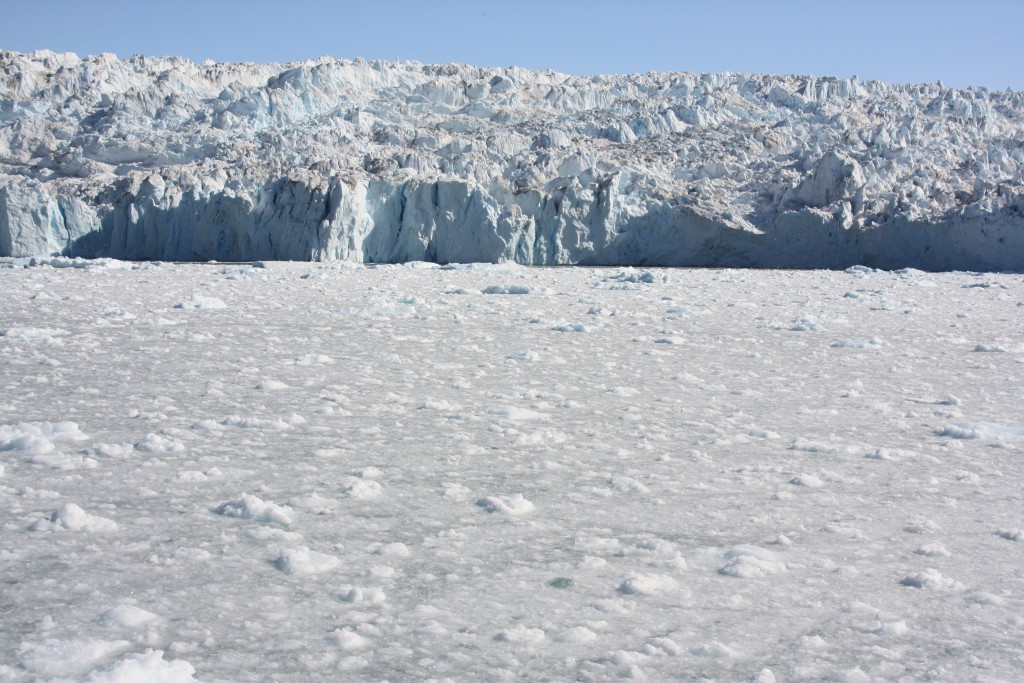
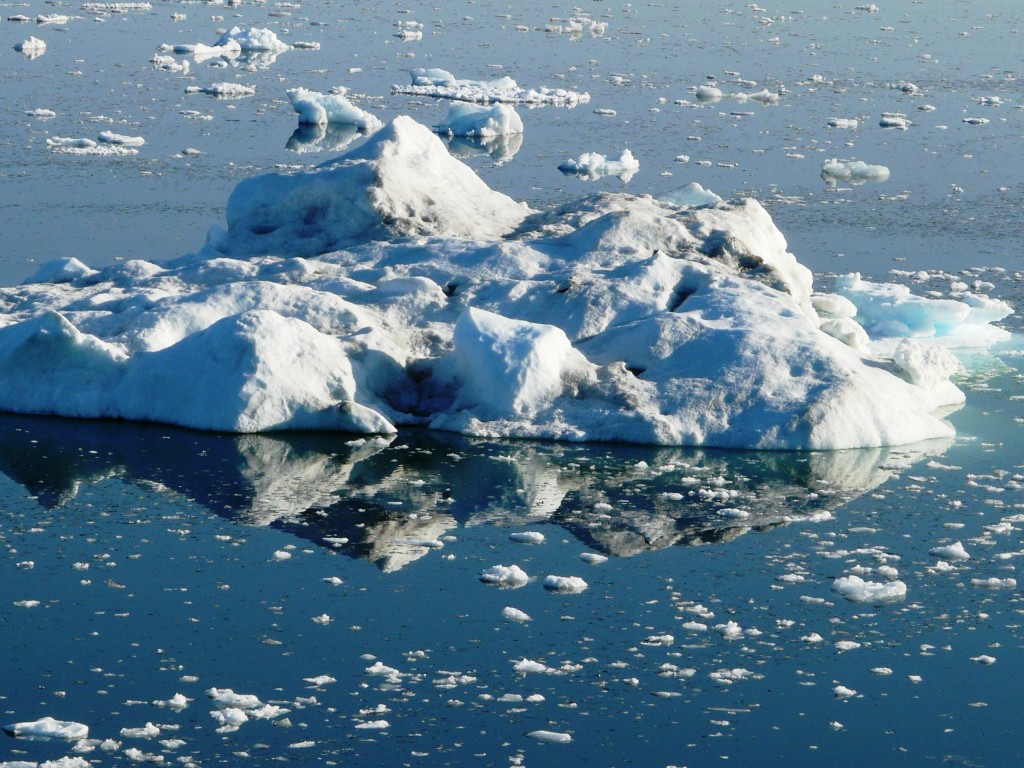
The first four months of this year were the hottest ever recorded. Even the “ice island” of Greenland has seen temperatures spiking in April, typically a cold month. NOAA says 2016 could be off to a similar start to 2012, when the surface of the ice sheet started melting early and then experienced the most extensive melting since the start of the satellite record in 1978. We have had several reports of islands being submerged by rising seas and devastating forest fires in Canada and now Russia, which experts say will be more common as the planet warms.
Close to my office here in Bonn, Germany’s UN city, the first official working meeting of all the parties to the Paris Agreement started on Monday, going on until next Friday. I have been there, on and off, talking to people, listening in, trying to get a sense of what is happening – or not, as the case may be.
But the atmosphere in Bonn’s new World Conference Centre is definitely low-key compared with the hype surrounding the Paris Climate Conference. Yet the world climate agreement will be worthless if the countries of the world do not succeed in transmitting it into actions in the very near future.
Time to deliver
The President of the Paris COP21, French Environmenent Minister Segolene Royal, and the incoming President of COP22, which will be held in Marrakech, Morocco’s Foreign Minister Salaheddine Mezouar, have made it clear that it is time to shift the focus from negotiation to implementation and rapid action.
The challenge ahead, they say, is to “operationalize the Paris Agreement: to turn intended nationally determined contributions into public policies and investment plans for mitigation and adaptation and to deliver on our promises.”
Indeed. There is no lack of evidence to support the urgent need for faster action on climate change. An increasing number of extreme weather events are being attributed to climate change. The CO2 concentration in the atmosphere is climbing steadily and is likely to cross the critical 400 ppm mark permanently in the not-too-distant future. The global temperature is already one degree Celsius higher than it was at the onset of industrialization. That means very rapid action is needed to keep it to the agreed target of limiting warming to two degrees and preferably keeping it below 1.5 degrees.
Three degrees and more?
The Paris Agreement was hailed widely as a breakthrough, with all parties finally accepting the need to combat climate change by reducing emissions of greenhouse gases. Countries have put pledges on the table, outlining their emissions reduction targets. But so far, the reductions pledged would still take the world closer to a three-degree rise in temperature.
At the Bonn meeting, the International Energy Agency (IEA), issued a warning that governments can only reach their climate goals if they drastically accelerate climate action and make full use of existing technologies and policies.
“The ambition to peak greenhouse gas emissions very soon is anchored in the Paris agreement, but we don’t see the actions right now to make this happen”, said Takashi Hattori, Head of the IEA’s Environment and Climate Change Unit. “At the same time, there are ‘GDP-neutral’ ways and means to get emissions to peak and then fall whilst maintaining economic growth, and that’s what we need to focus on.”
GDP-neutral means that a technology or policy does not negatively impact the economic growth of a country, and can actually contribute to the growth of that country.
In Bonn, Hattori presented what the IEA calls a “bridge scenario” involving the use of five technologies and policies which it says can bridge the gap between what has been pledged by governments so far and what is required to keep the global average temperature to as low as 1.5 degrees Celsius as part of what the agency terms a “well below 2 degrees world”
The five key measures which the IEA say could achieve a peak in emissions around 2020 are energy efficiency, reducing inefficient coal, renewables investment, methane reductions and fossil-fuel subsidy reform. That sounds to me like a very sensible – and practicable set of measures. But that doesn’t mean it will be easy.
Takashi Hattori stressed that “one size does not fit all” when it comes to climate and energy policies. Different measures will be required in different parts of the world. In the Middle East, for example, the greatest potential to reduce emissions is through reducing fossil fuel subsidies, he argued, while energy efficiency would have the greatest potential in Europe and China. He recommended the “massive deployment of renewables” in India and Latin America.
Other solutions outlined include smart grids, hydrogen as fuel that can be generated with renewable sources of energy, and “smart” agriculture.
The IEA says governments should make the energy transition not only because of rising temperatures, but because of other benefits, such as a reduction of air pollution. That makes sense. People in congested cities are more worried about pollution damaging their health than about climate change, the experts say.
I am reminded of an interview I conducted recently with Chinese expert Lina Li, when she told me she thought China’s air pollution problem would speed up the country’s ratification and implementation of the Paris Agreement.
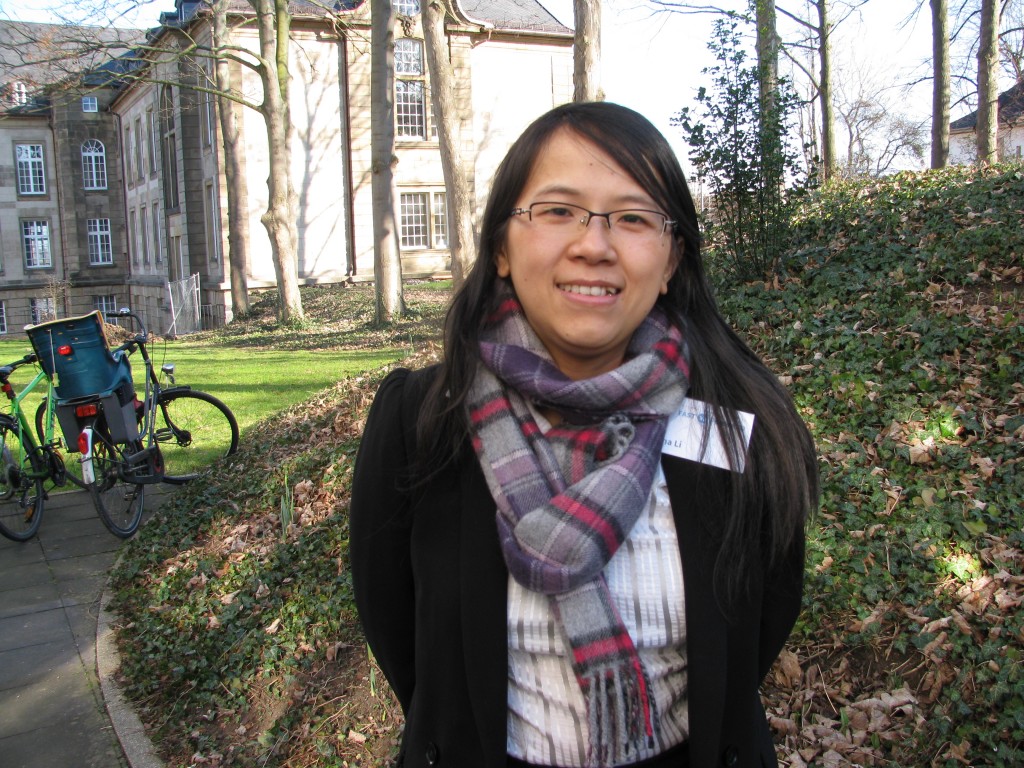

Lina Li from the Adelphi think-tank told me pollution concerns could speed up China’s climate action (Pic. I.Quaile)
The cost argument
Although many scientists are alarmed at the slow pace of emissions reductions, IPCC chief scientist Hoesung Lee told the Guardian in an interview it was still possible to keep to the two-degree target. The current UN climate chief Christina Figueres, who will hand over to Mexican Patricia Espinosa later this year, has said emissions would have to peak by 2020 if that limit is to be kept to. But Lee is keen to keep the options open, saying it would still be possible to keep to the limits if emissions peaked later. But he warned the costs could be “phenomenal”. He believes expensive and controversial geoengineering methods may be necessary to withdraw CO2 from the atmosphere and store it.
A report published this week by UNEP says the cost for assisting developing countries to adapt to climate change could reach up to 500 billion dollars annually by 2050. This is five times higher than previous estimates, the report says.
UNEP urged countries to channel more funds towards adaptation, saying the costs would rise “sharply”, even if countries succeed in limiting global temperature increase to two degrees Celsius.
I asked Mattias Söderberg, Co-Chair of the Climate change advisory group with the climate justice ACT alliance, how he felt about the progress of climate action and the role of the current Bonn meeting. He said the UNEP report, along with the alarming news about islands disappearing under rising seas in the Pacific, highlighted the urgent need for action. “Climate change is not a matter of tomorrow, but a crisis we need to deal with today.”
Time to ratify!
So far, 177 parties have signed the Agreement. But only 16 parties have ratified the treaty. It must be ratified by 55 parties representing 55 percent of total global emissions to enter into force. Söderberg called on wealthy, industrialized countries to move ahead with ratification:
“I am happy to see many of the poor and vulnerable countries moving fast with their ratification, and I hope other countries will follow soon. I am worried about the EU, which seems to be delayed”. Söderberg says the EU, could find itself on the sidelines, overtaken by others.
But the increasing concern over refugees and migration here in Europe could make a lot of countries look more closely at climate change, which is likely to increase the number of people having to leave their homes and look for a better life elsewhere.
“Go, world, go!”
NGO representatives stress that the Bonn talks can only help kick off the series of measures necessary to halt global climate change. Greenpeace climate policy chief Martin Kaiser told me the main work had to be done in the countries themselves, which have to work out their timetables to reach the goals agreed in Paris. That means an early transition to a fossil-free future. Kaiser called on host country Germany in particular, often cited as a model for its shift to renewable energy, to come up with a binding exit strategy for coal by 2030.
“Without an exit from coal, Germany’s signature under the Paris Agreement is worthless”, he told me.
The world’s top emitters, the USA and China, will also have to take major steps to halt climate warming. The delegates meeting in Bonn until May 26 have their work cut out for them. I have always been skeptical about the mass jubilation over the Paris Agreement. Yes, we needed it. But the proof of every pudding is in the eating. All the indications are that 2016 will be the hottest year on record, and probably by the largest margin ever. If the Paris document is to be more than a lot of pieces of paper, we will have to see things happening very soon – and definitely not just in the conference rooms of Bonn and elsewhere.
Arctic sea ice, Greenland and Europe’s weird weather
As I write this, I am sitting in a short-sleeved shirt with the window open, enjoying an unusually warm start to the month of May. It’s around 27 degrees Celsius in this part of Germany, pleasant, but somewhat unusual at this time. The first four months of this year have been the hottest of any year on record, according to satellite data.
The Arctic is not the first place people tend to think of when it comes to explaining weather that is warmer – as opposed to colder – than usual in other parts of the globe. But several recent studies have increased the evidence that what is happening in the far North is playing a key role in creating unusual weather patterns further south – and that includes heat, at times.
Why sea ice matters
The Arctic has been known for a long time to be warming at least twice as fast as the earth as a whole. As discussed here on the Ice Blog, the past winter was a record one for the Arctic, including its sea ice. The winter sea ice cover reached a record low. Some scientists say the prerequisites are in place for 2016 to see the lowest sea ice extent ever.
Several recent studies have increased the evidence that these variations in the Arctic sea ice cover are strongly linked to the accelerating loss of Greenland’s land ice, and to extreme weather in North America an Europe.
“Has Arctic Sea Ice Loss Contributed to Increased Surface Melting of the Greenland Ice Sheet”, by Liu, Francis et.al, published in the journal of the American Meteorological Society, comes to the conclusion: “Reduced summer sea ice favors stronger and more frequent occurrences of blocking-high pressure events over Greenland.” The thesis is that the lack of summer sea ice (and resulting warming of the ocean, as the white cover which insulates it and reflects heat back into space disappears and is replaced by a darker surface that absorbs more heat) increases occurrences of high pressure systems which get “ stuck and act like a brick wall, “blocking” the weather from changing”, as Joe Romm puts it in an article on “Climate Progress”.
Everything is connected
The study abstract says the researchers found “a positive feedback between the variability in the extent of summer Arctic sea ice and melt area of the summer Greenland ice sheet, which affects the Greenland ice sheet mass balance”. As Romm sums it up:“that’s why we have been seeing both more blocking events over Greenland and faster ice melt.”
He quotes co-author Jennifer Francis of Rutgers University, New Jersey, explaining how these “blocks” can lead to additional surface melt on the Greenland ice sheet, as well as “persistent weather patterns both upstream (North America) and downstream (Europe) of the block.
“Persistent weather can result in extreme events, such as prolonged heat waves, flooding, and droughts, all of which have repeatedly reared their heads more frequently in recent years”, Romm concludes.
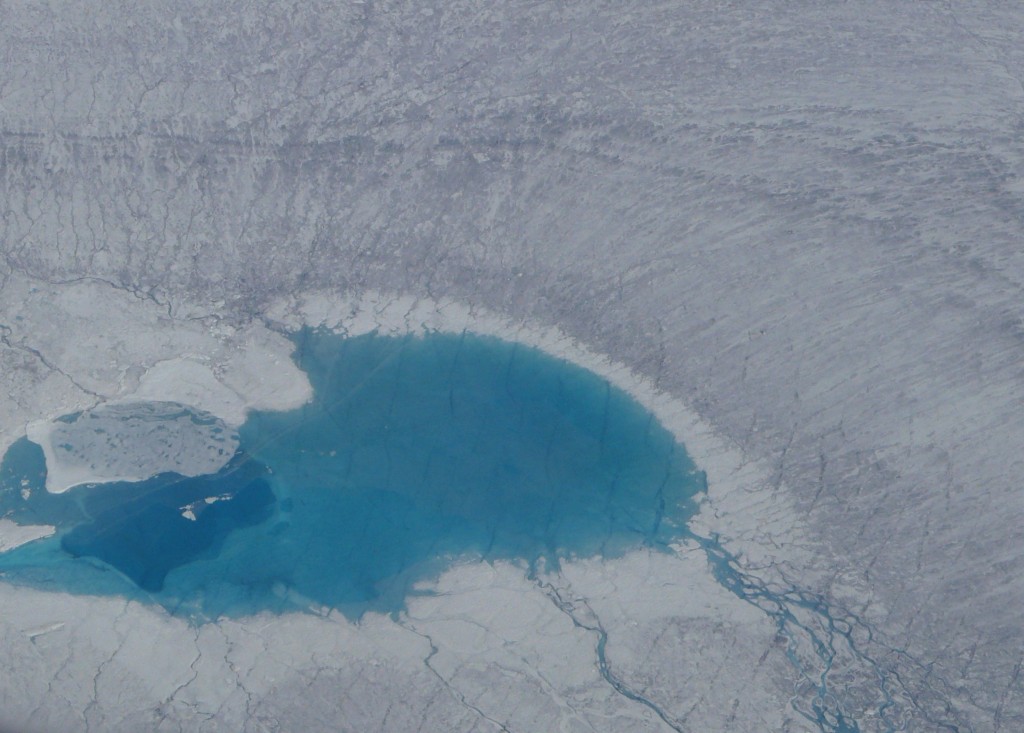
“Greenland melt linked to weird weather in Europe and USA” is the headline of an article by Catherine Jex in Science Nordic. People are usually interested in changes in the Greenland ice sheet because of its importance for global sea level, which could rise by around seven metres if it were to melt completely. But Jex also draws attention to the significance of changes to the Greenland ice for the Earth’s climate system as a whole.
The jet stream
“Some scientists think that we are already witnessing the effects of a warmer Arctic by way of changes to the polar jet stream. While an ice-free Arctic Ocean could have big impacts to weather throughout the US and Europe by the end of this century”.
She also notes some scientists warning of “superstorms”, if melt water from Greenland were eventually to shut down ocean circulation in the North Atlantic.
The site contains an interactive map to indicate how changes in Greenland and the Arctic could be driving changes in global climate and environment.
The jet streams drive weather systems in a west-east direction in the northern hemisphere. They are influenced by the difference in temperature between cold Arctic air and warmer mid-latitudes. With the Arctic warming faster than the rest of the planet, this temperature contrast is shrinking, and scientists say the jet streams are weakening.
Jex quotes meteorologist Michael Tjernström, from Stockholm University, Sweden: “Climatology of the last five years shows that the jet has weakened,” says. Its effect on weather around the world is a hot topic.
“We’ve had strange weather for a couple of years. But it’s difficult to say exactly why.”
One explanation, Jex writes, is that a weak jet stream meanders in great loops, which can bring extremes in either cold dry polar air or warmer wetter air from the south, depending on which side of the loop you find yourself. If the jet stream gets “stuck” in this kind of configuration, these extreme conditions can persist for days or even weeks.
Experts have attributed extreme events like the record cold on the east coast of the USA in early 2015, a record warm winter later the same year, and the summer heat waves and mild wet winters with exceptional flooding in the UK to these kind of “kinks” in the jet stream.
Greenland and the ocean
The changes to Greenland’s vast land ice sheet also have consequences for ocean circulation, because they mean an influx of the cold fresh water flowing into the salty sea. And the sea off the east coast of Greenland plays a key role in the movement of water, transporting heat to different parts of the world’s oceans and influencing atmospheric circulation and weather systems.
There have often been “catastrophe scenarios” suggesting the Gulf Steam, which brings warm water and weather from the tropics to the USA and Europe could ultimately be halted, leading to a new ice age. (Remember the “Day after Tomorrow?)
Although this extreme scenario is currently considered unlikely, research does suggest that the major influx of fresh water from melting ice in Greenland and other parts of the Arctic could slow the circulation and result in cooler temperatures in north western Europe.
Jex goes into the theory of a “cold blob” of ocean just south of Greenland, where melt water from the ice sheet accumulates. Some scientists say this indicates that ocean circulation is already slowing down. The “blob” appeared in global temperature maps in 2014. While the rest of the world saw record breaking warm temperatures, this patch of ocean remained unusually cold.
According to a recent study led by James Hansen, from Columbia University, USA, the ‘cold blob’ could become a permanent feature of the North Atlantic by the middle of this century. Hansen and his colleagues claim that a persistent ‘cold blob’ and a full shut down of North Atlantic Ocean circulation could lead to so-called ‘superstorms’ throughout the Atlantic. And there is geological evidence that this has happened before, they say. But the paper was controversial and many climate scientists questioned the strength of the evidence.
However, some scientists already attribute western Europe’s warm and wet winter of 2015 to the “cold blob”, Jex notes, which may have altered the strength and direction of storms via the jet stream.
The good old British weather
The UK’s Independent goes into a new study by researchers at Sheffield University, which indicates soaring temperatures in Greenland are causing storms and floods in Britain. The Independent’s author Ian Johnston says the study “provides further evidence climate change is already happening”.
It never ceases to amaze me that evidence is still being sought for that, but, clearly, there are still those who are yet to be convinced our human behavior is changing the world’s climate. So every bit of scientific evidence helps – especially if it relates to that all-time favourite topic of the weather.
The study also looks at the static areas of high pressure blocking the jet stream. With amazing temperature rises of up to ten degrees Celsius during winter on the west coast of Greenland in just two decades, it is not hard to imagine how this can effect the jet stream, and so our weather in the northern hemisphere.” If forced to go south, the jet stream picks up warm and wet air – and Britain can expect heavy rain and flooding. If forced north, the UK is likely to be hit by cold air from the Arctic”, Johnston writes.
The article quotes Professor Edward Hanna from the University of Sheffield, lead author of a paper about the research published in the International Journal of Climatology, and says seven of the strongest 11 blocking effects in the last 165 years had taken place since 2007, resulting in unusually wet weather in the UK in the summers of 2007 and 2012.
Hanna told the Independent computer models used 10 to 15 years ago to predict the extent of sea ice in the Arctic had significantly underestimated how quickly the region would warm.
“It’s very interesting to look at the observed changes in the Arctic … the actual observations are showing far more dramatic changes than the computer models,” Professor Hanna said.
“You do get sudden starts and jumps. It’s the sudden changes that can take us by surprise and there certainly does seem to have been an increase in extreme weather in certain places.”
Drawing conclusions (or not?)
In the Washington Post, (reprinted on Alaska Dispatch News) Chelsea Harvey sums up the conclusions of the latest research in an article entitled “Dominoes fall: Vanishing Arctic ice shifts jet stream, which melts Greenland glaciers”:
“There are a more complex set of variables affecting the ice sheet than experts had imagined. A recent set of scientific papers have proposed a critical connection between sharp declines in Arctic sea ice and changes in the atmosphere, which they say are not only affecting ice melt in Greenland, but also weather patterns all over the North Atlantic”.
So what do we learn from all of this? Sometimes I ask myself how many times we have to hear a message before we really take it in and decide to do something about it.
Here in Bonn, not far from the office where I am sitting now, the first round of UN climate talks since the Paris Agreement at the end of last year will be kicking off this coming weekend. The aim is to stop the rise in global temperature from going about two, preferably 1.5 degrees C. We have already passed the one degree mark. In an interview with the Guardian this week, the head of the IPCC Hoesung Lee says it is still possible to keep below two degrees, although the costs could be “phenomenal”. But many scientists and other experts are increasingly dubious about whether emissions can really peak in time to achieve the goal. Current commitments by countries to emissions reductions still leave us on the track for three degrees at least.
The concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is, as the Guardian puts it, “teetering on the brink of no return”, which the landmark 400 ppm measured for the first time at the Australian station at Cape Grim and unlikely to go below the mark again at the Mauna Loa station in Hawaii.
On my desk, I have a book entitled “Arctic Tipping Points”, by Carlos M. Duarte and Paul Wassmann. It was published in 2011. Before that, Professor Duarte had explained the global significance of what is happening in the Arctic to me
at an Arctic Frontiers conference in Tromso, Norway. How much more evidence do we need? Science takes a long time to research, evaluate and publish solid evidence of change and its consequences, with complex review processes. If politicians delay much longer, the pace of climate change will be so fast that action to avert the worst cannot keep up. Meanwhile, that Arctic ice keeps dwindling – and I sense another major storm on the approach.



























Feedback